Abstract
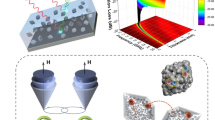
An effective strategy for improving microwave absorbing performance was proposed in atomically dispersed bimetallic carbon-based composite materials. The atomically dispersed ZnCo-NC@rGO composites were synthesized though metal-mediated formamide (FA) condensation and carbonization. By adjusting the Co/Zn sites loading, the electromagnetic parameters and absorption performance could be effectively optimized. With the Co/Zn ratio of around 0.01, the minimum reflection loss (RLmin) reached − 26.63 dB at absorbing thickness of 1.50 mm, and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth (EAB, RL < − 10 dB) was up to 4.52 GHz (12.78–17.30 GHz) at absorbing thickness of 1.60 mm, covering almost the Ku band. A stronger RLmin of − 59.63 dB was obtained with a thickness of 4.70 mm. Different loading of atomically dispersed metal sites induces variations in metal center and ligand structure. This endows ZnCo-NC@rGO excellent impedance matching and synergistic electromagnetic loss effects. In addition, the maximum radar cross section (RCS) reduction value was up to 26.94 dB m2 at a scattering angle of 0°. This study points out a feasible path for the fabrication of carbon-based ultralight synergistic absorbers.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
N. Chen, C. Wang, Y. Xiao, R. Han, Q. Wu, N. Song, Tunable microwave absorption properties of anisotropic Nd2Co17 micro-flakes. J. Alloys Compd. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169554
J. Qiu, J. Liao, G. Wang, R. Du, N. Tsidaeva, W. Wang, Implanting N-doped CQDs into rGO aerogels with diversified applications in microwave absorption and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 443, 136475 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136475
C. Wang, N. Chen, Y. Xiao, J. He, R. Han, N. Song, Exceeding natural resonance frequency limit and enhanced microwave absorption performance of Fe3O4 nanorods coated with SiO2 layer. Ceram. Int. 49, 36233–36243 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.08.304
J. Ding, L. Cheng, Core-shell Fe3O4@ SiO2@ PANI composite: preparation, characterization, and applications in microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 881, 160574 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160574
W. Gu, S.J.H. Ong, Y. Shen, W. Guo, Y. Fang, G. Ji, Z. Xu, A lightweight, elastic, and thermally insulating stealth foam with high infrared-radar compatibility. Adv. Sci. 9, 2204165 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202204165
M. Wu, X. Liang, Y. Zheng, C. Qian, D. Wang, Excellent microwave absorption performances achieved by optimizing core@ shell structures of Fe3O4@ 1T/2H-MoS2 composites. J. Alloys Compd. 910, 164881 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164881
B. Jiang, C. Qi, H. Yang, X. Wu, W. Yang, C. Zhang, S. Li, L. Wang, Y. Li, Recent advances of carbon-based electromagnetic wave absorption materials facing the actual situations. Carbon 208, 390–409 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.04.002
J. Sun, X. Huang, Y. Liu, K. Zhang, Y. Yan, Y. Liu, X. Yan, Enhanced microwave absorption performance originated from interface and unrivaled impedance matching of SiO2/carbon fiber. Appl. Surface Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157029
W. Yu, G. Shao, Morphology engineering of defective graphene for microwave absorption. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 640, 680–687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.02.140
Y. Qi, Y. Yang, H. Sun, Y. Zhang, Y. Ma, C. Ni, X. Zhang, B. Wang, R. Yu, W. Du, Three-dimensional melamine sponge hollow carbon/Ni3ZnC0. 7/carbon nanotubes with tunable high-performance microwave absorption performance. Synth. Met. 295, 117351 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2023.117351
L. Zhang, X. Zhao, Y. Ma, Y. Shu, R. Zhang, J. Xiang, B. Wang, C. Mu, K. Zhai, T. Xue, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of tellurium doped black phosphorus nanoflakes and graphite nanoflakes composites. J. Alloys Compd. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.168700
Q. Ma, Z. Xu, X. Li, X. Cheng, Core-shell CuCo2S4 based microspheres composited with carbon black nanoparticles for effective microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 938, 168577 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.168577
W. Ye, J. Fu, Q. Wang, C. Wang, D. Xue, Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of NiCoP alloy nanoparticles decorated on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 395, 147–151 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.07.087
C. Qian, X. Liang, M. Wu, X. Zhang, Lightweight chain-typed magnetic Fe3O4@ rGO composites with enhanced microwave-absorption properties. Nanomaterials 12, 3699 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203699
