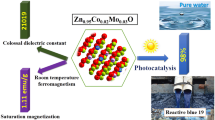
Abstract
In this study, Ni0.97Mn0.01Fe0.01Co0.01O composition exhibits a giant dielectric permittivity and strong ferromagnetic hysteresis loop at ambient temperature. Pure, (Mn, Co) codoped and (Mn, Fe, Co) tri-doped NiO powders were synthesized by sol–gel route. The crystal structure based on X-ray diffraction analysis verified that all samples have a cubic NiO phase with small crystallite sizes within 11–14 nm. The field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) image of pure NiO powder reveals the formation of particles have sheets shape. The FESEM micrographs of Ni0.97Mn0.015Co0.015O and Ni0.97Mn0.01Fe0.01Co0.01O powders show a flower-like microstructure with homogenous size and distribution. The flower-like microstructure mostly made up of thin nanosheets particles. The band gap energy (Eg) of NiO, Ni0.97Mn0.015Co0.015O and Ni0.97Mn0.01Fe0.01Co0.01O compositions was estimated to be 3.45, 3 and 2.9 eV, respectively. Both treated NiO compositions have long absorption impurity states until nearly 1.8 eV, indicating a high harvesting capacity for visible light spectrum. Ni0.97Mn0.015Co0.015O and Ni0.97Mn0.01Fe0.01Co0.01O samples reveal giant dielectric permittivity with measured values of 6325 and 27,934 at 42 Hz, respectively. Magnetically, the tri-doping by (Mn, Fe, Co) blend noticeably advance the ferromagnetic performance and multiple the magnetic parameters of NiO with measured saturation magnetization, coercivity and remanence of 3.12 emu/g, 290 Oe and 0.58 emu/g, respectively. The obtained results indicated that the (Mn, Fe, Co) tri-doped NiO semiconductor is a highly promising system for capacitive charge energy storage and spin-electronics devices.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are existing in the essential text.
Change history
24 May 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12824-w
References
T.P. Mokoena, H.C. Swart, D.E. Motaung, A review on recent progress of p-type nickel oxide based gas sensors: future perspectives. J. Alloy. Compd. 805, 267–294 (2019)
B. Wang, Y. Huang, S. Zhao, R. Li, D. Gao, H. Jiang, R. Zhang, Novel self-assembled porous yolk-shell NiO nanospheres with excellent electrochromic performance for smart windows. Particuology 84, 72–80 (2024)
S. Li, R. Guo, J. Li, Y. Chen, W. Liu, Synthesis of NiO–ZrO2 powders for solid oxide fuel cells. Ceram. Int. 29, 883–886 (2003)
H. Far, M. Hamici, N. Brihi, K. Haddadi, M. Boudissa, T. Chihi, M. Fatmi, High-performance photocatalytic degradation of NiO nanoparticles embedded on a-Fe2O3 nanoporous layers under visible light irradiation. J. Market. Res. 19, 1944–1960 (2022)
S.H.S. Pai, S.K. Pandey, E.J.J. Samuel, J.U. Jang, A.K. Nayak, H. Han, Recent advances in NiO-based nanostructures for energy storage device applications. J. Energy Storage 76, 109731 (2024)
M.B.J.G. Freitas, Nickel hydroxide powder for NiO·OH/Ni(OH)2 electrodes of the alkaline batteries. J. Power Sour. 93, 163–173 (2001)
S. Seo, I.J. Park, M. Kim, S. Lee, C. Bae, H.S. Jung, N.-G. Park, J.Y. Kim, H. Shin, An ultra-thin, un-doped NiO hole transporting layer of highly efficient (16.4%) organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale 8, 11403–11412 (2016)
G. Nabi, S. Rehman, M.B. Tahir, N. Malik, R. Yousaf, M. Maraj, M. Rizwan, M. Tanveer, Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of pure and vanadium-doped NiO microstructures for spintronics applications. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 34, 1801–1806 (2021)
C.C. Aivalioti, E.G. Manidakis, N.T. Pelekanos, M. Androulidaki, K. Tsagaraki, Z. Viskadourakis, E. Spanakis, E. Aperathitis, Niobium-doped NiO as p-type nanostructured layer for transparent photovoltaics. Thin Solid Films 778, 139910 (2023)
