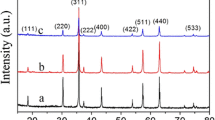
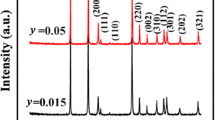
Abstract
SiCN ceramic is a candidate material for high-temperature sensors because of its stability and semiconductor characteristics at high temperatures. The free carbon content within the SiCN ceramics is a main factor that affects its conductivity. This study adjusted the free carbon content inside amorphous SiCN by adding divinylbenzene into the precursor. The electrical properties of SiCN ceramics with different free carbon contents were explored using ultraviolet fluorescence spectrum and temperature-resistant experiments. The results showed that with the increase of divinylbenzene from 0 to 20%, the conductivity of SiCN ceramics at room temperature increases from 2.77 × 10−9 to 3.66 × 10−4 S/cm, and the forbidden bandwidth decreases from 3.81 to 2.25 eV. At the same time, the increase of divinylbenzene content would promote the hybridization extent of free carbon from sp3 to sp2 and improve the degree of order. This work could pave the way for applying amorphous SiCN serving as temperature sensors.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
R. Riedel, A. Kienzle, W. Dressler, L. Ruwisch, J. Bill, F. Aldinger, A silicoboron carbonitride ceramic stable to 2000 °C. Nature 382, 796–798 (1996)
H. Zhao, L. Chen, X. Luan, X. Zhang, J. Yun, T. Xu, Synthesis, pyrolysis of a novel liquid SiBCN ceramic precursor and its application in ceramic matrix composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37(4), 1321–1329 (2017)
Y. Iwamoto, W. Völger, E. Kroke, Crystallization behavior of amorphous silicon carbonitride ceramics derived from organometallic precursors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84(10), 2170–2178 (2010)
D.L. Poerschke, A. Braithwaite, D. Park, F. Lauten, Crystallization behavior of polymer-derived Si–O–C for ceramic matrix composite processing. Acta Mater. 147, 329–341 (2018)
N. Janakiraman, F. Aldinger, Yielding, strain hardening, and creep under nanoindentation of precursor-derived Si–C–N ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(3), 821–829 (2010)
H.-Y. Ryu, Q. Wang, R. Raj, Ultrahigh-temperature semiconductors made from polymer-derived ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 1668 (2010)
Y. Wang, T. Jiang, L. Zhang, L. An, Electron transport in polymer-derived amorphous silicon oxycarbonitride ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92(7), 1603–1606 (2009)
Y. Yu, W. Xu, J. Xu, J. Zhu, M. Cong, Conductivity of SiCNO–BN composite ceramics and their application in wireless passive temperature sensor. Ceram. Int. 47(10), 14490–14497 (2021)
L.A. Liew, R.A. Saravanan, V.M. Bright, Processing and characterization of silicon carbon-nitride ceramics application of electrical properties towards MEMS thermal actuators. Sens. Actuators Phys. 103(1–2), 171–181 (2003)
R. Zhao, G. Shao, Y. Cao, L. An, C. Xu, Temperature sensor made of polymer-derived ceramics for high-temperature applications. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 219, 58–64 (2014)
X. Ren, S. Ebadi, H. Cheng, Y. Chen, G. Xun, Wireless resonant frequency detection of SiCN ceramic resonator for sensor applications, IEEE international symposium on antennas & propagation (2011) 1856–1859
P. Colombo, G. Mera, R. Riedel, G.D. Sorarù, Polymer-derived ceramics: 40 years of research and innovation in advanced ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(7), 1805–1837 (2010)
R. Riedel, G. Mera, R. Hauser, Silicon based polymer derived ceramics synthesis properties and applications a review. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 114(1330), 425–444 (2006)
L. Frediani, M.W. Usrey, O.A. Watts, Technical opportunities for high temperature smart P3 sensors and electronics for distributed engine control. 52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference (2016)
A. Von Moll, A.R. Behbahani, G.C. Fralick, J.D. Wrbanek, G.W. Hunter, A review of exhaust gas temperature sensing techniques for modern turbine engine controls. 50th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference (2014)