X. Gao, X. Wang, J. Cai, Y. Zhang, J. Zhang, S. Bi, Z.-L. Hou, CNT cluster arrays grown on carbon fiber for excellent green EMI shielding and microwave absorbing. Carbon 211, 118083 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118083
L. Yan, L. Li, X. Ru, D. Wen, L. Ding, X. Zhang, H. Diao, Y. Qin, Core-shell, wire-in-tube and nanotube structures: carbon-based materials by molecular layer deposition for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 173, 145–153 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.10.095
W. Yang, B. Jiang, Z. Liu, R. Li, L. Hou, Z. Li, Y. Duan, X. Yan, F. Yang, Y. Li, Magnetic coupling engineered porous dielectric carbon within ultralow filler loading toward tunable and high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 70, 214–223 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.08.059
G.M. Li, B.S. Zhu, L.P. Liang, Y.M. Tian, L.C. Wang, Core-shell Co3Fe7@ C composite as efficient microwave absorbent. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 33, 1715–1720 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3866/PKU.WHXB201704174
H. Wang, Z. Yan, J. An, J. He, Y. Hou, H. Yu, N. Ma, G. Yu, D. Sun, Iron cobalt/polypyrrole nanoplates with tunable broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. RSC Adv. 6, 92152–92158 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA16003D
L. Liang, Q. Li, X. Yan, Y. Feng, Y. Wang, H.-B. Zhang, X. Zhou, C. Liu, C. Shen, X. Xie, Multifunctional magnetic Ti3C2T x MXene/graphene aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Nano 15, 6622–6632 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c09982
P. Liu, S. Gao, G. Zhang, Y. Huang, W. You, R. Che, Hollow engineering to Co@ N-doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Adv. Func. Mater. 31, 2102812 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202102812
L. Zhang, X. Yu, H. Hu, Y. Li, M. Wu, Z. Wang, G. Li, Z. Sun, C. Chen, Facile synthesis of iron oxides/reduced graphene oxide composites: application for electromagnetic wave absorption at high temperature. Sci. Rep. 5, 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09298
X. Ding, Y. Huang, S. Li, N. Zhang, J. Wang, 3D architecture reduced graphene oxide-MoS2 composite: preparation and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 90, 424–432 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.08.006
Y. Qiao, J. Xiao, Q. Jia, L. Lu, H. Fan, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of ZnFe2O4/polyaniline/graphene oxide composite. Results Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102221
F. Ebrahimi-Tazangi, J. Seyed-Yazdi, S.H. Hekmatara, α-Fe2O3@CoFe2O4/GO nanocomposites for broadband microwave absorption by surface/interface effects. J. Alloys Compd. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.1633406
X. Xu, G. Wang, G. Wan, S. Shi, C. Hao, Y. Tang, G. Wang, Magnetic Ni/graphene connected with conductive carbon nano-onions or nanotubes by atomic layer deposition for lightweight and low-frequency microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 382, 122980 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122980
W. Li, Y. Liu, F. Guo, Y. Du, Y. Chen, Self-assembly sandwich-like Fe Co, or Ni nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide composites with excellent microwave absorption performance. Appl. Surface Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150212
P. Xie, Y. Liu, M. Feng, M. Niu, C. Liu, N. Wu, K. Sui, R.R. Patil, D. Pan, Z. Guo, Hierarchically porous Co/C nanocomposites for ultralight high-performance microwave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 4, 173–185 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00202-z
P. Liu, Y. Huang, J. Yan, Y. Zhao, Magnetic graphene@ PANI@ porous TiO2 ternary composites for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 6362–6370 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC01718E
Z. Li, X. Li, Y. Zong, G. Tan, Y. Sun, Y. Lan, M. He, Z. Ren, X. Zheng, Solvothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene decorated by superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their applications as enhanced synergistic microwave absorbers. Carbon 115, 493–502 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.01.036
Y. Qu, Z. Liu, X. Li, Y. Si, R. Xu, D. Liu, Ultrafine well-dispersed Co nanocrystals onto crumpled sphere-like rGO for superior low-frequency microwave absorption. Carbon 213, 118280 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118280
Y. Wang, X. Wu, W. Zhang, S. Huang, Facile synthesis of Ni/PANI/RGO composites and their excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Synth. Met. 210, 165–170 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2015.09.022