Y. Yang, Y. Liang, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhang, H. Wu, Z. Hu, Morphology well-controlled synthesis of NiO by solvothermal reaction time and their morphology-dependent pseudocapacitive performances. J. Alloy. Compd. 658, 621–628 (2016)
A.C. Gandhi, H.-H. Chiu, K.-T. Wu, C.-L. Cheng, S.Y. Wu, Surface-spin driven room temperature magnetic memory effect in Fe-substituted NiO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 536, 147856 (2021)
J. Wu, C.-W. Nan, Y. Lin, Y. Deng, Giant dielectric permittivity observed in Li and Ti doped NiO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 217601 (2022)
S.M. Yakout, Spintronics: Future technology for new data storage and communication devices. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 33, 2557–2580 (2020)
C. Gómez-Polo, S. Larumbe, J.M. Pastor, Room temperature ferromagnetism in non-magnetic doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 17B511 (2013)
L.B. Chandrasekar, K. Gnanasekar, M. Karunakaran, Spintronics—A mini review. Superlattices Microstruct. 136, 106322 (2019)
Y. Liu, C. Zhai, K. Zhang, L. Du, M. Zhu, M. Zhang, Origin of ferromagnetism in Sm-doped In2S3 nanoparticles: Experimental and theoretical insights. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 503, 166618 (2020)
T. Diet, A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat. Mater. 9, 965–974 (2010)
A. Gupta, R. Zhang, P. Kumar, V. Kumar, A. Kumar, Nano-structured dilute magnetic semiconductors for efficient spintronics at room temperature. Magnetochemistry 6, 15 (2020)
S. Kumar, R. Kumar, R. Kumar, P. Vaibhav, R.K. Singh, N. Kumar, R.K. Singh, S. Sharma, Spin-polarized room temperature ferromagnetism in co-doped ZnO synthesized by electrodeposition. Chinese J. Phys. 73, 622–633 (2021)
J. Huang, D. Oka, Y. Hirose, M. Negishi, T. Fukumura, A transparent room-temperature ferromagnetic semiconductor on glass: anatase Co-doped TiO2 oriented thin films with improved electrical conduction. CrystEngComm 25, 4907–4913 (2023)
H. Abbas, K. Nadeem, A. Hassan, S. Rahman, H. Krenn, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Ferromagnetic Fe-doped NiO nanoparticles. Optik 202, 163637 (2020)
J. Wang, J. Cai, Y.-H. Lin, C.-W. Nan, Room-temperature ferromagnetism observed in Fe-doped NiO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 202501 (2005)
S. Manna, A.K. Deb, J. Jagannath, S.K. De, Synthesis and room temperature ferromagnetism in Fe doped NiO nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 10659–10662 (2008)
S. Layek, H.C. Verma, Room temperature ferromagnetism in Mn-doped NiO nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 397, 73–78 (2016)
K. Noipa, S. Labuayai, E. Swatsitang, S. Maensiri, Room-temperature ferromagnetism in nanocrystalline Fe-doped NiO powders synthesized by a simple direct thermal decomposition method. Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 147–152 (2014)
W. Yan, W. Weng, G. Zhang, Z. Sun, Q. Liu, Z. Pan, Y. Guo, P. Xu, S. Wei, Y. Zhang, S. Yan, Structures and magnetic properties of (Fe, Li)-codoped NiO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 052508 (2008)
J. Al Boukhari, A.A. Azab, Z. Bitar, R. Awad, Influence of (Mg, Cu) codoping on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of NiO nanoparticles synthesized by coprecipitation method. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 663, 415004 (2023)
P. Lunkenheimer, S. Krohns, S. Riegg, S.G. Ebbinghaus, A. Reller, A. Loidl, Colossal dielectric constants in transition-metal oxides. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 180, 61–89 (2010)
L. Wang, X. Liu, M. Zhang, X. Bi, Z. Ma, J. Li, J. Chen, X. Sun, Colossal dielectric behavior of (Nb, Ga) co-doped TiO2 single crystal. J. Alloy. Compd. 921, 166053 (2020)
N.T. Taylor, F.H. Davies, S.G. Davies, C.J. Price, S.P. Hepplestone, The fundamental mechanism behind colossal permittivity in oxides. Adv. Mater. 31, 1904746 (2019)
