Abstract
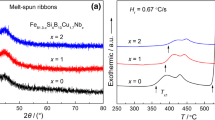
(Fe74Si15B7Cu1Nb3)100−xCox (x = 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) nanocrystalline alloys prepared by melt spinning were investigated. The results indicate that the saturation magnetic flux density (Bs) of these alloys could be efficiently enhanced from 1.29 to 1.40 T, accompanying with good soft magnetic properties. Glass-forming ability of these alloys decreased with increasing Co content, whereas the temperature interval (ΔTx = Tx2 − Tx1) increased significantly. The coercivity (Hc) of these alloys almost keep constant in a wide annealing temperature range. Crystallization kinetics shows that the activation energy of the alloy decreases with the increment of Co content, implying the nucleation and growth of α-Fe(Co) grains become easier. Microstructural analysis indicates that the mean grain size of the α-Fe(Co) grains increases gradually with increasing Co content. Irregular and disorder domain walls observed on the ribbon surface may originate from the pinning effects of surface crystallites, resulting in the deterioration of soft magnetic properties.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
J.M. Silveyra, E. Ferrara, D.L. Huber et al., Soft magnetic materials for a sustainable and electrified world. Science 362(6413), eaao195 (2018)
D. Yuting, M. Guofeng, Research Progress of fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys. IOP Conf. Series. 565(1), 12048 (2020)
F.C. Li, T. Liu, J.Y. Zhang et al., Amorphous–nanocrystalline alloys: fabrication, properties, and applications. Mater. Today Adv. 4, 100027 (2019)
T. Gheiratmand, H.R.M. Hosseini, Finemet nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy: investigation of glass forming ability, crystallization mechanism, production techniques, magnetic softness and the effect of replacing the main constituents by other elements. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 408, 177–192 (2016)
Y. Yoshizawa, S. Oguma et al., New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 323–330 (1988)
T. Liu, A. Wang, C. Zhao et al., Compositional design and crystallization mechanism of High Bs nanocrystalline alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 112, 323–330 (2019)
G. Herzer, Modern soft magnets: amorphous and nanocrystalline materials. Acta Mater. 61, 718–734 (2013)
M.A. Willard, M. Daniil, Chapter Four-Nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys two decades of progress, in Handbook of Magnetic Materials. ed. by K.H.J. Buschow (Amsterdam, Elsevier, 2013), pp.173–342
H.R. Lashgari, D. Chu, S. Xie et al., Composition dependence of the microstructure and soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys: a review study. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 391, 61–82 (2014)
K. Suzuki, R. Parsons, B. Zang et al., Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials from binary alloy precursors with high saturation magnetization. AIP Adv. 9, 35311 (2019)
R. Shi, Z. Wang, H. Duan, Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and soft magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe80.5−xCoxCu1.5Si4B14 alloys (x = 0, 2, 4, 10). J. Mater. Sci. 32(14), 19110–19116 (2021)
R. Parsons, Z. Li, K. Suzuki, Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials with a saturation magnetization greater than 2 T. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 485, 180–186 (2019)
H. Li, A. Wang, T. Liu et al., Design of Fe-based nanocrystalline alloys with superior magnetization and manufacturability. Mater. Today 42, 49–56 (2020)
C. Zhao, A. Wang, A. He et al., Correlation between soft-magnetic properties and Tx1-Tc in high Bs FeCoSiBPC amorphous alloys. J. Alloy Compd. 659, 193–197 (2016)
F. Wang, A. Inoue, Y. Han et al., Soft magnetic Fe–Co-based amorphous alloys with extremely high saturation magnetization exceeding 19 T and low coercivity of 2 A/m. J. Alloys Compd. 723, 376–384 (2017)
T. Liu, F. Kong, L. Xie et al., Fe(Co)SiBPCCu nanocrystalline alloys with high Bs above 1.83 T. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 441, 174–179 (2017)
W. Li, C.X. Xie, C.L. Yao et al., Amorphous formation and magnetic properties of Co-containing FeSiBPCu nanocrystalline alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 505, 87–91 (2019)
M. Müller, H. Grahl, N. Mattern et al., The influence of Co on the structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline FeSiBCuNb and FeZrBCu-based alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 160, 284–286 (1996)
P. Marín, L. Pascual, A. Hernando et al., Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe73.5−xCoxSi13.5B9Cu1Nb3 alloys. Phys. Rev. B 65(2), 24433 (2001)
Z. Gercsi, F. Mazaleyrat, L.K. Varga, High-temperature soft magnetic properties of Co-doped nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302(2), 454–458 (2006)
E. Lopatina, I. Soldatov, V. Budinsky et al., Surface crystallization and magnetic properties of Fe84.3Cu0.7Si4B8P3 soft magnetic ribbons. Acta Mater. 96, 10–17 (2015)
A. Takeuchi, A. Inoue, Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 46, 2817–2829 (2005)
A. He, J. Li, M. Wang et al., Microstructure, magnetic domain and dynamic loss of surface-textured Fe-based nanocrystalline alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 120, 1–7 (2022)
Y. Ling, A. He, R. Zhang et al., Surface crystallization suppressed mechanism and enhanced magnetic softness of FeCuSiBNb alloys with the ultralow Dy content. Appl. Surf. Sci. 601, 154320 (2022)
F. Bai, Y. Dong, L. Xie et al., Effect of pre-existing nuclei on microstructure and magnetic properties of high Bs FINEMET-like nanocrystalline alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 56(15), 9254–9262 (2021)
K. Hono, D.H. Ping, M. Ohnuma et al., Cu clustering and Si partitioning in the early crystallization stage of an Fe73.5Si13.5B9Nb3Cu1 amorphous alloy. Acta Mater. 47(3), 997–1006 (1999)
R. Hasegawa, Advances in amorphous and nanocrystalline magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 304(2), 187–191 (2006)
H.E. Kissinger, Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal. Chem. 29(11), 1702–1706 (1957)
Y. Li, G. Zhang, L. Wu et al., Effects of annealing temperature and heating rate on microstructure, magnetic, and mechanical properties of high-Bs Fe81.7−xSi4B13NbxCu1.3 nanocrystalline alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 56(3), 2572–2583 (2021)
W. Lin, Y.Z. Yang, J. Xu et al., Effect of Nb, Si and Cu on the crystallization process and magnetic properties of FeNbBP alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 735, 1195–1199 (2018)
G. Herzer, Anisotropies in soft magnetic nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 294(2), 99–106 (2005)
R. Schäfer, M. Rührig, A. Hubert, Loss optimization for iron-rich metallic glasses. Phys. Scr. 40(4), 552 (1989)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51971093) and the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant Nos. 2021YFB3802900 and 2022YFB2404102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by YX and HC. Data collection, data analysis, and novelty were directed by YX, SZ, and BD. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YX and all authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Y., Dong, B., Zhou, S. et al. Microstructure, crystallization behavior, and soft magnetic properties of Co-doped Finemet-type nanocrystalline alloys. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1496 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10816-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10816-w