Y. Yin, M. Zeng, J. Liu, W. Tang, H. Dong, R. Xia, R. Yu, Enhanced high-frequency absorption of anisotropic Fe3O4/graphene nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 6, 25075 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25075
X. Zheng, J. Feng, Y. Zong, H. Miao, X. Hu, J. Bai, X. Li, Hydrophobic graphene nanosheets decorated by monodispersed superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals as synergistic electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 4452–4463 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TC00313J
J. Yang, W. Li, D. Wang, Y. Li, Electronic metal–support interaction of single-atom catalysts and applications in electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 32, 2003300 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202003300
C. Zhu, S. Fu, Q. Shi, D. Du, Y. Lin, Single-atom electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 13944–13960 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201703864
H. Lv, Z. Yang, P.L. Wang, G. Ji, J. Song, L. Zheng, H. Zeng, Z. Xu, A voltage-boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv. Mater. 30, 1706343 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706343
J. Xu, M. Liu, X. Zhang, B. Li, X. Zhang, X. Zhang, C. Zhu, Y. Chen, Atomically dispersed cobalt anchored on N-doped graphene aerogels for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption with an ultralow filler ratio. Appl. Phys. Rev. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0067791
H. Yuan, B. Li, C. Zhu, Y. Xie, Y. Jiang, Y. Chen, Dielectric behavior of single iron atoms dispersed on nitrogen-doped nanocarbon. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5143154
R. Patil, T. Dey, L. Kang, S. Liu, S.C. Jun, S. Dutta, Electronic and structural engineering of atomically dispersed isolated single-atom and alloy architectures. Small 19, 2301675 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202301675
X. Zhang, Y. Shi, J. Xu, Q. Ouyang, X. Zhang, C. Zhu, X. Zhang, Y. Chen, Identification of the intrinsic dielectric properties of metal single atoms for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 1–17 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00773-6
B. Li, Z. Ma, J. Xu, X. Zhang, Y. Chen, C. Zhu, Regulation of impedance matching and dielectric loss properties of N-doped carbon hollow nanospheres modified with atomically dispersed cobalt sites for microwave energy attenuation. Small (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202301226
R. Shu, W. Li, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, G. Zhang, M. Zheng, Fabrication of nitrogen-doped cobalt oxide/cobalt/carbon nanocomposites derived from heterobimetallic zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with superior microwave absorption properties. Compos. B Eng. 178, 107518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107518
H. Xu, X. Yin, M. Zhu, M. Li, H. Zhang, H. Wei, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Constructing hollow graphene nano-spheres confined in porous amorphous carbon particles for achieving full X band microwave absorption. Carbon 142, 346–353 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.10.056
R. Shu, W. Li, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, G. Zhang, Nitrogen-doped Co-C/MWCNTs nanocomposites derived from bimetallic metal–organic frameworks for electromagnetic wave absorption in the X-band. Chem. Eng. J. 362, 513–524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.090
Y. Jia, Y. Wang, G. Zhang, C. Zhang, K. Sun, X. Xiong, J. Liu, X. Sun, Pyrolysis-free formamide-derived N-doped carbon supporting atomically dispersed cobalt as high-performance bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst. J. Energy Chem. 49, 283–290 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2020.01.0341
G. Zhang, Y. Jia, C. Zhang, X. Xiong, K. Sun, R. Chen, W. Chen, Y. Kuang, L. Zheng, H. Tang, A general route via formamide condensation to prepare atomically dispersed metal–nitrogen–carbon electrocatalysts for energy technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 1317–1325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EE00162J
M. Li, X. Yin, H. Xu, X. Li, L. Cheng, L. Zhang, Interface evolution of a C/ZnO absorption agent annealed at elevated temperature for tunable electromagnetic properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 5305–5315 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.16404
D. Ding, Y. Wang, X. Li, R. Qiang, P. Xu, W. Chu, X. Han, Y. Du, Rational design of core-shell Co@ C microspheres for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 111, 722–732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.10.059
