Abstract
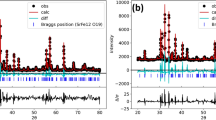
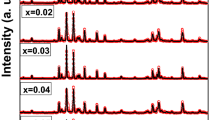
The Mo6+ ions-doped SrNi-hexaferrites, Sr0.8Ni0.2MoxFe12−2xO19 (x ≤ 0.35) HFs, were manufactured by sol–gel approach. Microstructure was analyzed through XRD, SEM–EDX, TEM, and HR-TEM. The effect of Mo6+ ions substitution on the electric-dielectric features of SrNi-HFs has been studied versus frequency and at different temperatures by impedance spectroscopy technique. It has been pointed out that the ac conductivity obeys the power law rule of f, and it is found that the dependencies of both T and substitution ratios in SrNi-HFs are highly influential for grains and grain boundaries. The levels of activation (Ea) determined from dc electrical conductivity fluctuate with the Mo6+ ion substitution into SrNi-HFs implying that the mechanism of conduction is due to the contribution of both polaron and electron hopping. The dielectric parameters were found to be f dependent at T up to 120 °C for various Mo6+ substitution ratios. The complex impedance of Cole–Cole plots shows a semicircle of different dimensions that depend on T, indicating that the resistive and capacitive responses of SrNi-HFs are because of the contribution of grain boundaries and grains formed in the HFs` structures. It has been detected that although the Mo6+ ion substitution creates relatively small differences on grain resistance, it causes a notable change in grain boundary resistance in the SrNi-HFs` system.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are available within this article.
References
Q. Li, Y. Chen, C. Yu, K. Qian, V.G. Harris, Permeability spectra of planar M-type barium hexaferrites with high Snoek’s product by two-step sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 103, 5076–5085 (2020)
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Progr. Mater. Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012)
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, H. Gungunes, M. Sertkol, M. Nawaz, A. Baykal, Tb3+ substituted strontium hexaferrites: structural, magnetic and optical investigation and cation distribution. Rare Earths 38(4), 402–410 (2020)
C. Orozco, A. Melendez, S. Manadhar, S.R. Singamaneni, K.M. Reddy, K. Gandha, L.C. Niebedim, C.V. Ramana, Effect of molybdenum incorporation on the structure and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 25463–25471 (2017)
N. Kaveri, J. Balavijayalakshmi, Impact of molybdenum on structural and morphological properties of manganese ferrite nanoparticles by hydrothermal method. Mater. Today 33, 2390–2395 (2020)
B. Domenichini, D. Aymes, P. Perriat, B. Gillot, Evidence of a hopping mechanism between Mo3+ and Mo4+ octahedral cations in molybdenum spinel ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 39, 80–84 (1994)
A. Roy, S. Kumar, D. Banerjee, J. Ghose, Mossbauer studies on titanium substituted molybdenum ferrite. Solid State Commun. 114, 143–148 (2000)
B. Gillot, J. Lorimier, F. Bernard, V. Nivoix, S. Douard, Ph. Tailhades, Thermal behavior and cation distribution in nanosized Mo-Co ferrite spinels Mo0.5CoyFe2.5−yO4 (0 ≤ y ≤ 1) studied by DTG, FT–IR and DC conductivity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 61, 199 (1999).
Z.K. Heiba, N.Y. Mostafa, O.H. Abd-Elkader, Structural and magnetic properties correlated with cation distribution of Mo-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 368, 246 (2014)
A.K. Pradhan, P.R. Mandal, K. Bera, S. Saha, T.K. Nath, The effect of Mo doping on the structural and dielectric properties of Co-Zn ferrite. Physica B 525, 1–6 (2017)
B.V. Rao, A.D.P. Rao, Influence of Mo6+ on magnetic and micro-structural properties of copper ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 708, 141–145 (2017)
M.A. Malana, R.B. Qureshi, M.N. Ashiq, M.F. Ehsan, Synthesis, structural, magnetic and dielectric characterizations of molybdenum doped calcium strontium M-type hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 42, 2686–2692 (2016)
G.H. Dushaq, S.H. Mahmood, I. Bsoul, H.K. Juwhari, B. Lahlouh, M.A. AlDamen, Effects of molybdenum concentration and valence state on the structural and magnetic properties of BaFe11.6MoxZn0.4−xO19 hexaferrites. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 26(5), 509–516 (2013).
