Abstract
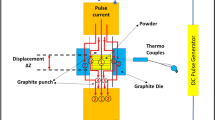
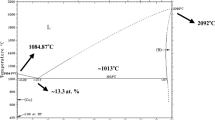
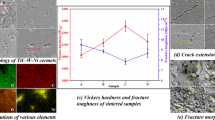
The MnZn/NiZn ferrite laminated co-fired ceramics were successfully prepared via spark plasma sintering (SPS) method. The interface between MnZn and NiZn ferrite layers in the co-fired ceramics has no obvious diffusion due to the short sintering time (less than 3 min) and low temperature (~ 1000 °C). The density and hardness of the co-fired samples increased with the increase of the sintering temperature. Due to the unique sintering process of SPS technique and the difference in electrical conductivity of the two ferrites, the MnZn ferrite layer is dense while the NiZn ferrite layer is loose in the co-fired ceramics. To adjust the sintering compatibility of NiZn ferrite and MnZn ferrite, the sintering additive Bi2O3 was used. Finally, the MnZn/Bi2O3-modified NiZn ferrite laminated co-fired ceramic composites with high density, hardness and good magnetic properties (MS-NiZn=68.71 emu/g, HC-NiZn=27.04 Oe, MS-MnZn=33.05 emu/g, HC-MnZn=11.05 Oe) were prepared by spark plasma sintering method. This work provides a simple and feasible method for preparing laminated co-fired ceramics.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
M. Jiménez-Melendo, F. Gutiérrez-Mora, A. Domínguez-Rodríguez, Effect of layer interfaces on the high-temperature mechanical properties of alumina/zirconia laminate composites. Acta. Mater. 48, 4715–4720 (2000)
L. Ren, M. Zhang, H. Zhou, Co-firing compatibility of LTCC hetero-laminates with low and middle permittivity. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 31, 12282–12291 (2020)
S. Dinesh Kumar, S. Gupta, A.B. Swain, V. Subramanian, M.K. Padmanabhan, R.L. Mahajan, Large converse magnetoelectric effect in Sm doped Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)-PbTiO3 and NiFe2O4 laminate composite. J. Alloys Compd. 858, 157684 (2021)
N. Shara Sowmya, A. Srinivas, P. Saravanan, K. Venu Gopal Reddy, S.V. Kamat, J. Paul Praveen, D. Das, G. Murugesan, S. Dinesh Kumar, V. Subramanian, Studies on magnetoelectric coupling in lead-free [(0.5) BCT-(0.5) BZT]-NiFe2O4 laminated composites at low and EMR frequencies. J. Alloys Compd. 743, 240–248 (2018)
S. Dinesh Kumar, J. Magesh, V. Subramanian, Temperature dependent magnetoelectric studies in co-fired bilayer laminate composites. J. Alloys Compd. 753, 595–600 (2018)
D. Zhou, Y. Chen, D. Zhang, H. Liu, Y. Hu, S. Gong, Fabrication and characterization of the multilayered PTCR ceramic thermistors by slip casting. Sens. Actuators A 116, 450–454 (2004)
M.J. Kim, T.Y. Yang, Y.B. Lee, H.C. Park, Dispersion stability of Y-TZP/Ce-TZP powder system and slip casting. J. Mater. Sci. 37, 1661–1665 (2002)
B. Ferrari, S. González, R. Moreno, C. Baudín, Multilayer coatings with improved reliability produced by aqueous electrophoretic deposition. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 27–36 (2006)
Y.J. Wu, N. Uekawa, K. Kakegawa, Sandwiched BaNd2Ti4O12/Bi4Ti3O12/BaNd2Ti4O12 ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Lett. 57, 4088–4092 (2003)
Z. Lou, M. Qin, P. Zhang, T. Su, Z. Shi, J. Xu, F. Gao, Microstructure and thermoelectric properties of Sr0.9La0.1TiO3/TiO2 biphase composite ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 861, 158552 (2021)
X. Liu, X.M. Chen, M.D. Liu, Z.D. Yu, J.J. Lan, X. Zhan, J.B. Lu, H.M. Jing, Improved dielectric and ferroelectric properties of fine-grained K0.5Na0.5NbO3 ceramics via hot-press sintering. Ceram. Int. 48, 11615–11622 (2022)
M. Yang, L. Wang, H. Li, S. Wang, L. Wang, P. Xing, Y. Zhuang, Microstructure and mechanical properties of B4C matrix composites prepared via hot-pressing sintering with Pr6O11 as additive. Ceram. Int. 48, 7897–7904 (2022)
M.G. Tokarev, E.A. Potanina, A.I. Orlova, S.A. Khainakov, M.S. Boldin, E.A. Lantsev, N.V. Sakharov, A.A. Murashov, S. Garcia-Granda, A.V. Nokhrin, V.N. Chuvildeev, Thermal expansion of Scheelite-Like molybdate powders and ceramics. Inorg. Mater 55, 730–736 (2019)
