Abstract
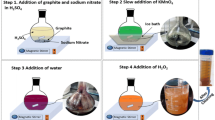
The graphene oxide composite (GO), iron oxide (Fe3O4), and titanium dioxide (TiO2) were prepared by the sol–gel process. The surface of GO is coated with TiO2 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles, and the composite contains 10.26% C, 23.70% O, 57.17% Ti, and 8.87% Fe. The formation of anatase TiO2 and magnetite Fe3O4 on the surface of GO was detected by XRD and Raman analysis. The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm and pore size distribution results showed the formation of a mesoporous material with a specific surface area of 233.3 m2/g, a total pore volume of 0.298 cm3/g, and an average pore diameter of 7.7 nm. The GO–Fe3O4–TiO2 composite’s dielectric characteristics were examined in the frequency and temperature ranges of 0.1 Hz–5 MHz and 293–373 K, respectively. The Nyquist plot suggests the non-Debye conduction behaviour, which may be related to the distribution of relaxation times within the composite material. The contribution of grains and grain boundaries to the total conductivity is confirmed by impedance spectroscopy. Jonscher’s power law was used to examine AC conductivity graphs, and the variation in the exponent “s” revealed that CBH models accurately characterize the conduction mechanism in the composite. The dielectric measurements reveal Maxwell–Wagner polarization and a thermal-activated relaxation process.












Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
Not applicable.
References
A.K. Geim, K.S. Novoselov, J. Nat. Mater. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1849
J.H. Chen, C. Jang, S. Xiao, M. Ishigami, M.S. Fuhrer, J. Nat. Nanotechnol. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.58
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, I.V. Grigorieva, A.A. Firsov, J Sci. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102896
S. Uruş, M. Çaylar, H. Eskalen, Å. Özgan, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07625-4
M. Zangiabadi, T. Shamspur, A. Saljooqi, A. Mostafavi, J. Appl. Organomet. Chem. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4813
A.M. Haji, A. Hossein, A. Samadi, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07777-x
H. Lensch, J. Doerr, A. Schütze, T. Sauerwald, J Sens. Actuators B Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128497
M. Morsy, A. Elzwawy, A.I. Abdel-Salam, M.M. Mokhtar, A.B. El Basaty, J. Diam. Relat. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109040
S. Gonuguntla, S. Sk, A. Tiwari, H. Mandal, P.N. Lakavath, V. Perupoga, U. Pal, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05848-z
S. Bai, M. Yang, J. Jiang, X. He, J. Zou, Z. Xiong, G. Liao, S. Liu, J. 2D Mater. Appl. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41699-021-00259-4
M. Yang, Y. Zou, L. Ding, Y. Yu, J. Ma, L. Li, A.F. Rafryanto, J. Zou, H. Wang, J. Carbon Lett. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-022-00456-1
J.-C. Chou, C.-M. Chu, Y.-H. Liao, C.-H. Lai, Y.-J. Lin, P.-H. You, W.-Y. Hsu, C.-C. Lu, Y.-H. Nien, J. IEEE Electron. Devices Soc. 5, 32 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2016.2618839
V. Harnchana, S. Chaiyachad, S. Pimanpang, C. Saiyasombat, P. Srepusharawoot, V. Amornkitbamrung, J. Sci. Rep. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38050-z
D.C. Marcano, D.V. Kosynkin, J.M. Berlin, A. Sinitskii, Z. Sun, A. Slesarev, L.B. Alemany, W. Lu, J.M. Tour, ACS Nano (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1006368
A. Angermann, J. Töpfer, J. Mater. Sci. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2738-3
N.K. Cakmak, Z. Said, L.S. Sundar, Z.M. Ali, A.K. Tiwari, J. Powder Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2738-3
M.A. Baghchesara, H.R. Azimi, A.G. Shiravizadeh, M.A.M. Teridi, R. Yousefi, J. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.082
V.S. Sumi, M.S. Meera, M.A. Sha, S.M.A. Shibli, J. Hydrog. Energy (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.11.167
A.C. Ferrari, D.M. Basko, Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 235 (2013)
H.D. Ngoc, D.M. Xuan, T.M. Van, Catalysts. 10, 1 (2020)
J.C. Parker, R.W. Siegel, J. Mater. Res. (1990). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1990.1246
S. Banerjee, P. Benjwal, M. Singh, K.K. Kar, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.085
R. Bardestani, G.S. Patience, S. Kaliaguine, J. Can. J. Chem. Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.23632
N. Yadav, R. Dhar, S. Mod. Tech, Basics Inst. Appl. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6084-6_19
W. Ben Soltan, S. Nasri, M.S. Lassoued, S. Ammar, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6356-1
A. Rouahi, A. Kahouli, F. Challali, M.-P. Besland, C. Vallée, B. Yangui, S. Salimy, A. Goullet, A. Sylvestre, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/46/6/065308
F.I.H. Rhouma, A. Dhahri, N. Farhat, J. Dhahri, K. Khirouni, J. EPJ Web Conf. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/20122900023
C.G. Koops, J. Phys. Rev. (1951). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.83.121
V.R. Palkar, J. John, R. Pinto, J. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1458695
S. Hcini, A. Omri, M. Boudard, M.L. Bouazizi, A. Dhahri, K. Touileb, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8674-3
A. Guerrero, J. Bisquert, G. Garcia-Belmonte, J. Chem. Rev. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00214
M. Mumtaz, M. Naveed, B. Amin, M. Imran, M.N. Khan, J. Ceram. Int. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.029
K. Ben Brahim, A. Oueslati, M. Gargouri, J. RSC Adv. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA07671E
A. Oueslati, J. Ionics. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1878-8
S.T. Hameed, T.F. Qahtan, A.M. Abdelghany, A.H. Oraby, J. Mater. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07134-7
K. Ben Brahim, A. Oueslati, F. Hlel, M. Gargouri, J. Mater. Res. Bull. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110505
A.K. Jonscher, J Nat. (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/267673a0
K. Funke, Prog. Solid State Chem. (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6786(93)90002-9
S.R. Elliott, J. Adv. Phys. (1987). https://doi.org/10.1080/00018738700101971
N. Sahu, S. Panigrahi, M. Kar, J. Mater. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/802123
A.A. Alkathiri, A.A. Atta, M.S. Refat, S. Shakya, A.M. Hassanien, S.A. Algarni, E.M.A. Ahmed, S.E. Alomariy, M. Alsawat, N. Algethami, J. Rare Earths. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2022.03.010
B.P. Choudhary, N.B. Singh, Bull. Mater. Sci. 39, 1651 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-016-1329-1
L.S. Lobo, A.R. Kumar, J. Non Cryst. Solids. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2018.11.004
A.M. Badr, H.A. Elshaikh, I.M. Ashraf, J. Mod. Phys. (2011). https://doi.org/10.4236/jmp.2011.21004
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by NKÇ, KBB and AA. The writing of the manuscript was written by AA, AO and MG and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ateş, A., brahim, K.b., Çakmak, N.K. et al. Investigation of structural, morphology, and conduction mechanism of GO–Fe3O4–TiO2 composite material. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1703 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11126-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11126-x