S.H. Mahmood, A.N. Aloqaily, Y. Maswadeh, A. Awadallah, I. Bsoul, M. Awawdeh, H. Juwhari, Effects of heat treatment on the phase evolution, structural, and magnetic properties of BaFe12-4xMoxZn3xO19 hexaferrites. Solid State Phenom. 232, 65–92 (2015)
A.H. Salama, A.M. Youssef, Y.S. Rammahand, M. El-Khatib, YBCO as a transition metal oxide ceramic material for energy storage. Bull. Natl. Res. Centre 43(1), 89 (2019)
S. Asiri, S. Güner, A.D. Korkmaz, Md. Amir, A. Baykal, Magneto-optical properties of BaCryFe12−yO19 (0.0 ≤ y ≤ 1.0) hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 463–472 (2018).
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A. Baykal, Structural and magnetic properties of Ce-doped strontium hexaferrite. Cer. Int. 44, 9000–9008 (2018)
S. Kochowski, K. Nitsch, Description of the frequency behaviour of metal-SiO2-GaAs structure characteristics by electrical equivalent circuit with constant phase element. Thin Solid Films 415, 133–137 (2002)
I. Ali, M.U. Islam, M.N. Ashiq, M.A. Iqbal, H.M. Khan, N. Karamat, Effect of Tb–Mn substitution on DC and AC conductivity of Y-type hexagonal ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 579, 576–582 (2013)
A.K. Jonscher, The universal dielectric response. Nature 267, 673–679 (1977)
K. Ugendar, G. Markandeyulu, S. Mallesh, Polaron conduction mechanism in Nickel ferrite and its rare-earth derivatives. Physica B 606, 412819 (2021)
W. Khan, A.H. Naqvi, M. Gupta, S. Husain, R. Kumar, Small polaron hopping conduction mechanism in Fe doped LaMnO3. J. Chem. Phys. 135, 054501 (2011)
B. Unal, M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A. Baykal, A.V. Trukhanov, The conductivity and dielectric properties of niobium substituted Sr–NHFs. Nanomaterials 9, 1168 (2019)
M.A. Gabal, Y.M. Al Angari, Effect of diamagnetic substitution on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of NiFe2O4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 115, 578–584 (2009).
S.S. Narayanan-Potty, M.A. Khadar, Dielectric properties of nanophase Ag2HgI4 and Ag2HgI4-Al2O3 nanocomposites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 23(5), 361–367 (2000)
S. Sui-Lin, Z. Ling-Zhen, L. Jun-Shou, Electrical and dielectric properties of multiwall carbon nanotube/polyaniline composites. J. Polym. Res. 16, 395–399 (2009)
H.M. El Ghanem, S.A. Jawad, M.H. Al-Saleh, Y.A. Hussain, W. Salah, Effect of dc-bias on the dielectric behavior of CNT/ABS nanocomposites. Physica B. 418, 41–46 (2013)
B. Ünal, M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A. Baykal. A.V. Trukhanov, The conductivity and dielectric properties of niobium substituted Sr-hexaferrites. Nanomaterials 9(8), 1168 (2019)
A. Munar, A. Andrio, R. Iserte, V. Compan, Ionic conductivity and diffusion coefficients of lithium salt polymer electrolytes measured with dielectric spectroscopy. J. Noncrystalline Solids 357, 3064–3069 (2011)
J. Malathi, M. Kumaravadivel, G.M. Brahmanandhan, M. Hema, R. Baskaran, S.J. Selvasekarapandian, Structural, thermal and electrical properties of PVA–LiCF3SO3 polymer electrolyte. Noncrystalline Solids. 356, 2277–2281 (2010)
H.E. Atyia, N.A. Hegab, M.A. Affi, M.I. Ismail, Influence of temperature and frequency on the AC conductivity and dielectric properties for Ge15Se60Bi25amorphous films. J. Alloys Compd. 574, 345–353 (2013)
Y.P. Mamunya, V.V. Davydenko, P. Pissis, E.V. Lebedev, Electrical and thermal conductivity of polymers filled with metal powders. European. Poly. J. 38, 1887–1897 (2002)
M. Pandey, G. M. Joshi, K. Deshmukh. M. Khutia, N.N. Ghosh, Optimized AC conductivity correlated to structure, morphology and thermal properties of PVDF/PVA/Nafion composites. Ionics 20(10), 1427–1433 (2014).
K. Pandey, M. M. Dwivedi, M. Singh, S. L. Agrawal, Studies of dielectric relaxation and a.c. conductivity in [(100−x)PEO + xNH4SCN]: Al-Zn ferrite nano composite polymer electrolyte. J. Polym. Res. 17, 127–133 (2010).
