Abstract
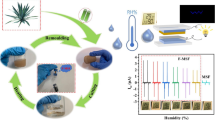
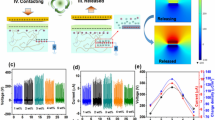
Composite membrane of relaxor ferroelectrics (RFE) Sr0.7Bi0.2TiO3 and bacterial cellulose is proposed to enhance the output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) in this work. As the added RFE contents increase, the output performance first becomes better and then deteriorates. The optimal open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current are, respectively, 640 V and 23.0 µA, to generate areal output power of 148 µW/cm2, which is achieved in the 1-wt% RFE composite-based TENG. The effects of the RFE adding contents on the output performance can be explained by the balance between the polarization contribution of the RFE and the effect of surface roughness. Such excellent output performance is comparable to or better than those TENGs using the similar friction layers with additional metal nanowires, which is attributed to highly efficient releasing energy capability of RFE. Moreover, both the good recyclability and biodegradability of the composite membrane are demonstrated. This work suggests that the environmental-friendly composite membrane provides an opportunity to replace traditional friction materials and enhance the output performance of TENG.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
P. Basset, S.P. Beeby, C. Bowen, Z.J. Chew, A. Delbani, R.D.I.G. Dharmasena, B. Dudem, F.R. Fan, D. Galayko, H.Y. Guo, J.H. Hao, Y.C. Hou, C.G. Hu, Q.S. Jing, Y.H. Jung, S.K. Karan, S. Kar-Narayan, M. Kim, S.-W. Kim, Y. Kuang, K.J. Lee, J.L. Li, Z.L. Li, Y. Long, S. Priya, X.J. Pu, T.W. Ruan, S.R.P. Silva, H.S. Wang, K. Wang, X.D. Wang, Z.L. Wang, W.Z. Wu, W. Xu, H.M. Zhang, Y. Zhang, M.L. Zhu, Roadmap on nanogenerators and piezotronics. APL Mater. 10, 109201 (2022)
M. Jiang, Y. Lu, Z.Y. Zhu, W.Z. Jia, Advances in smart sensing and medical electronics by self-powered sensors based on triboelectric nanogenerators. Micromachines 12, 698 (2021)
Z. Lou, L.L. Wang, K. Jiang, Z.M. Wei, G.Z. Shen, Reviews of wearable healthcare systems: materials, devices and system integration. Mat. Sci. Eng. R. 140, 100523 (2020)
H.-J. Kim, E.-C. Yim, J.-H. Kim, S.-J. Kim, J.-Y. Park, I.-K. Oh, Bacterial nano-cellulose triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 33, 130 (2017)
C.H. Yao, X. Yin, Y.H. Yu, Z.Y. Cai, X.D. Wang, Chemically functionalized natural cellulose materials for effective triboelectric nanogenerator development. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1700794 (2017)
C.H. Yao, A. Hernandez, Y.H. Yu, Z.Y. Cai, X.D. Wang, Triboelectric nanogenerators and power-boards from cellulose nanofibrils and recycled materials. Nano Energy. 30, 103 (2016)
X. He, H.Y. Zou, Z.S. Geng, X.F. Wang, W.B. Ding, F. Hu, Y.L. Zi, C. Xu, S.L. Zhang, H. Yu, M.Y. Xu, W. Zhang, C.H. Lu, Z.L. Wang, A hierarchically nanostructured cellulose fiber-based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered healthcare products. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1805540 (2018)
W.X. Song, B.H. Gan, T. Jiang, Y. Zhang, A.F. Yu, H.T. Yuan, N. Chen, C.W. Sun, Z.L. Wang, Nanopillar arrayed triboelectric nanogenerator as a self-powered sensitive sensor for a sleep monitoring system. ACS Nano 10, 8097 (2016)
W. Seung, M.K. Gupta, K.Y. Lee, K.-S. Shin, J.-H. Lee, T.Y. Kim, S. Kim, J.J. Lin, J.H. Kim, S.-W. Kim, Nanopatterned textile-based wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 9, 3501 (2015)
H.Y. Li, L. Su, S.Y. Kuang, C.F. Pan, G. Zhu, Z.L. Wang, Significant enhancement of triboelectric charge density by fluorinated surface modification in nanoscale for converting mechanical energy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 5691 (2015)