V.M. Klymenko, Spark plasma sintering of porous materials made of 1Kh18N9T corrosion-resistant steel fibers. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 58, 23–28 (2019)
T.M. Takeuchi, Synthesis of dense lead titanate ceramics with submicrometer grains by spark plasma sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc 83, 541–544 (2000)
H. Wang, B. Fan, L. Feng, D. Chen, H. Lu, H. Xu, C.A. Wang, R. Zhang, The fabrication and mechanical properties of SiC/ZrB2 laminated ceramic composite prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 38, 5015–5022 (2012)
B. Ratzker, R. Shrem, I. Ayalon, A. Shirakov, Z. Burshtein, S. Kalabukhov, N. Maman, V. Ezersky, A. Ishaaya, E. Galun, N. Frage, Co2+:MgAl2O4 saturable absorber transparent ceramics fabricated by high-pressure spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42, 6067–6074 (2022)
D.Y. Kosyanov, R.P. Yavetskiy, A.V. Tolmachev, A.A. Vornovskikh, A.V. Pogodaev, E.A. Gridasova, O.O. Shichalin, T.A. Kaidalova, V.G. Kuryavyi, Fabrication of highly-doped Nd3+:YAG transparent ceramics by reactive SPS. Ceram. Int. 44, 23145–23149 (2018)
M.A. Bousnina, F. Schoenstein, L.S. Smiri, N. Jouini, Facile synthesis of metastable Ni–P nanostructured materials by a novel bottom-up strategy. Solid. State. Sci. 40, 13–19 (2015)
A. Sedaghat Ahangari, H. Zadeh, E. Taheri-Nassaj, Densification behaviour and microstructure of spark plasma sintered alumina–mullite nanocomposite. Micro. Nano. Lett. 14, 957–961 (2019)
Y.J. Wu, N. Uekawa, Y. Sasaki, K. Kakegawa, Microstructures and pyroelectric properties of multicomposition 0.9PbZrO3·xPbTiO3·(0.1-x)pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc 85, 1988–1992 (2002)
A. Thakur, P. Mathur, M. Singh, Study of dielectric behaviour of Mn–Zn nano ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 68, 378–381 (2007)
N. Aggarwal, S.B. Narang, Magnetic characterization of Nickel-Zinc spinel ferrites along with their microwave characterization in Ku band. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 513, 167052 (2020)
Y. Yang, H. Zhang, J. Li, Y. Rao, G. Wang, G. Gan, Bi3+ doping-adjusted microstructure, magnetic, and dielectric properties of nickel zinc ferrite ceramics for high frequency LTCC antennas. Ceram. Int. 46, 25697–25704 (2020)
S. Taneja, D. Chahar, P. Thakur, A. Thakur, Influence of bismuth doping on structural, electrical and dielectric properties of Ni–Zn nanoferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 859, 157760 (2021)
A. Ghasemi, M.R. Loghman-Estarki, S. Torkian, M. Tavoosi, The microstructure and magnetic behavior of spark plasma sintered iron/nickel zinc ferrite nanocomposite synthesized by the complex sol-gel method. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 175, 107179 (2019)
P. Thakur, S. Taneja, D. Chahar, B. Ravelo, A. Thakur, Recent advances on synthesis, characterization and high frequency applications of Ni-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 530, 167925 (2021)
J. Hu, Z. Li, H. Yu, X. Zhong, Z. Liu, K. Long, J. Li, Modifying the soft magnetic Properties of Mn-Zn Ferrites by Ce2O3-Doping and sintering temperature optimization. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 6501–6509 (2020)
M.N. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, M. Ahmad, M.S. Nazir, M. Imran, A. Ali, A. Sattar, G. Murtaza, Evaluation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of CuZnNi (CuxZn0.5–Ni0.5Fe2O4) nanocrystalline ferrites for core, switching and MLCI’s applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421, 260–268 (2017)
C. Yang, F. Liu, T.L. Ren, L.T. Liu, G. Chen, X.K. Guan, A. Wang, Z.X. Yue, Ni-Zn ferrite film coated on-chip RF inductor fabricated by a novel powder-mixed-photoresist coating technique. IEEE Mtt S Int Micr Vols. 1–6, 465–468 (2007)
X. Niu, B. Zong, H. Hu, B. Wu, Influence of Sn4+-substituted on the magnetic properties and power loss of Ni-Zn soft magnetic ferrites. Optik. 134, 135–139 (2017)