L. Wang, R. Mao, M. Huang, H. Jia, Y. Li, X. Li, Y. Cheng, J. Liu, J. Zhang, L. Wu, Heterogeneous interface engineering of high-density MOFs-derived Co nanoparticles anchored on N-doped RGO toward wide-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. Mater. Today Phys. 35, 101128 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtphys.2023.101128
L. Yan, J. Xiang, G. Guan, H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, K. Zhang, Tunable high-performance microwave absorption of cobalt nanoparticles wrapped in N-self-doped carbon nanofibers at ultralow filler loadings. J. Alloys Compd. 933, 167808 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167808
S. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Sun, S. Qi, B. Wang, D. Li, G. Wu, Multifunctional carbon nanofibers coated Co-Zn alloy nanoparticles composite for efficient energy conversion and microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 932, 167458 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167458
X. Meng, S. Dong, Design and construction of lightweight C/Co heterojunction nanofibres for enhanced microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 810, 151806 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151806
J. Hu, C. Liang, J. Li, Y. Liang, S. Li, G. Li, Z. Wang, D. Dong, Flexible reduced graphene oxide@ Fe3O4/silicone rubber composites for enhanced microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 570, 151270 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151270
Y. Shi, B. Li, X. Jiang, X. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Chen, C. Zhu, The enhanced dielectric property of the graphene composite anchored with non-planar iron single-atoms. Appl. Phys. Lett. 121, 073102 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0099781
S. Wang, W. Wang, S. Gu, G. Zhang, N. Song, A general approach to homogeneous sub-nanometer metallic particle/graphene composites by S-coordinator. Solid State Commun. 273, 17–22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2018.02.007
S. Shi, P. Mou, D. Wang, X. Li, S. Teng, M. Zhou, X. Yu, Z. Deng, G. Wan, G. Wang, Co/carbon nanofiber with adjustable size and content of Co nanoparticles for tunable microwave absorption and thermal conductivity. Journal of Materiomics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2023.04.010
N. Yang, J. Zeng, J. Xue, L. Zeng, Y. Zhao, Strong absorption and wide-frequency microwave absorption properties of the nanostructure zinc oxide/zinc/carbon fiber multilayer composites. J. Alloys Compd. 735, 2212–2218 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.380
H. Xu, X. Yin, M. Zhu, M. Han, Z. Hou, X. Li, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 6332–6341 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b15826
N. Chen, Y. Xiao, C. Wang, J. He, N. Song, Dual resonance behavior and enhanced microwave absorption performance of Fe3O4@ C@ MoS2 composites with shape magnetic anisotropy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 48529–48542 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c10316
Y. Zhao, H. Zhang, X. Yang, H. Huang, G. Zhao, T. Cong, X. Zuo, S. Yang, L. Pan, In situ construction of hierarchical core–shell Fe3O4@ C nanoparticles–helical carbon nanocoil hybrid composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 171, 395–408 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.09.036
M. Yu, Y. Huang, X. Liu, X. Zhao, W. Fan, K. She, In situ modification of MXene nanosheets with polyaniline nanorods for lightweight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 208, 311–321 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.03.066
J. Shu, X. Yang, X. Zhang, X. Huang, M. Cao, L. Li, H. Yang, W. Cao, Tailoring MOF-based materials to tune electromagnetic property for great microwave absorbers and devices. Carbon 162, 157–171 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.02.047
C. Zhou, Z. Yao, B. Wei, W. Li, Z. Li, X. Tao, J. Zhou, Facile synthesis of ZIF-67 derived dodecahedral C/NiCO2S4 with broadband microwave absorption performance. Nanoscale 14, 10375–10388 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NR02490J
L. Olmedo, P. Hourquebie, F. Jousse, Microwave absorbing materials based on conducting polymers. Adv. Mater. 5, 373–377 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.19930050509
J. Yan, Z. Ye, W. Chen, P. Liu, Y. Huang, Metal Mo and nonmetal N, S co-doped 3D flowers-like porous carbon framework for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 216, 118563 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118563
F. Ebrahimi-Tazangi, S.H. Hekmatara, J. Seyed-Yazdi, Synthesis and remarkable microwave absorption properties of amine-functionalized magnetite/graphene oxide nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 809, 151779 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151779