X.S. Zhang, M.D. Han, R.X. Wang, B. Meng, F.Y. Zhu, X.M. Sun, W. Hu, W. Wang, Z.H. Li, H.X. Zhang, High-performance triboelectric nanogenerator with enhanced energy density based on single-step fluorocarbon plasma treatment. Nano Energy. 4, 123 (2014)
H. Wang, M.Y. Shi, K. Zhu, Z.M. Su, X.L. Cheng, Y. Song, X.X. Chen, Z.Q. Liao, M. Zhang, H.X. Zhang, High performance triboelectric nanogenerators with aligned carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale. 8, 18489 (2016)
G.Q. Suo, Y.H. Yu, Z.Y. Zhang, S.F. Wang, P. Zhao, J.Y. Li, Piezoelectric and triboelectric dual effects in mechanical-energy harvesting using BaTiO3/polydimethylsiloxane composite film. Appl. Mater. Inter. 8, 34335 (2016)
W. Seung, H.J. Yoon, T.Y. Kim, H. Ryu, J. Kim, J.H. Lee, J.H. Lee, S. Kim, Y.K. Park, Y.J. Park, Boosting power-generating performance of triboelectric nanogenerators via artificial control of ferroelectric polarization and dielectric properties. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1600988 (2017)
J. Chen, H.Y. Guo, X.M. He, G.L. Liu, Y. Xi, H.F. Shi, C.G. Hu, Enhancing performance of triboelectric nanogenerator by filling high dielectric nanoparticles into sponge PDMS film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 8, 736 (2016)
Z.G. Fang, K.H. Chan, X. Lu, C.F. Tan, G.W. Ho, Surface texturing and dielectric property tuning toward boosting of triboelectric nanogenerator performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 52, 10 (2018)
H. Oh, S.S. Kwak, B. Kim, E. Han, G.H. Lim, S.W. Kim, Highly conductive ferroelectric cellulose Composite Papers for efficient triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1904066 (2019)
Q.Y. Zhu, L. Dong, J.W. Zhang, K.X. Xu, Y.J. Zhang, H.J. Shi, H.W. Lu, Y.H. Wu, H.W. Zheng, Z.F. Wang, All-in-one hybrid tribo/piezoelectric nanogenerator with the point contact and its adjustable charge transfer by ferroelectric polarization ceram. Int 46, 28277 (2020)
A.K. Gupta, C.H. Hsu, S.N. Lai, C.S. Lai, ZnO-polystyrene composite as efficient energy harvest for self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator. ECS J. Solid State SC 9, 115019 (2020)
Z.Z. Sun, L. Yang, S.C. Liu, J.T. Zhao, Z.W. Hu, W.L. Song, A green triboelectric nano-generator composite of degradable cellulose, piezoelectric polymers of PVDF/PA6, and nanoparticles of BaTiO3. Sensors 20(2), 506 (2020)
S. Jang, J.H. Oh, Fabrication of microporous BaTiO3/PDMS nanocomposites for triboelectric nanogenerators through one-step microwave irradiation. Sci. Rep. Rapid 8, 14287 (2018)
H. Yu, Y. Shao, C. Luo, Y. Li, H.Z. Ma, Y.H. Zhang, B. Yin, J.B. Shen, M.B. Yang, Bacterial cellulose nanofiber triboelectric nanogenerator based on dielectric particles hybridized system. Compos. Part. A 151, 106646 (2021)
Q. Jiang, B. Chen, Y. Yang, Wind-driven triboelectric nanogenerators for scavenging biomechanical energy. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1(8), 4269–4276 (2018)
K. Hyungseok, K. Han, K. Seongsu, S. Hyeon Jin, C. Siuk, H. Ji-Hyeok, D.Y. Lee, L. Seungwoo, K. Sang‐Woo, Mechanically robust silver nanowires network for triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 7717–7724 (2016)
H. Palneedi, M. Peddigari, G.T. Hwang, D.Y. Jeong, J. Ryu, High-performance dielectric ceramic films for energy storage capacitors: progress and outlook. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(42), 1803665 (2018)
Z.T. Yang, H.L. Du, L. Jin, D. Poelman, High-performance lead-free bulk ceramics for electrical energy storage applications: design strategies and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. A 9(34), 18026–18085 (2021)
J.H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, N.N. Sun, Y.L.J.H. Du, L.P. Zhu, X.H. Hao, Enhancing output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator via large polarization difference effect. Nano Energy. 84, 105892 (2021)
