Abstract
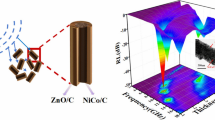
The ZnO/Co/C composite materials, consisting of ZnO and ferromagnetic Co embedded in a carbon skeleton were successfully synthesized through the pyrolysis of a ZnCo-MOF precursor. The evolution of phase and microstructure was systematically investigated. The results indicate that the EMW absorption performance is dependent on the degree of graphitization and phase compositions. When the precursor pyrolysis temperature is 800 ℃, the ZnO/Co/C composites benefiting from the synergistic effect of constituents and microstructure demonstrate exceptional EMW absorption performance, with a minimum reflection loss (RLmin) of -52.2 dB at 11.5 GHz and a sample thickness of 2.23 mm. The widest effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) harvests 6.7 GHz (11.3-18 GHz) with a sample thickness of 2 mm, encompassing the entire Ku band. Herein, this study shed light on exploring high-efficiency MOF-based EMW absorption materials with rational design of components and structure, and the as-prepared ZnO/Co/C composites are potential candidates for EMW absorption applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
X. Zhou, B. Wang, Z. Jia, X. Zhang, X. Liu, K. Wang, B. Xu, G. Wu, Dielectric behavior of Fe(3)N@C composites with green synthesis and their remarkable electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 582(Pt B), 515–525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.08.087
P. Xue, Y. Chen, Y. Xu, C. Valenzuela, X. Zhang, H.K. Bisoyi, X. Yang, L. Wang, X. Xu, Q. Li, Bioinspired MXene-Based Soft Actuators Exhibiting Angle-Independent Structural Color. Nano-Micro Lett. 15(1), 1 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00977-4
J. Qian, S. Ren, A. shui, B. Du, C. He, S. Zeng, M. Cai, X. Zhong, A design of core-shell structure for γ-MnO2 microspheres with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Ceram. Int. 48(12), 744–753 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.02.224
Y. Jiang, X. Fu, Z. Zhang, W. Du, P. Xie, C. Cheng, R. Fan, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Fe3C/C nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. J. Alloy Compd. 804, 305–313 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.038
Y. Guo, M. Zhang, T. Cheng, Y. Xie, L. Zhao, L. Jiang, W. Zhao, L. Yuan, A. Meng, J. Zhang, T. Wang, Z. Li, Enhancing electromagnetic wave absorption in carbon fiber using FeS2 nanoparticles. Nano Res. 16(7), 9591–9601 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5776-x
B. Li, N. Wu, Q. Wu, Y. Yang, F. Pan, W. Liu, J. Liu, Z. Zeng, From 100% utilization of MAX/MXene to Direct Engineering of Wearable, multifunctional E-Textiles in Extreme environments. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(41), 2307301 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202307301
Y.-L. Wang, S.-H. Yang, H.-Y. Wang, G.-S. Wang, X.-B. Sun, P.-G. Yin, Hollow porous CoNi/C composite nanomaterials derived from MOFs for efficient and lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber. Carbon. 167, 485–494 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.06.014
Z. Wang, L. Wu, J. Zhou, B. Shen, Z. Jiang, Enhanced microwave absorption of Fe3O4 nanocrystals after heterogeneously growing with ZnO nanoshell. RSC Adv. 3(10), 3309 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2RA23404A
Z. Li, X. Han, Y. Ma, D. Liu, Y. Wang, P. Xu, C. Li, Y. Du, MOFs-Derived Hollow Co/C Microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(7), 8904–8913 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b01270
J. Zhu, H. Gu, Z. Luo, N. Haldolaarachige, D.P. Young, S. Wei, Z. Guo, Carbon nanostructure-derived polyaniline metacomposites: electrical, dielectric, and giant magnetoresistive properties. Langmuir. 28(27), 46–55 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/la302031f
N. Wu, H. Lv, J. Liu, Y. Liu, S. Wang, W. Liu, Improved electromagnetic wave absorption of Co nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes derived from synergistic magnetic and dielectric losses. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18(46), 542–550 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP06066H
L. Zhao, Y. Guo, Y. Xie, T. Cheng, A. Meng, L. Yuan, W. Zhao, C. Sun, Z. Li, M. Zhang, Construction of SiCNWS@NiCo2O4@PANI 1D hierarchical nanocomposites toward high-efficiency microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 592, 153324 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153324
M. Cai, A. Shui, X. Wang, C. He, J. Qian, B. Du, A facile fabrication and high-performance electromagnetic microwave absorption of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy Compd. 842, 155638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155638
B. Du, M. Cai, X. Wang, J. Qian, C. He, A. Shui, Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption property of binary ZnO/NiCo2O4 composites. J. Adv. Ceram. 10(4), 832–842 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-021-0476-z