D. Li, H. Liao, H. Kikuchi, T. Liu, Microporous Co@ C nanoparticles prepared by dealloying CoAl@ C precursors: achieving strong wideband microwave absorption via controlling carbon shell thickness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 44704–44714 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13538
Y. Xiao, J. He, N. Chen, C. Wang, N. Song, Enhanced microwave absorption performance of large-sized monolayer two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx based on loaded Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Acta Physica Sinica (2023). https://doi.org/10.7498/aps.72.20231200
P. Toneguzzo, G. Viau, O. Acher, F. Fiévet-Vincent, F. Fiévet, Monodisperse ferromagnetic particles for microwave applications. Adv. Mater. 10, 1032–1035 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-4095(199809)10:13%3c1032::AID-ADMA1032%3e3.0.CO;2-M
R. Han, P. Shen, L. Qiao, H. Chen, Y. Fang, Z. Guo, S. Dong, M. Zhu, D. Zhou, F. Li, High frequency properties of 2D Sm2Fe14B nanoflakes with bianisotropy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 529, 167859 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.167859
C. Qiang, J. Xu, Z. Zhang, L. Tian, S. Xiao, Y. Liu, P. Xu, Magnetic properties and microwave absorption properties of carbon fibers coated by Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 506, 93–97 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.06.193
X. Liu, X. Lu, H. Guan, X. Liu, M. Wang, C. Wang, D. Zhao, Z. Xia, Rational design of ZnO/ZnO nanocrystal-modified rGO foam composites with wide-frequency microwave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 47, 33584–33595 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.268
X. Zhao, Y. Huang, X. Liu, J. Yan, L. Ding, M. Zong, P. Liu, T. Li, Core-shell CoFe2O4@ C nanoparticles coupled with rGO for strong wideband microwave absorption. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 607, 192–202 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.08.203
Z. Hou, J. Xue, H. Wei, X. Fan, F. Ye, S. Fan, L. Cheng, L. Zhang, Tailorable microwave absorption properties of RGO/SiC/CNT nanocomposites with 3D hierarchical structure. Ceram. Int. 46, 18160–18167 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.137
A. Das, P. Negi, S.K. Joshi, A. Kumar, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Co and Ni co-doped iron (II, III)/reduced graphene oxide composites at X-band frequency. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 19325–19334 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02293-x
C. Fu, D. He, Y. Wang, X. Zhao, Enhanced microwave absorption performance of RGO-modified Co@ C nanorods. Synth. Met. 257, 116187 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2019.116187
I. Abdalla, A. Elhassan, J. Yu, Z. Li, B. Ding, A hybrid comprised of porous carbon nanofibers and rGO for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 157, 703–713 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.11.004
Y. Wu, S. Tan, P. Liu, Y. Zhang, P. Li, G. Ji, Controllable heterogeneous interfaces and dielectric regulation of hollow raspberry-shaped Fe3O4@ rGO hybrids for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 151, 10–18 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.12.018
G. Li, S. Ma, Z. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Diao, L. Xia, Z. Zhang, Y. Huang, High-quality ferromagnet Fe3GeTe2 for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding with wideband radar cross section reduction. ACS Nano 16, 7861–7879 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c00512
F. Dong, B. Dai, H. Zhang, Y. Shi, R. Zhao, X. Ding, H. Wang, T. Li, M. Ma, Y. Ma, Fabrication of hierarchical reduced graphene oxide decorated with core-shell Fe3O4@ polypyrrole heterostructures for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Coll. Interface Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.06.085
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (51872021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JH: Sample preparation, experiment, data collection, interpretation of the results, and writing of the manuscript. GZ: Sample preparation. YX and CW contributed to the analysis and discussion for the results. NS: Conceptualization, supervision, interpretation of results, reviewing and editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Zhang, G., Xiao, Y. et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of rGO composites modified with atomically dispersed bi-metalic znic/cobalt sites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 354 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12080-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12080-y