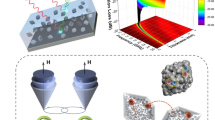
Abstract
Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) are considered to have remarkable electromagnetic (EM) wave attenuation due to their perfect dielectric property and graphene-like structure, but they still often fail to function due to impedance mismatch problems. Here, using a multilayer coating strategy, we prepared flower-like Fe3O4@SiO2@MoSe2 absorbers with core–shell structure. SiO2 can form the Fe3O4-SiO2 and SiO2-MoSe2 heterogeneous interfaces when it is applied to the Fe3O4 surface as an impedance matching layer in the Fe3O4@SiO2@MoSe2 composite, increasing the interfacial polarization loss to the absorber. In addition, Fe3O4@SiO2 as a magnetic core also reduces the relative density of the substance compared to Fe3O4. Products with the absorption performance of various electromagnetic waves were produced by varying the amount of magnetic components (Fe3O4@SiO2) in the absorber. With a minimal reflect loss (RL) of − 51.86 dB and an effective absorption bandwidth (EAB, RL < -10 dB) of 4.96 GHz at a matching thickness of 1.8 mm, the Fe3O4@SiO2@MoSe2 (sample S3) demonstrated exceptional properties in EM wave absorption. In addition, we synthesized Fe3O4@MoSe2 and determined its RL value and maximum EAB (EABmax) in order to highlight the significance of the impedance matching layer SiO2. Fe3O4@MoSe2 appears to perform less well than Fe3O4@SiO2@MoSe2 in terms of EM wave absorption, with a minimal RL value of -50.20 dB and an EABmax of only 2.00 GHz at the matching thickness of 4.8 mm. The remarkable properties in EM wave absorption of Fe3O4@SiO2@MoSe2 is the result of the combined effect from impedance match and loss mechanisms of various compositions, so the component SiO2 has a non-negligible function as an impedance matching layer. This study has blazed the trail for developing the lightweight and excellent performance of absorbers.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
L. Gai, Y. Zhao, G. Song et al., Construction of core-shell PPy@MoS2 with nanotube-like heterostructures for electromagnetic wave absorption: Assembly and enhanced mechanism. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 136, 105965 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.105965
S. Gao, Y. Zhang, H. Xing, H. Li, Controlled reduction synthesis of yolk-shell magnetic@void@C for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 387, 124149 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124149
Z. Gao, D. Lan, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Simultaneous Manipulation of Interfacial and Defects Polarization toward Zn/Co Phase and Ion Hybrids for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Adv Funct Mater. 31(50), 2106677 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202106677
J. Liu, L. Zhang, D. Zang, H. Wu, A competitive reaction strategy toward binary metal sulfides for tailoring electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Funct Mater. 31(45), 2105018 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202105018
W. Huang, Z. Tong, Y. Bi et al., Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of coralloid core-shell structure NiS/Ni3S4@PPy@MoS2 nanowires. J Colloid Interface Sci. 599, 262–270 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.107
Y. Yuan, S. Wei, Y. Liang et al., Solvothermal assisted synthesis of CoFe2O4/CNTs nanocomposite and their enhanced microwave absorbing properties. J Alloys Compd. 867, 159040 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159040
L. Wang, M. Huang, X. Qian et al., Confined magnetic-dielectric balance boosted electromagnetic wave absorption. Small 17(30), 2100970 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202100970
F. Zeng, L. Li, C. Liu, Z. Lin, Hollow CoS2 nanobubble prisms derived from ZIF-67 through facile two-step self-engaged method for electromagnetic wave absorption. ChemistrySelect 6(17), 4344–4353 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202100792
M. Ning, P. Jiang, W. Ding et al., Phase manipulating toward molybdenum disulfide for optimizing electromagnetic wave absorbing in gigahertz. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31(19), 2011229 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202011229
H. Zhang, J. Cheng, H. Wang et al., Initiating VB-group laminated NbS2 electromagnetic wave absorber toward superior absorption bandwidth as large as 6.48 GHz through phase engineering modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202108194
X. Cao, X. Liu, J. Zhu et al., Optimal particle distribution induced interfacial polarization in hollow double-shell composites for electromagnetic waves absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 634, 268–278 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.12.048
L. Najafi, S. Bellani, R. Oropesa-Nuñez et al., Engineered MoSe2 -based heterostructures for efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Energy Mater. 8(16), 1703212 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201703212
H. Wang, X. Lan, D. Jiang et al., Sodium storage and transport properties in pyrolysis synthesized MoSe2 nanoplates for high performance sodium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 283, 187–194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.02.096
Md.S. Hassan, S. Bera, D. Gupta, S.K. Ray, S. Sapra, MoSe2–Cu2S vertical p–n Nanoheterostructures for high-performance photodetectors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 11(4), 4074–4083 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b16205
