Abstract
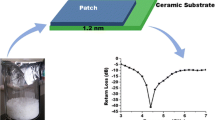
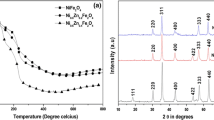
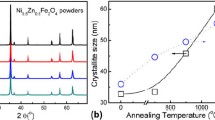
Nanoferrites with chemical formulae of CuFe2O4 (CFO), Mn0.5Cu0.5Fe2O4 (MCFO), and Mn0.5Cu0.5SmxFe2−xO4 (SMCFO) were synthesized by the sonochemical method as substrate material for microstrip patch antennas. The structural, oxidation, and vibrational characteristics of the nanoferrite substrate were analyzed through X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron, and infrared spectroscopy. The lattice constant of the CFO nanoferrite is 8.413 Å, whereas that of MCFO is 8.429 Å, which is smaller than that of SMCFO nanoferrite. The spherical morphology of the nanoferrite substrate was observed through field-emission scanning electron microscopy images. The magnetic properties of the pristine and Sm3+-doped Mn0.5Cu0.5Fe2O4 nanoferrites were studied using a vibrating sample magnetometer. The dielectric permittivity (εr) and dielectric loss tangent (tan δe) of the prepared nanoferrites were used as substrate to design the microstrip patch antenna by simulation using a high-frequency structure simulator. The RL value of the simulated microstrip patch antennas was in the range of − 17.80 to − 46.28 dB at a frequency of 25 GHz. The voltage standing wave ratio values of the simulated microstrip patch antenna were between 0.08 and 2.41. Thus, it was concluded that the prepared materials can play an important role in developing flexible substrates for antennas in 5G mobile application.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing and data citation is encouraged and the authors declare that [the/all other] data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Change history
04 October 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11401-x
References
M.A. Rahman, M.T. Islam, M.J. Singh, I. Hossain, H. Rmili, M. Samsuzzaman, Magnetic, dielectric and structural properties of CoxZn(0.90–x)Al0.10Fe2O4 synthesized by sol–gel method with application as flexible microwave substrates for microstrip patch antenna. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 16, 934–943 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.12.058
R. Cicchetti, E. Miozzi, O. Testa, Wideband and UWB antennas for wireless applications: a comprehensive review. Hindawi. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2017, 2390808 (2017)
S.R. Bhongale, H.R. Ingavale, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Microwave sintered MgCd ferrite substrates for microstrip patch antennas in X-band. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 96, 246–251 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2018.09.040
A. Motevasselian, W.G. Whittow, Patch size reduction of rectangular microstrip antennas by means of a cuboid ridge. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 9(15), 1727–1732 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map.2014.0559
H. Mosallaei, K. Sarabandi, Magneto-dielectrics in electromag-netics: concept and applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 52, 1558–1567 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2004.829413
K. Borah, N.S. Bhattacharyya, Magneto-dielectric composite with ferrite inclusions as substrates for microstrip patch antennas at microwave frequencies. Compos. Part B 43, 1309–14 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.11.067
S.R. Bhongale, Mg–Nd–Cd ferrite as substrate for X-band microstrip patch antenna. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 499, 165918 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165918
N.K. Saxena, N. Kumar, P.K. Pourush, Radiation characteristics of microstrip rectangular patch antenna fabricated on LiTiMg ferrite substrate. AEU—Int. J. Electr. Commun. 69(12), 1741–1744 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2015.08.005
S. Bae, Y.K. Kong, A. Lyle, Effect of Ni–Zn ferrite on bandwidth and radiation efficiency of embedded antenna for mobile phone. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 07E929 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2838619
C.A. Stergiou, G. Litsardakis, Y-type hexagonal ferrites for microwave absorber and antenna applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 405, 54–61 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.12.027