S.S. Bellad, S.C. Watawe, B.K. Chougule, Some ac electrical properties of Li–Mg ferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 34(7), 1099–1106 (1999)
I. Haldar, M. Biswas, A.J. Nayak, Preparation and evaluation of microstructure, dielectric and conductivity (ac/dc) characteristics of a polyaniline/poly N-vinyl carbazole/Fe3O4 nanocomposite. Polym. Res. 19, 9951 (2012)
T. Naoki, S. Hara, Direct synthesis of conducting polymers from simple monomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 20, 155–183 (1995)
A. Pradeep, P. Priyadharsini, G. Chandrasekaran, Production of single-phase nano size NiFe2O4 particles using sol–gel auto combustion route by optimizing the preparation conditions. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 572–576 (2008)
K. Roumaih, The transport properties of the mixed Ni–Cu ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 465, 291–295 (2008)
M. Gupta, B.S. Randhawa, Microstructural, magnetic and electric properties of mixed Cs–Zn ferrites prepared by solution combustion method. Solid State Sci. 14, 849–856 (2012)
B. Ünal, M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A. D. Korkmaz, A. Baykal, A study on the electrical and dielectric properties of SrGdxFe12−xO19 (x = 0.00–0.05) nanosized M-type hexagonal ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 18317–18329 (2021).
K.V.G. Kutty, C.K. Mathews, T.N. Rao, U.V. Varadaraju, Oxide ion conductivity in some substituted rare earth pyrozirconates. Solid State Ionics 80, 99–110 (1995)
X.L. Xia, J.H. Ouyang, Z.G. Liu, Influence of CaO on structure and electrical conductivity of pyrochlore-type Sm2Zr2O7. Power Sour. 189, 888–893 (2009)
A. Elahi, M. Ahmad, I. Ali, M.U. Rana, Preparation and properties of sol–gel synthesized Mg-substituted Ni2Y hexagonal ferrites. Ceram. Int. 39, 983–990 (2013)
L.J. Berchmans, R.K. Selvan, P.N.S. Kumar, C.O. Augustin, Structural and electrical properties of Ni1−xMgxFe2O4 synthesized by citrate gel process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 279, 103–110 (2004)
A. K. Jonscher A new understanding of the dielectric relaxation of solids. J. Mater. Sci. 16, 2037–2060 (1981).
T. Honegger, K. Berton, E. Picard, D. Peyrade, Determination of Clausius-Mossotti factors and surface capacitances for colloidal particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 181906 (2011)
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121–124 (1951)
K.M. Batoo, R. Verma, A. Chauhan, R. Kumar, M. Hadi, O.M. Aldossary, Y. Al-Douri, Improved room temperature dielectric properties of Gd3+ and Nb5+ co-doped barium titanate ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 883, 160836 (2021)
E. Ata, M.A. Ahmed, Dielectric and AC conductivity for BaCo2−xCuxFe16O27 ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 208, 27–36 (2000)
S. Narang, A. Singh, K. Singh, High frequency dielectric behavior of rare earth substituted Sr-M hexaferrite. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 8(5), 347–351 (2007)
K.W. Wagner, On the theory of imperfect dielectrics. Ann. Phys. 345, 817 (1913)
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at radiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 817 (1951)
E. Barsoukov, J.S. Macdonald, Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications, 3rd edn. (Wiley, New York, 2018)
J.R. Dygas, G. Fafilek, M.W. Breiter, Study of grain boundary polarization by two-probe and fourprobe impedance spectroscopy. Solid State Ion. 119, 115–125 (1999)
M. Rekaby, Dielectric response and Cole–Cole plot analysis for (Zn0.91Mn0.03Co0.06O)x/Cu0.5Tl0.5Ba2Ca2Cu3O10–δ diluted magnetic semiconductor/superconductor composites. Appl. Phys. A 126, 664-669 (2020)
H.T. Langhammer, D. Makovec, Y. Pu, H.P. Abicht, M. Drofenik, Grain boundary re-oxidation of donor doped barium titanate ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2899–2907 (2006)
Acknowledgements
MAA, AB, and YS acknowledged the Institute for Research and Medical Consultations of Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University (Dammam, Saudi Arabia) for providing laboratory facilities.
Funding
There is no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BÜ, MAA contributed to conceptualization and design of the work. BÜ contributed to investigation, writing, and explaining. YS and MAA contributed to formal analysis. AB and RJ contributed to project administration, editing, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article doesn't contain any studies involving animals performed by any authors. Also, this article does not contain any studies involving human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ünal, B., Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y. et al. The role of Mo6+ ion substitution on the electrical and dielectric features of SrNi-hexaferrites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1386 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10744-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10744-9