Y. Wang, W. Jie, C. Yang, X. Wei, J. Hao, Colossal permittivity materials as superior dielectrics for diverse applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1808118 (2019)
K. Deshmukh, T. Kovářík, T. Křenek, D. Docheva, T. Stich, J. Pola, Recent advances and future perspectives of sol–gel derived porous bioactive glasses: a review. RSC Adv. 10, 33782–33835 (2020)
D. Bokov, A.T. Jalil, S. Chupradit, W. Suksatan, M.J. Ansari, I.H. Shewael, G.H. Valiev, E. Kianfar, Nanomaterial by sol-gel method: synthesis and application. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 5102014 (2021)
D. Nath, F. Singh, R. Das, X-ray diffraction analysis by Williamson-Hall, Halder-Wagner and size-strain plot methods of CdSe nanoparticles- a comparative study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 239, 122021 (2020)
A.M. Abu-Dief, A.A. Essawy, A.K. Diab, W.S. Mohamed, Facile synthesis and characterization of novel Gd2O3–CdO binary mixed oxide nanocomposites of highly photocatalytic activity for wastewater remediation under solar illumination. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 148, 109666 (2021)
W.S. Mohamed, N.M. Hadia, M. Alzaid, A.M. Abu-Dief, Impact of Cu2+ cations substitution on structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of Co1-xCuxFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by a facile hydrothermal approach. Solid State Sci. 125, 106841 (2022)
S. Koppala, R. Balan, I. Banerjee, K. Li, L. Xu, H. Liu, D.K. Kumar, K.R. Reddy, V. Sadhu, Room temperature synthesis of novel worm like tin oxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 4, 113–118 (2021)
X. Gao, G. Huang, H. Gao, C. Pan, H. Wang, J. Yan, Y. Liu, H. Qiu, N. Ma, J. Gao, Facile fabrication of Bi2S3/SnS2 heterojunction photocatalysts with efficient photocatalytic activity under visible light. J. Alloy. Compd. 674, 98–108 (2016)
U.S.U. Thampy, A. Mahesh, K.S. Sibi, I.N. Jawahar, V. Biju, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO–NiO nanocomposites synthesized through a facile sonochemical route. SN Applied Sci. 1, 1478 (2019)
S. Pooyandeh, S. Shahidi, A. Khajehnezhad, R. Mongkholrattanasit, In situ deposition of NiO nano particles on cotton fabric using sol-gel method- photocatalytic activation properties. J. Market. Res. 12, 1–14 (2021)
A. Khatri, P.S. Rana, Visible light assisted photocatalysis of Methylene Blue and Rose Bengal dyes by iron doped NiO nanoparticles prepared via chemical co-precipitation. Phys. B: Phys. Condens. Matter 579, 411905 (2020)
S. Agrawal, A. Parveen, A. Azam, Microwave assisted synthesis of Co doped NiO nanoparticles and its fluorescence properties. J. Lumin. 184, 250–255 (2017)
R. Kant, R. Singh, A. Bansal, A. Kumar, Effect of Mn-adding on microstructure, optical and dielectric properties Zn0.95Al0.05O nanoparticles. Phys. E: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 131, 114726 (2021)
H. Saadi, Z. Benzarti, P. Sanguino, J. Pina, N. Abdelmoula, J.S.S. de Melo, Enhancing the electrical conductivity and the dielectric features of ZnO nanoparticles through Co doping effect for energy storage applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 116 (2023)
H. Saadi, Z. Benzarti, F.I.H. Rhouma, P. Sanguino, S. Guermazi, K. Khirouni, M.T. Vieira, Enhancing the electrical and dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles through Fe doping for electric storage applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 1536–1556 (2021)
M.N. Siddique, P. Tripathi, Lattice defects formulated ferromagnetism in nonmagnetic La (III) ion doped NiO nanostructures: Role of oxygen vacancy. J. Alloy. Compd. 825, 154071 (2020)
R. Kant, R. Singh, A. Bansal, A. Kumar, Effect of Mn-adding on microstructure, optical and dielectric propzerties Zn0.95Al0.05O nanoparticles. Phys. E: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 131, 114726 (2021)