S. Dong, X. Zhang, W. Zhang, J. Han, P. Hu, A multiscale hierarchical architecture of a SiC whiskers–graphite nanosheets/polypyrrole ternary composite for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(40), 804–814 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TC03683G
S. Dong, W. Tang, P. Hu, X. Zhao, X. Zhang, J. Han, P. Hu, Achieving excellent Electromagnetic Wave absorption capabilities by construction of MnO Nanorods on Porous Carbon composites Derived from Natural Wood via a simple Route. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7(13), 795–805 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02100
J. Qian, B. Du, C. He, M. Cai, X. Zhong, S. Ren, J. Lou, A. Shui, Morphology-controlled preparation and tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance of manganese dioxide nanostructures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 105(5), 3339–3352 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.18296
Y. Deng, Y. Zheng, D. Zhang, C. Han, A. Cheng, J. Shen, G. Zeng, H. Zhang, A novel and facile-to-synthesize three-dimensional honeycomb-like nano-Fe3O4@C composite: electromagnetic wave absorption with wide bandwidth. Carbon. 169, 118–218 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.021
M. Fu, Q. Jiao, Y. Zhao, Preparation of NiFe2O4 nanorod–graphene composites via an ionic liquid assisted one-step hydrothermal approach and their microwave absorbing properties. J. Mater. Chem. A (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA10402H
B. Li, Y. Yang, N. Wu, S. Zhao, H. Jin, G. Wang, X. Li, W. Liu, J. Liu, Z. Zeng, Bicontinuous, High-Strength, and multifunctional chemical-cross-linked MXene/Superaligned Carbon Nanotube Film. ACS Nano. 16(11), 19293–19304 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c08678
X. Gu, W. Zhu, C. Jia, R. Zhao, W. Schmidt, Y. Wang, Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of highly ordered mesoporous crystalline NiFe2O4. Chem. Commun. 47(18), 337–339 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC05800A
N. Wu, C. Liu, D. Xu, J. Liu, W. Liu, Q. Shao, Z. Guo, Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave absorption of three-dimensional porous Fe3O4/C composite flowers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(9), 471–480 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03097
Z. Li, H. Lin, Y. Xie, L. Zhao, Y. Guo, T. Cheng, H. Ling, A. Meng, S. Li, M. Zhang, Monodispersed Co@C nanoparticles anchored on reclaimed carbon black toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 124, 182–192 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.03.004
Y. Xie, Y. Guo, T. Cheng, L. Zhao, T. Wang, A. Meng, M. Zhang, Z. Li, Efficient electromagnetic wave absorption performances dominated by exchanged resonance of lightweight PC/Fe3O4@PDA hybrid nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.141205
D. Ding, Y. Wang, X. Li, R. Qiang, P. Xu, W. Chu, X. Han, Y. Du, Rational design of core-shell Co@C microspheres for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon. 111, 722–732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.10.059
L. Wang, X. Bai, B. Wen, Z. Du, Y. Lin, Honeycomb-like Co/C composites derived from hierarchically nanoporous ZIF-67 as a lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. Compos. Part. B: Eng. 166, 464–471 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.02.054
D. Liu, Y. Du, P. Xu, N. Liu, Y. Wang, H. Zhao, L. Cui, X. Han, Waxberry-like hierarchical Ni@C microspheres with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 7(17), 5037–5046 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TC00771G
T. Cheng, Y. Guo, Y. Xie, L. Zhao, T. Wang, A. Meng, Z. Li, M. Zhang, Customizing the structure and chemical composition of ultralight carbon foams for superior microwave absorption performance. Carbon. 206, 181–191 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.02.052
L. Huang, J. Li, Z. Wang, Y. Li, X. He, Y. Yuan, Microwave absorption enhancement of porous C@CoFe2O4 nanocomposites derived from eggshell membrane. Carbon. 143, 507–516 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.11.042
M. Zhang, L. Zhao, W. Zhao, T. Wang, L. Yuan, Y. Guo, Y. Xie, T. Cheng, A. Meng, Z. Li, Boosted electromagnetic wave absorption performance from synergistic induced polarization of SiCNWs@MnO2@PPy heterostructures. Nano Res. 16(2), 3558–3569 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5289-z
X. Li, H. Yi, J. Zhang, J. Feng, F. Li, D. Xue, H. Zhang, Y. Peng, N.J. Mellors, Fe3O4–graphene hybrids: nanoscale characterization and their enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption in gigahertz range. J. Nanopart. Res. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1472-1