I.S. Kwon, I.H. Kwak, T.T. Debela et al., Se-Rich MoSe2 nanosheets and their superior electrocatalytic performance for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 14(5), 6295–6304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c02593
H. Mittal, M. Khanuja, Hydrothermal in-situ synthesis of MoSe2-polypyrrole nanocomposite for efficient photocatalytic degradation of dyes under dark and visible light irradiation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 254, 117508 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117508
Y. Cheng, Y. Zhao, H. Zhao et al., Engineering morphology configurations of hierarchical flower-like MoSe2 spheres enable excellent low-frequency and selective microwave response properties. Chem. Eng. J. 372, 390–398 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.174
H. Wang, J. Lu, J. Liang, J. Yu, M. Yan, C. Wu, Evolution from core-shell, yolk-shell to hollow structure of hierarchical SiO2@MoSe2@FeNi3 for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 884, 161020 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161020
B. Deng, Z. Liu, F. Pan, Z. Xiang, X. Zhang, W. Lu, Electrostatically self-assembled two-dimensional magnetized MXene/hollow Fe3O4 nanoparticle hybrids with high electromagnetic absorption performance and improved impendence matching. J Mater. Chem A. 9(6), 3500–3510 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA10551A
J. Liao, M. Ye, A. Han, J. Guo, C. Chen, Nanosheet architecture of Cu9S5 loaded with Fe3O4 microspheres for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Ceram. Int. 47(7), 8803–8811 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.11.246
L.L. Adebayo, H. Soleimani, N. Yahya et al., Recent advances in the development OF Fe3O4-BASED microwave absorbing materials. Ceram. Int. 46(2), 1249–1268 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.209
J. Liu, H. Liang, H. Wu, Hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4/MoS2 composites for selective broadband electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 130, 105760 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105760
Z. Wu, D. Tan, K. Tian et al., Facile preparation of core−shell Fe3O4@polypyrrole composites with superior electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Phys. Chem. C. 121(29), 15784–15792 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b04230
G. Xiang, M. Chen, Z. Ni, Y. Shen, L. Xu, Synthesis of a hollow-structured flower-like Fe3O4 @MoS2 composite and its microwave-absorption properties. RSC Adv. 11(33), 20180–20190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA02095A
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi et al., CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 28(3), 486–490 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201503149
S. Chong, X. Wei, Y. Wu et al., Expanded MoSe 2 nanosheets vertically bonded on reduced graphene oxide for sodium and potassium-ion storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 13(11), 13158–13169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c22430
Z. Zhang, X. Yang, Y. Fu, K. Du, Ultrathin molybdenum diselenide nanosheets anchored on multi-walled carbon nanotubes as anode composites for high performance sodium-ion batteries. J. Power Sour. 296, 2–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.07.008
H. Shi, H. Zhang, M. Li, Y. Wang, D. Wang, Nanoflower-like 1T/2H mixed-phase MoSe2 as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Alloys. Compd. 878, 160381 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160381
H. Wu, J. Liu, H. Liang, D. Zang, Sandwich-like Fe3O4/Fe3S4 composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 393, 124743 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124743
Y. Yin, Y. Zhang, T. Gao et al., Synergistic phase and disorder engineering in 1T-MoSe2 nanosheets for enhanced hydrogen-evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 29(28), 1700311 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201700311
S. Deng, Y. Zhong, Y. Zeng et al., Directional construction of vertical nitrogen-doped 1T–2H MoSe2/graphene Shell/Core Nanoflake arrays for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 29(21), 1700748 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201700748
J. Ma, X. Wang, W. Cao et al., A facile fabrication and highly tunable microwave absorption of 3D flower-like Co3O4-rGO hybrid-architectures. Chem Eng J. 339, 487–498 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.152
J. Liao, M. Ye, A. Han, J. Guo, Q. Liu, G. Yu, Boosted electromagnetic wave absorption performance from multiple loss mechanisms in flower-like Cu9S5/RGO composites. Carbon 177, 115–127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.02.060
C. Wang, B. Wang, X. Cao et al., 3D flower-like Co-based oxide composites with excellent wideband electromagnetic microwave absorption. Compos. Part B Eng. 205, 108529 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108529
B. Quan, X. Liang, G. Ji et al., Dielectric polarization in electromagnetic wave absorption: review and perspective. J Alloys Compd. 728, 1065–1075 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.09.082
D. Zhang, J. Chai, J. Cheng et al., Highly efficient microwave absorption properties and broadened absorption bandwidth of MoS2-iron oxide hybrids and MoS2-based reduced graphene oxide hybrids with Hetero-structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 462, 872–882 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.152
J. Wang, B. Wang, Z. Wang et al., Synthesis of 3D flower-like ZnO/ZnCo2O4 composites with the heterogeneous interface for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 586, 479–490 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.111