L.B. Kong, Z.W. Li, G.Q. Lin, Y.B. Gan, Ni-Zn ferrites composites with almost equal values of permeability and permittivity for low-frequency antenna design. IEEE Trans. Magn. 43, 6–10 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2006.886321
S. Li, M. Zhao, J. Xue, R. Zhao, Effects of edge type and reconstruction on the electronic properties and magnetism of 1T′-ReS2 nanoribbons: a study based on DFT calculations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 567, 170351 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.170351
H. Zhang, Y. Xiao, Z. Xu, M. Yang, L. Zhang, L. Yin, S. Chai, G. Wang, L. Zhang, X. Cai, Effects of Ni-decorated reduced graphene oxide nanosheets on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu composite solders. Intermetallics 150, 107683 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2022.107683
M. Fu, W. Chen, Y. Lei, H. Yu, Y. Lin, M. Terrones, Biomimetic construction of ferrite quantum Dot/graphene heterostructure for enhancing Ion/charge transfer in supercapacitors. Adv. Mater. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202300940
M.M. Syazwan, A.N. Hapishah, M.N. Hamidon, I. Ismail, I.H. Hasan, Design and development of Ni0.75Zn0.25Fe2O4/MWCNT microstrip patch antenna (MPA) for ISM band spectrum applications. Synth. Metals 271, 116630 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2020.116630
R. Vinaykumar, J. Bera, Characterizations of low-temperature sintered, BaCo1.3Ti1.3Fe9.4O19 M-type ferrite for high-frequency antenna application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 614–619 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.11.120
R.R. Kanna, Structural, morphological and optomagnetic properties of GO/Nd/Cu-Mn ferrite ternary nanocomposite. Ceram. Int. 45(13), 16138–16146 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.132
S. Yuvaraj, N. Manikandan, G. Vinitha, Influence of copper ions on structural and non-linear optical properties in manganese ferrite nanomaterials. Opt. Mater. 73, 428–436 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2017.08.027
J.J. Vijaya, G. Sekaran, M. Bououdina, Effect of Cu2+ doping on structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 particles/sheets/flakes-like nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 41(1), 15–26 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.10.145
R. Rajesh Kanna, K. Sakthipandi, Structural, morphological, and optomagnetic properties of La/Cu/Cu-Mn ferrite ternary nanocomposites. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 1110–1119 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07729-y
E.R. Kumar, R. Jayaprakash, G.S. Devi, P.S.P. Reddy, Magnetic, dielectric and sensing properties of manganese substituted copper ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 355, 87–92 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.11.051
M.A. Ahmed, A.A. Azab, E.H. El-Khawas, E.A. El Bast, Characterization and transport properties of mixed ferrite system Mn1-xCuxFe2O4; 0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.7. Synthesis and reactivity in inorganic. Metal-Org. Nano-Metal Chem. 46(3), 376–384 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2014.988243
R.R. Kanna, K. Sakthipandi, S.M.S. Mohamed Aliar Maraikkayar, N. Lenin, M. Sivabharathy, Doping effect of rare-earth (lanthanum, neodymium and gadolinium) ions on structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of copper nanoferrites. J. Rare Earths 36(12), 1299–1309 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.03.033
R.R. Kanna, N. Lenin, K. Sakthipandi, M. Sivabharathy, Impact of lanthanum on structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of Mn1-xCuxFe1.85La0.15O4 spinel nanoferrites. Ceram. Int. 43(17), 15868–15879 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.160
P. Thakur, R. Sharma, M. Kumar, S.C. Katyal, P.B. Barman, V. Sharma, P. Sharma, Structural, morphological, magnetic and optical study of co-precipitated Nd3+ doped Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 479, 317–325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.02.048
S. Singh, P. Kaur, V. Kumar, K.B. Tikoo, S. Singhal, Traversing the advantageous role of samarium doped spinel nanoferrites for photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants. J. Rare Earths 39(7), 781–789 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2020.12.008
M.K. Kokare, N.A. Jadhav, V. Singh, S.M. Rathod, Effect of Sm substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of NiCo nanoferrites. Opt. Laser Technol. 112, 107–116 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.10.045
