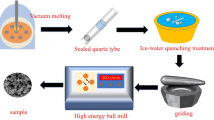
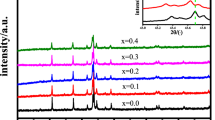
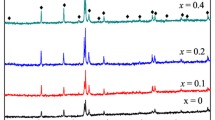
Abstract
The Dy2Co17 compound series has garnered considerable attention due to its high saturation magnetization and Curie temperature, making it a promising candidate for microwave absorption applications. The ideal electromagnetic wave absorbing material should possess exceptional electromagnetic wave attenuation and optimal impedance matching. Doping the material can improve its electromagnetic wave attenuation and impedance matching value, thereby enhancing its electromagnetic wave absorbing ability. In this study, Dy2Co17−xNix samples were designed to increase their attenuation capability. The addition of Ni elements caused lattice distortion, which modulated the relaxation polarization and resonance loss capability, resulting in the best impedance matching value. The data on attenuation constant, impedance matching value, electromagnetic parameters, magnetism, eddy current loss, and reflection loss of Dy2Co17−xNix were investigated and analyzed. The results revealed that the samples have a plate-like morphology, and at a frequency of 7.12 GHz and a thickness of 2 mm, the RLmin of Dy2Co16.7Ni0.3 reached − 44.50 dB, indicating good impedance matching. Furthermore, based on CST simulation, the samples demonstrated an effective reduction in the RCS value, highlighting its excellent electromagnetic wave attenuation ability.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Z.X. Xu, T.R. Xia, L.C. Cheng., R. Xiang, Q.R. Yao, Q.X. Long, Z. Lu, Effect of Tb Doping amount on microwave absorption performance of Dy2Co17 alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 3132–3145 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10249-5
L. Saini, M.K. Patra, R.K. Jani, G.K. Gupta, A. Dixit, S.R. Vadera, Tunable Twin Matching Frequency (fm1/fm2) Behavior of Ni1−xZnxFe2O4/NBR Composites over 2–12.4 GHz: A Strategic Material System for Stealth Applications. Sci. Rep. 7, 44457 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44457
M. Wang, Q. Yang, Y. Jiang, Z. Li, Z. Xiao, S. Gong, Y. Wang, C. Guo, H. Wei, Effects of Fe content on microstructure and properties of Cu–Fe alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 140, 3039–3049 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6326(21)65713-8
Y. Duan, Z. Liu, H. Jing, Y. Zhang, S. Li, Novel microwave dielectric response of Ni/Co-doped manganese dioxides and their microwave absorbing properties. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 18291–18299 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM33124A
A. Radoń, A. Hawełek, D. Łukowiec, J. Kubacki, P. Włodarczyk, Dielectric and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of high entropy (Zn,Fe,Ni,mg,cd)Fe2O4 ferrite. Sci. Rep. 9, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56586-6
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, X. Zhao, H. Bi, C. Wang, D.S. Wu, R. Che, Insights into size-dominant magnetic microwave absorption properties of coni microflowers via off-axis electron holography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 4233–4240 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/am508527s
H. Chen, W.H.S. Sankar, W. Wallace, Magnetic anisotropy phase diagrams of R2(Co1 – xFex)17 compounds (R = Y, pr, Sm, Gd, Dy, Er). Journal of Magnetism and magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 78, 203–207 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(89)90268-0
B. Liang, B.G. Shen, F.W. Wang, T.Y. Zhao, Z.H. Cheng, S.Y. Zhang, H.-Y. Gong, W.S. Zhan, The magnetic properties of Gd2Co17 – xGax compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 82, 3452–3455 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.365757
F. Mulder, R. Thiel, R. Coehoorn, T.H. Jacobs, Buschow. 155Gd Mössbauer effect and magnetic properties of Gd2Co17Nx. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 117(3), 413–418 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(92)90098-9
J. Shen, P. Qian, N. Che, Theoretical study on the structure for R2Co17 (R = Y, ce, pr, nd, Sm, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er) and R2Co17T (T = be, C). J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 65(7), 1307–1315 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2004.02.011
J. Wang, B. Shen, S. Zhang, W. Zhan, L. Zhang, Structure, exchange interactions and magnetic anisotropy of Ho2Co17 – xSix compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 427–431 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.371879
J. Wu, X. Guo, Q. Yan, Diffusion behavior of iron and samarium atoms in Sm2Fe17 alloy compound layer. Intermetallics. 148, 0966–9795 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2022.107645
Z. Qiao, S. Pan, J. Xiong, L. Cheng, Q. Yao, Structure and microwave absorption properties of Nd-Co-Ni alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 7487 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4726-8
F. Liu, W. Ao, Y. Jian, J. Li, Effect of substitution of Ga on the structure and magnetic properties of Dy2CO17-xGax (0 <= x <= 7) compounds. Powder Diffr. 22(3), 223–226 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1154/1.2756060