F. Wang, W. Gu, J. Chen et al., Improved electromagnetic dissipation of Fe doping LaCoO3 toward broadband microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 105, 92–100 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.06.058
T. Kim, J. Lee, K. Lee, B. Park, B.M. Jung, S.B. Lee, Magnetic and dispersible FeCoNi-graphene film produced without heat treatment for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 361, 1182–1189 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.172
X. Shu, J. Zhou, W. Lian et al., Size-morphology control, surface reaction mechanism and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics of Fe3O4 hollow spheres. J. Alloys Compd. 854, 157087 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157087
L. Zhang, P. Dai, X. Yu et al., The preparation of Fe3O4 cube-like nanoparticles via the ethanol reduction of α-Fe2O3 and the study of its electromagnetic wave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 359, 723–728 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.10.163
S. Dong, W. Zhang, X. Zhang, P. Hu, J. Han, Designable synthesis of core-shell SiCw@C heterostructures with thickness-dependent electromagnetic wave absorption between the whole X-band and Ku-band. Chem. Eng. J. 354, 767–776 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.062
Z. Li, H. Lin, S. Ding et al., Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 167, 148–159 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.070
M. Wu, Y.D. Zhang, S. Hui et al., Microwave magnetic properties of Co50/(SiO2)50 nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett. 80(23), 4404–4406 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1484248
L. Wang, X. Li, Q. Li, Y. Zhao, R. Che, Enhanced Polarization from Hollow Cube-like ZnSnO3 Wrapped by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes: As a Lightweight and High-Performance Microwave Absorber. ACS Appl Mater. Interf. 10(26), 22602–22610 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b05414
L. Wang, H. Xing, S. Gao, X. Ji, Z. Shen, Porous flower-like NiO@graphene composites with superior microwave absorption properties. J Mater Chem C. 5(8), 2005–2014 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC05179K
X. Li, L. Wang, W. You et al., Morphology-controlled synthesis and excellent microwave absorption performance of ZnCo2O4 nanostructures via a self-assembly process of flake units. Nanoscale 11(6), 2694–2702 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR08601J
F. Zhang, W. Cui, B. Wang et al., Morphology-control synthesis of polyaniline decorative porous carbon with remarkable electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities. Compos. Part B Eng. 204, 108491 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108491
L. Cui, C. Tian, L. Tang et al., Space-confined synthesis of core-shell BaTiO3@carbon microspheres as a high-performance binary dielectric system for microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(34), 31182–31190 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b09779
Z. Ma, C.T. Cao, Q.F. Liu, J.B. Wang, A new method to calculate the degree of electromagnetic impedance matching in one-layer microwave absorbers. Chin. Phys. Lett. 29(3), 038401 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/29/3/038401
D. Liu, Y. Du, P. Xu et al., Waxberry-like hierarchical Ni@C microspheres with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C. 7(17), 5037–5046 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TC00771G
Z. Ma, Y. Zhang, C. Cao, J. Yuan, Q. Liu, J. Wang, Attractive microwave absorption and the impedance match effect in zinc oxide and carbonyl iron composite. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 406(24), 4620–4624 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.09.039
J. He, S. Gao, Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, H. Li, N-doped residual carbon from coal gasification fine slag decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 104, 98–108 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.06.052
M. Ren, F. Li, B. Wang, J. Wei, Q. Yu, Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of carbon nanotubes loaded Fe3O4 composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 513, 167259 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167259
X. Chen, T. Shi, G. Wu, Y. Lu, Design of molybdenum disulfide@polypyrrole compsite decorated with Fe3O4 and superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 572, 227–235 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.089
Y. Cai, Q. Sun, L. Sun, X. Long, T. Ji, W. Ye, Effect of preparation conditions on structure and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of sandwich-like Fe3O4-rGO nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 503, 166656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166656
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QL: Data search and integration, Software, Data Analysis, Writing & Revision; GYU: Conceptualization, Formal analysis; MY: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing—review & editing, Funding acquisition; AH: Funding acquisition, Supervision; QL: Software; YS: Conceptualization; CC: Software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the research reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Yu, G., Ye, M. et al. Rational design of flower-like core–shell Fe3O4@SiO2@MoSe2 composites for high performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1723 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11098-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11098-y