M.A. Abdo, A.A. El-Daly, Sm-substituted copper-cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: preparation and assessment of structural, magnetic and photocatalytic properties for wastewater treatment applications. J. Alloys Comp. 883, 160796 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160796
M. Yousaf, A. Noor, S. Xu, M.N. Akhtar, B. Wang, Magnetic characteristics and optical band alignments of rare earth (Sm, Nd ) doped garnet ferrite nanoparticles (NPs). Ceram. Int. 46(10), 16524–16532 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.219
Y. Slimani, M.A. Almessiere, S. Guner, B. Aktas, S.E. Shirsath, M.V. Silibin, A.V. Trukhanov, A. Baykal, Impact of Sm3+ and Er3+ cations on the structural, optical, and magnetic traits of spinel cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: comparison investigation. ACS Omega 7(7), 6292–6301 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c06898
A.B. Mugutkar, S.K. Gore, U.B. Tumberphale, V.V. Jadhav, R.S. Mane, S.M. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, S.S. Jadhav, Role of composition and grain size in controlling the structure sensitive magnetic properties of Sm3+ substituted nanocrystalline Co-Zn ferrites. J. Rare Earths 38(10), 1069–1075 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2019.09.013
M.A. Mahdi, S.R. Yousefi, L.S. Jasim, M. Salavati-Niasari, Green synthesis of DyBa2Fe3O7.988/DyFeO3 nanocomposites using almond extract with dual eco-friendly applications: photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 47(31), 14319–14330 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.02.175
S.R. Yousefi, M. Ghanbari, O. Amiri, Z. Marzhoseyni, P. Mehdizadeh, M. Hajizadeh-Oghaz, M. Salavati-Niasari, Dy2BaCuO5/Ba4DyCu3O9.09 S-scheme heterojunction nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.17696
S.R. Yousefi, H.A. Alshamsi, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, photocatalyst for discoloration of organic dye contaminants in wastewater and antibacterial properties. J. Mol. Liq. 337, 116405 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116405
S.R. Yousefi, A. Sobhani, H.A. Alshamsic, M. Salavati-Niasari, Green sonochemical synthesis of BaDy2NiO5/Dy2O3 and BaDy2NiO5/NiO nanocomposites in the presence of core almond as a capping agent and their application as photocatalysts for the removal of organic dyes in water. RSC Adv. 11, 11500–11512 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA10288A
S.R. Yousefi, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, Control sonochemical parameter to prepare pure Zn0.35Fe2.65O4 nanostructures and study their photocatalytic activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 58, 104619 (2019)
S.R. Yousefi, M. Masjedi-Arani, M.S. Morassaei, M. Salavati-Niasari, H. Moayedi, Hydrothermal synthesis of DyMn2O5/Ba3Mn2O8 nanocomposite as a potential hydrogen storage material. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44(43), 24005–24016 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.07.113
S.R. Yousefi, A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, A new nanocomposite superionic system (CdHgI4/HgI2): synthesis, characterization and experimental investigation. Adv. Powder Technol. 28(4), 1258–1262 (2017)
S.R. Yousefi, D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Hassanpour, Photo-degradation of organic dyes: simple chemical synthesis of Ni(OH)2 nanoparticles, Ni/Ni(OH)2 and Ni/NiO magnetic nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 1244–1253 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3882-6
P. Mehdizadeh, M. Jamdar, M.A. Mahdi, W.K. Abdulsahib, L.S. Jasim, S.R. Yousefi, M. Salavati-Niasari, Rapid microwave fabrication of new nanocomposites based on Tb-Co-O nanostructures and their application as photocatalysts under UV/Visible light for removal of organic pollutants in water. Arab. J. Chem. 16(4), 104579 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104579
S. Pan, M. Lin, M. Xu, S. Zhu, L.A. Bian, G. Li, A low-profile programmable beam scanning holographic array antenna without phase shifters. IEEE Internet Things 9(11), 8838–8851 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3116158
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, S. Guner, M. Sertkol, A.D. Korkmaz, S.E. Shirsath, A. Baykal, Sonochemical synthesis and physical properties of Co0.3Ni0.5Mn0.2EuxFe2−xO4 nano-spinel ferrites. Ultrason. Sonochem. 58, 104654 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104654