S. Zhou, L. He, S. Zhao, Y. Guo, J. Zhao, L. Shi, Size-dependent structural and magnetic properties of LaCoO3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 13522–13526 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9003032
J. Singh, C. Singh, D. Kaur, S. Bindra Narang, R. Jotania, R. Joshi, Investigation on structural and microwave absorption property of Co2+ and Y3+ substituted M-type Ba-Sr hexagonal ferrites prepared by a ceramic method. J. Alloys Compd. 734, 344 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.002
P.G.B. Gueye, J.L. Sánchez, E. Navarro, A. Serrano, P. Marín, Control of the length of Fe73.5Si13.5Nb3Cu1B9 microwires to be used for magnetic and Microwave Absorbing purposes(article). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12, 15644–15656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21865
P. Xu, R. Zhang, X. Qian, X. Li, Q. Zeng, W. You, C. Zhang, J. Zhang, Che. C/MnO@void@C with triple balances for superior microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 13(27), 32037–32045 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c08555
T. Hou, Z. Jia, S. He, Y. Su, X. Zhang, B. Xu, X. Liu, G. Wu, Design and synthesis of NiCo/Co4S3@C hybrid material with tunable and efficient electromagnetic absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 583, 321–330 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.054
Q. Huang, C. Bao, Q. Wang, C. Dong, H. Guan, Tuning the microwave absorption capacity of TiP2O7 by composited with biomass carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 515, 145974 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145974
T.Q. Hou, J. Wang, T.T. Zheng, Y. Liu, G.L. Wu, P.F. Yin, Anion Exchange of Metal Particles on Carbon-Based Skeletons for Promoting Dielectric Equilibrium and High-Efficiency Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Small 19, e2303463 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202303463
J.X. Zhou, Z.R. Jia, Y. Zhang, G.L. Wu, Construction of 3D conductive network by flower-like V2O3 synergy with magnetic NiCo for superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Mater. Today Phys. 29, 100902 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtphys.2022.100902
Z.H. Zhou, Q.Q. Zhu, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, Construction of self-assembly based Tunable Absorber: Lightweight, Hydrophobic and Self-Cleaning properties. Nano-Micro Lett. 15(1), 137 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01108-3
H.X. Zhang, K.G. Sun, K.K. Sun, L. Chen, G.L. Wu, Core–shell Ni3Sn2@C particles anchored on 3D N-doped porous carbon skeleton for modulated electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 158, 242–252 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023.01.053
Y.L. Pan, Q.Q. Zhu, J.H. Zhu, Y.H. Cheng, B.W. Yu, Z.R. Jia, G.L. Wu, Macroscopic electromagnetic synergy network-enhanced N-doped Ni/C gigahertz microwave absorber with regulable microtopography. Nano Res. 7, 10666–10677 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5687-x
L.F. Sun, Q.Q. Zhu, Z.R. Jia, Z.Q. Guo, W.R. Zhao, G.L. Wu, CrN attached multi-component carbon nanotube composites with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon. 208, 1–9 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.03.021
Z.R. Jia, X.Y. Zhang, Z. Gu, G.L. Wu, MOF-derived Ni-Co bimetal/porous carbon composites as electromagnetic wave absorber. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 6(1), 28 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00615-y
L. Liang, R. Yang, G. Han, Y. Feng, B. Zhao, R. Zhang, Y. Wang, C. Liu, Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing performance of magnetic nanoparticles-anchored 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12, 2644–2654 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18504
J. Luo, L. Yue, H. Ji, K. Zhang, N. Yu, Investigation on the optimization, design and microwave absorption properties of BaTb0.2Eu0.2Fe11.6O19/PANI decorated on reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 54(8), 6332–6346 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-03305-7
R. Shu, W. Li, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, G. Zhang, M. Zheng, Fabrication of nitrogen-doped cobalt oxide/cobalt/carbon nanocomposites derived from heterobimetallic zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with superior microwave absorption properties. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 178, 1359–8368 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107518
Y. He, S.K. Pan, L.C. Cheng, J.L. Luo, J.J. Yu, Improving microwave absorbing property of flaky Ce2Co17 alloys by Ni content and carbonyl iron powder. J Electron. Mater. 48, 1574–1581 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-06868-y
C. Lei, Y. Du, Tunable dielectric loss to enhance microwave absorption properties of flakey FeSiAl /ferrite composites. J. Alloys Compd. 822, 0925–8388 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153674
F. Ren, Z. Guo, Y. Shi, L. Jia, Y. Qing, P. Ren, D. Yan, Lightweight and highly efficient electromagnetic wave-absorbing of 3D CNTs/GNS@CoFe2O4 ternary composite aerogels. J. Alloy Compd. 768, 6–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.209
C. Wang, X.J. Han, P. Xu, X.L. Zhang, Y.C. Du, S.R. Hu, J.Y. Wang, X.H. Wang, The electromagnetic property of chemically reduced graphene oxide and its application as microwave absorbing material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98(1–3), 072906 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3555436