B. Li, N. Wu, Y. Yang, F. Pan, C. Wang, G. Wang, L. Xiao, W. Liu, J. Liu, Z. Zeng, Graphene Oxide-assisted multiple cross-linking of MXene for Large-Area, High-Strength, Oxidation-Resistant, and multifunctional films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33(11), 2213357 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202213357
B. Wen, M.-S. Cao, Z.-L. Hou, W.-L. Song, L. Zhang, M.-M. Lu, H.-B. Jin, X.-Y. Fang, W.-Z. Wang, J. Yuan, Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon. 65, 124–139 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.110
Z. Zeng, G. Wang, B.F. Wolan, N. Wu, C. Wang, S. Zhao, S. Yue, B. Li, W. He, J. Liu, J.W. Lyding, Printable aligned single-walled Carbon Nanotube Film with outstanding thermal conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Nano-Micro Lett. 14(1), 179 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00883-9
M. Zong, Y. Huang, N. Zhang, H. Wu, Influence of (RGO)/(ferrite) ratios and graphene reduction degree on microwave absorption properties of graphene composites. J. Alloy Compd. 644, 491–501 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.05.073
Y. Yang, N. Wu, B. Li, W. Liu, F. Pan, Z. Zeng, J. Liu, Biomimetic porous MXene sediment-based hydrogel for high-performance and multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano. 16(9), 15042–15052 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c06164
W. Deng, T. Li, H. Li, A. Dang, X. Liu, J. Zhai, H. Wu, Morphology modulated defects engineering from MnO2 supported on carbon foam toward excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon. 206, 192–200 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.02.039
X. Zhu, H. Qiu, P. Chen, R. Wang, C. Ping, Porous C/Co (derived from ZIF-67) embedded in anazotic g-C3N4 (PC/Co/ACN) composite as a super electromagnetic wave absorber. Carbon. 207, 59–66 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.02.063
R. Shu, X. Li, J. Shi, Construction of porous carbon-based magnetic composites derived from iron zinc bimetallic metal-organic framework as broadband and high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 633, 43–52 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.11.078
X. Zhang, X.-L. Tian, Y. Qin, J. Qiao, F. Pan, N. Wu, C. Wang, S. Zhao, W. Liu, J. Cui, Z. Qian, M. Zhao, J. Liu, Z. Zeng, Conductive Metal–Organic frameworks with Tunable Dielectric properties for boosting Electromagnetic Wave absorption. ACS Nano. 17(13), 12510–12518 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c02170
J. Meng, C. Niu, L. Xu, J. Li, X. Liu, X. Wang, Y. Wu, X. Xu, W. Chen, Q. Li, Z. Zhu, D. Zhao, L. Mai, General oriented formation of Carbon nanotubes from Metal-Organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(24), 8212–8221 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b01942
R. Shu, W. Li, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, G. Zhang, Nitrogen-doped Co-C/MWCNTs nanocomposites derived from bimetallic metal–organic frameworks for electromagnetic wave absorption in the X-band. Chem. Eng. J. 362, 513–524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.090
M. Šćepanović, M. Grujić-Brojčin, K. Vojisavljević, S. Bernik, T. Srećković, Raman study of structural disorder in ZnO nanopowders. J. Raman Spectrosc. 41(9), 914–921 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2546
M. Cai, A. Shui, Y. Wang, H. Xiong, S. Zeng, C. He, J. Qian, B. Du, Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties of Surfactants Modified ZnO Particles Synthesized Directly via Sonochemistry Technique. ChemistrySelect (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202104016
S. Wang, X. Ke, S. Zhong, Y. Lai, D. Qian, Y. Wang, Q. Wang, W. Jiang, Bimetallic zeolitic imidazolate frameworks-derived porous carbon-based materials with efficient synergistic microwave absorption properties: the role of calcining temperature. RSC Adv. 7(73), 436–444 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA08882E
X. Zhao, S. Dong, C. Hong, X. Zhang, J. Han, Precursor infiltration and pyrolysis cycle-dependent microwave absorption and mechanical properties of lightweight and antioxidant carbon fiber felts reinforced silicon oxycarbide composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 568, 106–116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.02.045
J. Qian, Y. Pu, X. Wang, A. Shui, M. Cai, C. He, P. Hu, B. Du, Synthesis and microwave absorption performance of Fe-containing SiOC ceramics derived from silicon oxycarbide. J. Alloy Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156029
M. Zhang, H. Ling, T. Wang, Y. Jiang, G. Song, W. Zhao, L. Zhao, T. Cheng, Y. Xie, Y. Guo, W. Zhao, L. Yuan, A. Meng, Z. Li, An Equivalent Substitute Strategy for constructing 3D ordered porous Carbon foams and their electromagnetic attenuation mechanism. Nanomicro Lett. 14(1), 157 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00900-x
B. Han, W. Chu, X. Han, P. Xu, D. Liu, L. Cui, Y. Wang, H. Zhao, Y. Du, Dual functions of glucose induced composition-controllable Co/C microspheres as high-performance microwave absorbing materials. Carbon. 168, 404–414 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.07.005