M. Popela, J. Láčík, L. Dražan, Waveguide power phase shifter with a ferrite circulator in S-band. J. Electr. Eng. 73, 215–220 (2022)
T.V. Sagar, T.S. Rao, K.C.B. Naidu, Effect of calcination temperature on optical, magnetic and dielectric properties of Sol-Gel synthesized Ni0.2Mg0.8-xZnxFe2O4 (x = 0.0–0.8). Ceram. Int. 46, 11515–11529 (2020)
C.W. Nan, M.I. Bichurin, S. Dong, D. Viehland, G. Srinivasan, Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: historical perspective, status, and future directions. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 031101 (2008)
M.L.S. Teo, L.B. Kong, Z.W. Li, G.Q. Lin, Y.B. Gan, Development of magneto-dielectric materials based on Li-ferrite ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 459, 557–566 (2008)
M. Drofenik, A. Žnidaršič, D. Makovec, Influence of the addition of Bi2O3 on the grain growth and magnetic permeability of MnZn Ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 2841–2848 (1998)
J. Mürbe, J. Töpfer, Ni-Cu-Zn Ferrites for low temperature firing: II. Effects of powder morphology and Bi2O3 addition on microstructure and permeability. J. Electroceram. 16, 199–205 (2006)
H. Mahmud, J.U. Ahamed, M.N.I. Khan, Giant effect on structural, magnetic, electrical, and optical properties of lead-free Ba0.6Sr0.4Ti1-xAlxO3 ceramics via Sr and Al Co-doping engineering. Mater. Res. Express. 9, 112001 (2022)
M. Yan, X.L. Peng, Fundamentals of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials (Zhejiang University Press, Hangzhou, 2006), p. 110
Y.J. Huang, Z.W. Lan, Magnetic Materials (Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, 1994), pp. 1–92
N. Raghuram, T.S. Rao, K.C.B. Naidu, Magnetic properties of hydrothermally synthesized Ba1–xSrxFe12O19 (x = 0.0–0.8) nanomaterials. Appl. Phys. A. 125 (2019).
D. Sivakumar, K.C.B. Naidu, K.P. Nazeer, M.M. Rafi, G.R. Kumar, B. Sathyaseelan, G. Killivalavan, A.A. Begam, Structural characterization and dielectric studies of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Korean Ceram. Soc 55, 230–238 (2018)
D.F. Wan, X.L. Ma, Magnetic Physics (University of Electronic Science and Technology Press, Chengdu, 1994), pp. 342–380
Z. Cai, S. Li, Q. Zhang, C. Wang, Z. Jin, M. Fu, S. Zhang, M. Liang, Z. Wang, Y. Han, Derivation and verification of the relationship between ablation index and baseline impedance. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2021, 5574125 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Project of State Key Laboratory of Environment-friendly Energy Materials (No. 20fksy23 and 21fksy27) and Southwest University of Science and Technology (No. 22zx7157 and No. 20zg811002).
Funding
This study was supported by State Key Laboratory of Environment-friendly Energy Materials (No. 20fksy23 and 21fksy27), Southwest University of Science and Technology (No. 22zx7157 and No. 20zg811002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QN: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft. BD: Resources, Supervision, Writing—Review & Editing. YR: Supervision. GL: Formal analysis,Writing—Review & Editing. FX: Formal analysis. YZ: Investigation. XL: Investigation. XY: Funding acquisition, YW: Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All co-authors agreed to this submission, which has not been considered by any other journal.
Ethical approval
The full paper has not been submitted or published elsewhere and will not be submitted elsewhere until the journal editorial process is complete.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, Q., Dai, B., Ren, Y. et al. Electrical and magnetic properties of Ni0.75Zn0.25Fe2O4/Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 laminated co-fired ceramic composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1237 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10652-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10652-y