P. Ravikumar, B. Kisan, A. Perumal, Enhanced room temperature ferromagnetism in antiferromagnetic NiO nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 5, 087116 (2015)
Z.-Y. Chen, Y. Chen, Q.K. Zhang, X.Q. Tang, D.D. Wang, Z.Q. Chen, P. Mascher, S.J. Wang, Vacancy-induced ferromagnetic behavior in antiferromagnetic NiO nanoparticles: a positron annihilation study. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 6, P798–P804 (2017)
G. Bharathy, P. Raji, Pseudocapacitance of Co doped NiO nanoparticles and its room temperature ferromagnetic behavior. Phys. B: Phys. Condens. Matter 530, 75–81 (2018)
B. Gokul, P. Saravanan, V.T.P. Vinod, M. Černík, R. Sathyamoorthy, A study on the origin of room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni1-xGdxO nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 394, 179–184 (2015)
J. Al Boukhari, Z. Bitar, A.A. Azab, R. Awad, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Ni1–2xMgxRuxO nanoparticles. Phys. Scr. 98, 075934 (2023)
B. Choudhury, R. Verma, A. Choudhury, Oxygen defect assisted paramagnetic to ferromagnetic conversion in Fe doped TiO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 4, 29314–29323 (2014)
L.S. Nair, D. Chandran, V.M. Anandakumar, K.R. Babu, Structure and room-temperature ferromagnetism evolution of Sn and Mn-doped NiO synthesized by a sol-gel process. Ceram. Int. 43, 11090–11096 (2017)
P. Kathiravan, K. Thillaivelavan, G. Viruthagiri, Influence of Cu-ion doping in NiO NPs and their structural, morphological, optical and magnetic behaviors for optoelectronic devices and magnetic applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 308, 123745 (2024)
M. Subash, M. Chandrasekar, C. Inmozhi, G. Gobi, M.E.R. Saravanan, R. Uthrakumar, Synthesis, structural and magnetic properties of pure and Li2+ doped NiO nanomaterial. Mater. Today: Procee. 56, 3409–3412 (2022)
M.M. Shah, M. Fatema, D.A. Ansari, D.K. Gupta, M.D. Rather, Tuning the structural, magnetic, and electrochemical properties of Mo-doped NiO nanostructures prepared by coprecipitation method. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 151, 110641 (2023)
R. Krishnakanth, G. Jayakumar, A.A. Irudayaraj, A.D. Raj, Structural and magnetic properties of NiO and Fe-doped NiO nanoparticles synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Today: Procee. 3, 1370–1377 (2016)
M.N. Siddique, A. Ahmed, S.K. Riyajuddin, M. Faizan, K. Ghosh, P. Tripathi, Exploring the Ce3+ ions doping effect on optical and magnetic properties of NiO nanostructures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500, 166323 (2020)
M.A. Rahman, R. Radhakrishnan, R. Gopalakrishnan, Structural, optical, magnetic and antibacterial properties of Nd doped NiO nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation method. J. Alloy. Compd. 742, 421–429 (2018)
G. Bharathy, P. Raji, Room temperature ferromagnetic behavior of Mn doped NiO nanoparticles: a suitable electrode material for supercapacitors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 17889–17895 (2017)
E.M.M. Ibrahim, L.H. Abdel-Rahman, A.M. Abu-Dief, A. Elshafaie, S.K. Hamdan, A.M. Ahmed, The synthesis of CuO and NiO nanoparticles by facile thermal decomposition of metal-Schiff base complexes and an examination of their electric, thermoelectric and magnetic properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 107, 492–497 (2018)
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This work was carried out by Dr. Shar A. Alsherari.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alsherari, S.A. New ultrafine-flowers compositions based on Mn, Fe and Co multi-doped p-type NiO semiconductor: enhanced ferromagnetic and dielectric properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 983 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12718-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12718-x