S.L. Yang, C.Y. Zuo, F. Du, L. Chen, W.J. Jie, X.H. Wei, Submicron Sr0.7Bi0.2TiO3 dielectric ceramics for energy storage via a two-step method aided by cold sintering process. Mater. Des. 225, 111447 (2023)
C.Y. Zuo, S.L. Yang, Z.Q. Cao, H.T. Yu, X.H. Wei, Excellent energy storage and hardness performance of Sr0.7Bi0.2TiO3 ceramics fabricated by solution combustion-synthesized nanopowders. Chem. Eng. J. 442, 136330 (2022)
M.S. Chargot, J. Cybulska, A. Zdunek, Sensing the structural differences in cellulose from apple and bacterial cell wall materials by raman and FT-IR spectroscopy. Sensors 11, 5543 (2021)
F.Y. Xiao, J.M. Xu, L.L. Cao, S.Q. Jiang, Q.Y. Zhang, L.P. Wang, Environ. In situ hydrothermal fabrication of visible light-driven g-C3N4/SrTiO3 composite for photocatalytic degradation of TC. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27, 5788 (2020)
C.S. Wu, A.C. Wang, W.B. Ding, H.Y. Guo, Z.L. Wang, Triboelectric nanogenerator: a foundation of the energy for the new era. Adv. Energy Mater. 9, 1802906 (2019)
L.L. Zhou, D. Liu, J. Wang, Z.L. Wang, Triboelectric nanogenerators: fundamental physics and potential applications. Friction. 8, 481 (2020)
S. Niu, Z.L. Wang, Theoretical systems of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy. 14, 161 (2015)
X.S. Zhang, M.D. Han, R.X. Wang, F.Y. Zhu, Z.H. Li, W. Wang, H.X. Zhang, Frequency-multiplication high-output triboelectric nanogenerator for sustainably powering biomedical microsystems. Nano Lett. 13, 1168 (2013)
S. Jakmuangpak, T. Prada, W. Mongkolthanaruk, V. Harnchana, S. Pinitsoontorn, Engineering bacterial cellulose films by nanocomposite approach and surface modification for biocompatible triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2, 2498 (2020)
Y. Shao, C.P. Feng, B.W. Deng, B. Yin, M.B. Yang, Facile method to enhance output performance of bacterial cellulose nanofiber based triboelectric nanogenerator by controlling micro-nano structure and dielectric constant. Nano Energy. 62, 620 (2019)
S. Niu, S.H. Wang, L. Lin, Y. Liu, Y.S. Zhou, Y.F. Hu, Z.L. Wang, Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 3576 (2013)
S. Niu, Y. Liu, S.H. Wang, L. Lin, Y.S. Zhou, Y.F. Hu, Z.L. Wang, Theoretical investigation and structural optimization of single-electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 3332 (2014)
J.T. Zhang, S.M. Hu, Z.J. Shi, Y.F. Wang, Y.Q. Lei, J. Han, Y. Xiong, J. Sun, L. Zheng, Q.J. Sun, Z.L. Wang, Eco-friendly and recyclable all cellulosetriboelectric nanogenerator and self-powered interactive interface. Nano Energy. 89, 106354 (2021)
T.M. Woods, S.I. Mccrae, Synergism between enzymes involved in the solubilization of native cellulose. Adv. Chem. Ser. 181, 181–209 (1979)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Project of State Key Laboratory of Environment-friendly Energy Materials, Southwest University of Science and Technology (21FKSY17, 22FKSY16).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HM contributed to conceptualization, investigation, and writing of the original draft. SL contributed to investigation and validation. ZZ provided resources. XW contributed to conceptualization, writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript, supervision, and project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H., Li, S., Zheng, Z. et al. Biodegradable and recyclable composite membrane of relaxor ferroelectrics and bacterial cellulose with excellent output performance for triboelectric nanogenerator application. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1757 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11158-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11158-3