S. Xie, X.N. Guo, G.Q. Jin, X.Y. Guo, Carbon coated Co-SiC nanocomposite with high-performance microwave absorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15(38), 16104–16110 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp52735b
T. Xia, L. Cheng, M. Wang, Y. Chen, W. Yuan, T. Zeng, Z. Xu, Effect of La Doping on the microwave absorption performance of Dy2Co17 alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 6159–6170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09133-x
Y. Shen, Y. Wei, J. Ma, Y. Zhang, B. Ji, J. Tang, L. Zhang, P. Yan, X. Du, Self-cleaning functionalized FeNi/NiFe2O4/NiO/C nanofibers with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Ceram. Int. 46, 13397–13406 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.121
J. Ma, B. Quan, W. Liu, X. Liang, Y. Zhang, D. Li, Y. Cheng, G. Ji, Application of unit polarization strategy to achieve high-performance electromagnetic absorption by designing ternary SiO2@TiO2-C composite. J. Alloy Compd. 709, 796–801 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.187
T.T. Zhen, Z.R. Jia, Q.Q. Zhan, M.B. Ling, Y.D. Su, B.B. Wang, C.H. Zhang, G.L. Wu, Self-assembled multi-layered hexagonal-like MWCNTs/MnF2/CoO nanocomposite with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon. 186, 262–272 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.10.025
J. Guo, X. Li, Z.R. Chen, J.F. Zhu, X.M. Mai, R.B. Wei, K. Sun, H. Liu, Y.X. Chen, N. Naik, Z.H. Guo, Magnetic NiFe2O4/Polypyrrole nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 108, 64–72 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.08.049
Y. Jiang, X. Fu, Z. Zhang, W. Du, P. Xi, C. Cheng, R. Fan, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Fe3C/C nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. J. Alloy Comp. 804, 305–313 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.038
B. Zhao, W. Zhao, G. Shao, B. Fan, R. Zhang, Morphology-control synthesis of a Core-Shell Structured NiCu Alloy with Tunable Electromagnetic-Wave absorption capabilities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 12951–12960 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02716
X. Li, R. Shu, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, Z. Wan, Fabrication of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/cobalt ferrite hybrid nanocomposites as broadband electromagnetic wave absorbers in both X and Ku bands. Synth. Met. 271, 116621 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2020.116621
N. Gao, W. Li, W. Wang, D. Liu, Y. Cui, L. Guo, G. Wang, Balancing dielectric loss and magnetic loss in Fe–NiS. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12, 14416–14424 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b23379
W. Dai, H. Luo, F. Chen, X. Wang, Y. Xiong, Y. Cheng, R. Gong, Synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene wrapped SnO2 hollow spheres as high-performance microwave absorbers. RSC Adv. 9, 10745–10753 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA01556F
R. Yang, B. Wang, J. Xiang, C. Mu, C. Zhang, F. Wen, C. Wang, C. Su, Z. Liu, Fabrication of NiCo2-Anchored Graphene nanosheets by Liquid-Phase exfoliation for excellent microwave absorbers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 12673–12679 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b16144
J. Zhang, J. Li, G. Tan, R. Hu, J. Wang, C. Chang, X. Wang, Thin and Flexible Fe–Si–B/Ni–Cu–P metallic glass Multilayer composites for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 42192–42199 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b12504
R.S. Yadav, I. Kuřitka, J. Vilcakova, M. Machovsky, D. Skoda, P. Urbánek, M. Masař, M. Jurča, M. Urbánek, L. Kalina, J. Havlica, NiFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by Dextrin from corn-mediated Sol–Gel Combustion Method and its polypropylene Nanocomposites Engineered with reduced Graphene Oxide for the reduction of Electromagnetic Pollution. ACS Omega. 4, 22069–22081 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03191
Y. Zhang, X.J. Xu, Machine learning modeling of lattice constants for half Heusler alloys. AIP Adv. 10, 045121 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0002448
Y. Zhang, X.J. Xu, Transformation Temperature Predictions through Computational Intelligence for NiTi-Based shape memory alloys. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity. 6, 374–386 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40830-020-00303-0
Funding
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51861006), Guangxi Science and Technology Project (AD19110010), Guangxi Key Laboratory of information materials (221025-Z, 221036-Z, 211015-K, 221710-K), and Talents Project of Guilin University of Electronic Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TX and XX performed the experiment; XX performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; WY, JX, LC, and QY discuss the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, X., Cheng, L., Yuan, W. et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Ni-doped Dy2Co17 alloy. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2185 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11625-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11625-x