F. Dalcanale, J. Grossenbacher, G. Blugan, M.R. Gullo, A. Lauria, J. Brugger, H. Tevaearai, T. Graule, M. Niederberger, J. Kuebler, Influence of carbon enrichment on electrical conductivity and processing of polycarbosilane derived ceramic for MEMS applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(15), 3559–3570 (2014)
Y. Chen, X. Yang, Y. Cao, L. An, Effect of pyrolysis temperature on the electric conductivity of polymer-derived silicoboron carbonitride. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(10), 2163–2167 (2014)
S. Trassl, M. Puchinger et al., Electrical properties of amorphous SiCxNyHz-ceramics derived from polyvinylsilazane. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23(5), 781–789 (2003)
Y. Chen, F. Yang, L. An, On electric conduction of amorphous silicon carbonitride derived from a polymeric precursor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(23), 231902 (2013)
C. Drechsel, H. Peterlik, C. Gierl-Mayer, M. Stöger-Pollach, T. Konegger, Influence of DVB as linker molecule on the micropore formation in polymer-derived SiCN ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41(6), 3292–3302 (2021)
L. Hagelüken, P.V.W. Sasikumar, H.-Y. Lee, D. Di Stadio, Y. Chandorkar, M. Rottmar, K. Maniura-Weber, G. Blugan, J. Brugger, Multiscale 2D/3D microshaping and property tuning of polymer-derived SiCN ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42(5), 1963–1970 (2022)
G. Liu, J. Kaspar, L.M. Reinold, M. Graczyk-Zajac, R. Riedel, Electrochemical performance of DVB-modified SiOC and SiCN polymer-derived negative electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta. 106, 101–108 (2013)
B. Ma, Y. Cao, Y. Gao, Y. Wang, Fabrication of a thin double-layer thermistor based on DVB-modified polymer-derived SiCN ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 732, 491–497 (2018)
K. Liu, W. Peng, D. Han, Y. Liang, B. Fan, H. Lu, H. Wang, H. Xu, R. Zhang, G. Shao, Enhanced piezoresistivity of polymer-derived SiCN ceramics by regulating divinylbenzene-induced free carbon. Ceram. Int. 49, 2296 (2022)
G.D. Sorarù, S. Modena, E. Guadagnino, P. Colombo, J. Egan, C. Pantano, Chemical durability of silicon oxycarbide glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 1529–1536 (2002)
Y. Chen, X. Yang, Y. Cao, Z. Gan, L. An, Quantitative study on structural evolutions and associated energetics in polysilazane-derived amorphous silicon carbonitride ceramics. Acta Mater. 72, 22–31 (2014)
B. Ma, Y. Wang, K. Wang, X. Li, J. Liu, L. An, Frequency-dependent conductive behavior of polymer-derived amorphous silicon carbonitride. Acta Mater. 89, 215–224 (2015)
A.C. Ferrari, J. Robertson, Raman spectroscopy of amorphous, nanostructured, diamond-like carbon, and nanodiamond. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 362(1824), 2477–2512 (2004)
S. Chen, J. Li, H. Shi, X. Chen, G. Liu, S. Meng, J. Lu, Lightweight and geometrically complex ceramics derived from 4D printed shape memory precursor with reconfigurability and programmability for sensing and actuation applications. Chem. Eng. J. 455, 140655 (2023)
I. Štubňa, V. Trnovcová, L. Vozár, Å. Csáki, Uncertainty of the measurement of DC Conductivity of eramics at elevated temperatures. J. Electr. Eng. 66(1), 34–39 (2015)
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 15, 627–637 (1966)
P. Kubelka, F. Munk, An article on optics of paint layers. Z. Tech. Phys. 12, 593–601 (1931)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. 12090034, No. 11672087).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 12090034 and 11672087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, JL; methodology, HS and GZ; formal analysis, HS and GZ; investigation, HS; data curation, HS and GZ; writing and original draft preparation, HS; writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript, JL; supervision, JL; project administration, SM; funding acquisition, JL and SM. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, H., Li, J., Zhang, G. et al. Effect of free carbon content changed by divinylbenzene on the conductivity of SiCN ceramic. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1402 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10770-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10770-7