Y. Zhao, W. Wang, J. Wang, J. Zhai, X. Lei, W. Zhao, J. Li, H. Yang, J. Tian, J. Yan, Constructing multiple heterogeneous interfaces in the composite of bimetallic MOF-derivatives and rGO for excellent microwave absorption performance. Carbon. 173, 1059–1072 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.090
X. Lan, Z. Wang, Efficient high-temperature electromagnetic wave absorption enabled by structuring binary porous SiC with multiple interface. Carbon. 170, 517–526 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.08.052
J. Qian, B. Du, M. Cai, C. He, X. Wang, H. Xiong, A. Shui, Preparation of SiC Nanowire/Carbon Fiber Composites with Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance. Adv. Eng. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202100434
L. Xu, Y. Xiong, B. Dang, Z. Ye, C. Jin, Q. Sun, X. Yu, In-situ anchoring of Fe3O4/ZIF-67 dodecahedrons in highly compressible wood aerogel with excellent microwave absorption properties. Mater. Des. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108006
X. Xu, F. Ran, Z. Fan, Z. Cheng, T. Lv, L. Shao, Z. Xie, Y. Liu, Acidified bimetallic MOFs constructed Co/N co-doped low dimensional hybrid carbon networks for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Carbon. 171, 211–220 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.08.070
X. Xu, F. Ran, Z. Fan, H. Lai, Z. Cheng, T. Lv, L. Shao, Y. Liu, Cactus-inspired Bimetallic Metal-Organic Framework-Derived 1D-2D Hierarchical Co/N-Decorated Carbon Architecture toward enhanced Electromagnetic Wave absorbing performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(14), 564–573 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b00356
X. Zhang, F. Yan, S. Zhang, H. Yuan, C. Zhu, X. Zhang, Y. Chen, N.-D. Hollow, Carbon Polyhedron containing CoNi Alloy nanoparticles embedded within few-layer N-Doped Graphene as High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10(29), 920–929 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b07107
P. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, Y. Wang, J. Luo, Core-Shell CoNi@Graphitic Carbon decorated on B,N-Codoped Hollow Carbon polyhedrons toward Lightweight and high-efficiency microwave attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(28), 624–635 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b08525
L. Wang, X. Yu, X. Li, J. Zhang, M. Wang, R. Che, MOF-derived yolk-shell Ni@C@ZnO Schottky contact structure for enhanced microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123099
P. Yi, X. Zhang, L. Jin, P. Chen, J. Tao, J. Zhou, Z. Yao, Regulating pyrolysis strategy to construct CNTs-linked porous cubic Prussian blue analogue derivatives for lightweight and broadband microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132879
W. Zhang, F.-Z. Dai, H. Xiang, B. Zhao, X. Wang, N. Ni, R. Karre, S. Wu, Y. Zhou, Enabling highly efficient and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption by tuning impedance match in high-entropy transition metal diborides (HE TMB2). J. Adv. Ceram. 10(6), 1299–1316 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-021-0505-y
R. Shu, N. Li, X. Li, J. Sun, Preparation of FeNi/C composite derived from metal-organic frameworks as high-efficiency microwave absorbers at ultrathin thickness. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 606(Pt 2), 1918–1927 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.011
S. Han, S. Wang, W. Li, Y. Lai, N. Zhang, N. Yang, Q. Wang, W. Jiang, Synthesis of PPy/Ni/RGO and enhancement on its electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Ceram. Int. 44(9), 352–361 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.03.046
N. Wu, Y. Yang, C. Wang, Q. Wu, F. Pan, R. Zhang, J. Liu, Z. Zeng, Ultrathin cellulose nanofiber assisted ambient-Pressure-Dried, Ultralight, mechanically robust, multifunctional MXene aerogels. Adv. Mater. 35(1), 2207969 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202207969
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Shiyanjia lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for the support of TEM/HRTEM and XPS tests.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51972114, 52272062), National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (202010561010), and 100-Step Ladder Climbing Program of South China University of Technology (j2tw202302019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ren performed the experiment; Ren, Qian, Mo performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; Du, Shui, Qian helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, S., Mo, P., Shui, A. et al. ZnCo-MOF derived porous ZnO/Co/C composites as superior electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 530 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12148-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12148-9