R.R. Kanna, K. Sakthipandi, A.S. Kumar, N.R. Dhineshbabu, Synthesis of dysprosium/Mn–Cu ferrite binary nanocomposite: analysis of structural, morphological, dielectric, and optomagnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 46, 13695–13703 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.157
S.P. Keerthana, R. Yuvakkumar, P. Senthil Kumar, G. Ravi, D. Velauthapillai, Rare earth metal (Sm) doped zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4) for improved photocatalytic elimination of toxic dye from aquatic system. Environ. Res. 197, 111047 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111047
M. Yehia, A. Hashhash, Structural and magnetic study of Sm doped NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00988-9
N. Senthilkumar, E. Nandhakumar, P. Priya, M. Selvakumar, I. VethaPotheher, Green and sustainable preparation of flower-like ZnO nanostructures via soft bio-template approach for the enhancement of biomedical applications. Appl. Phys. A 78, 128 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05192-3
R.R. Kanna, N. Lenin, K. Sakthipandi, A.S. Kumar, Structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic studies of gadolinium-added Mn-Cu nanoferrites. J. Magn. Magn Mater. 453, 78–90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.01.019
S.E. Shirsath, R.H. Kadam, K.M. Batoo, D. Wang, S. Li, Co–Al-substituted strontium hexaferrite for rare earth free permanent magnet and microwave absorber application. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 54, 024001 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/abb9d5
M. Dhiman, S. Rana, K. Batoo, J.K. Sharma, M. Singh, Synthesis and characterization of Y and Sm doped Mg nanoferrites. Integr. Ferroelectr. 184, 151–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2017.1368634
M.M. Ahamed, K. Bhowmik, A.A. Suman, Analysis and design of rectangular microstrip patch antenna on different resonant frequencies for pervasive wireless communication. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 1, 108–111 (2012)
N. Irfan, M.C.E. Yagoub, K. Hettak, Design of a microstrip-line-fed inset patch antenna for RFID applications. IACSIT Int. J. Eng. Technol. 4, 558–561 (2012). https://doi.org/10.7763/IJET.2012.V4.432
A. Saini, A. Thakur, P. Thakur, Matching permeability and permittivity of Ni0.5Zn0.3 Co0.2In0.1Fe1.9O4 ferrite for substrate of large bandwidth miniaturized antenna. J. Mater Sci Mater. Electr. 27, 2816–2823 (2015)
SZ Nyunt (2018) Implementation of microstrip patch antenna for wi-fi applications, Am. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 1:63–73. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajcst.20180103.12
S. Palanivel Rajan, C. Vivek, Analysis and design of microstrip patch antenna for radar communication. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 14, 923–929 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-018-00072-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RRK: conceptualization, methodology, re-writing, reviewing and editing of the manuscript, correspondence of the manuscript. PJ: preparation and characterization of the samples; preparation of the manuscript. NL: data analyzing and preparation of data for tables, assisted for preparation of the manuscript. GM: supported for experimental data analyzing. MPK: supported for experimental data analyzing. TVK: supported for experimental data analyzing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
We are confirming that the article is original and unpublished, and is not being or having been submitted for publication to any other journal, and that all the authors have read the paper and agree with its submission to Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics.
Human and animal participants
No Research involving Human Participants and/or Animals in the prepared manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11401-x
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kanna, R.R., Jeyakumar, P., Lenin, N. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Synthesis and investigation of Sm3+-doped Mn0.5Cu0.5Fe2O4 nanoferrites for microstrip patch antenna application. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1417 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10815-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10815-x