Abstract
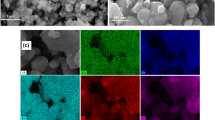
Barium strontium hexaferrite (BSFO) nanomaterial compositions were prepared using hydrothermal technique. The phase identification of BSFO revealed the hexagonal structure. The field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) techniques were used to study the surface morphology of BSFO nanostructures. TEM study showed the presence of distorted spheres like nanostructures of size 7–28 nm. Furthermore, the presence of metal oxides (Ba–O, Sr–O, and Fe–O) and functional groups were detected using Fourier transform infrared spectra (FTIR). Subsequently, magnetic nature of BSFO was confirmed using magnetization–magnetic field (M–H) and magnetic permeability–temperature (μi–T) plots. The μi–T plots suggested the enhancement of Tc from 703 K–753 K as a function of Sr-content (x). In addition, the variation of μi, magnetic loss (μ″) as well as relative magnetic loss factor (rlf: tanδ/μi) with respect to the frequency was performed for probable transformer and inductor core device applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data will be made available immediately based on the request.
References
B.K. Rai, S.R. Mishra, V.V. Nguyen, J.P. Liu, Synthesis and characterization of high coercivity rare-earth ion doped Sr0.9RE0.1Fe10Al2O19 (RE: Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, and Gd). J. Alloys Compd. 550, 198–203 (2013)
M.J. Iqbal, M.N. Ashiq, I.H. Gul, Physical, electrical and dielectric properties of Ca-substituted strontium hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 1720–1726 (2010)
S. Ramesh, D. Ravinder, K.C.B. Naidu, N.S. Kumar, K. Srinivas, D.B. Basha, B.C. Sekhar, A review on giant piezoelectric coefficient, materials and applications. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 9, 4205–4216 (2019)
M. Hashim, K.C.B. Naidu, G.H.R. Joice, J.L. Naik, D. Ravinder, Superparamagnetic and photocatalytic activity of CoCe0.02Dy0.02Fe1.96O4 nanoparticles synthesized by citrate-gel autocombustion technique. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 9, 4164–4167 (2019)
M.A. Ahmed, N. Helmy, S.I. El-Dek, Innovative methodology for the synthesis of Ba-M hexaferrite BaFe12O19 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 3394–3398 (2013)
B. Huang, C. Li, J. Wang, Template synthesis and magnetic properties of highly aligned barium hexaferrite (BaFe12O19) nanofibers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 335, 28–31 (2013)
Y. Li, Q. Wang, H. Yang, Synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties on nanocrystalline BaFe12O19 ferrite. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 1375–1380 (2009)
M.B. Kaynar, Ş. Özcan, S.I. Shah, Synthesis and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline BaFe12O19. Ceram. Int. 41, 11257–11263 (2015)
C.J. Li, B.-N. Huang, J.-N. Wang, Effect of aluminum substitution on microstructure and magnetic properties of electrospun BaFe12O19 nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 1702–1710 (2012)
J.-L. Mattei, C.N. Le, A. Chevalier, A. Maalouf, N. Noutehou, P. Queffelec, V. Laur, A simple process to obtain anisotropic self-biased magnets constituted of stacked barium ferrite single domain particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 208–213 (2018)
Z. Mosleh, P. Kameli, M. Ranjbar, H. Salamati, Effect of annealing temperature on structural and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 hexaferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 40, 7279–7284 (2014)
X. Shen, M. Liu, F. Song, X. Meng, Structural evolution and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Sol Gel. Sci. Technol. 53, 448–453 (2009)
K.S. Martirosyan, E. Galstyan, S.M. Hossain, Y.-J. Wang, D. Litvinov, Barium hexaferrite nanoparticles: synthesis and magnetic properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 8–13 (2011)
W.S. Castro, R.R. Corrêa, P.I. Paulim Filho, J.M. Rivas Mercury, A.A. Cabral, Dielectric and magnetic characterization of barium hexaferrite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 41, 241–246 (2015)
C. Hou, G. Liu, F. Dang, Z. Zhang, J. Chen, Effect of strontium substitution on microstructure and magnetic properties of electrospinning BaFe12O19 nanofibers. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 32, 871–874 (2017)
I. Bsoul, S.H. Mahmood, Magnetic and structural properties of BaFe12−xGaxO19 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 489, 110–114 (2010)
Y. Liu, M.G.B. Drew, Y. Liu, Optimizing the methods of synthesis for barium hexagonal ferrite-An experimental and theoretical study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 134, 266–272 (2012)
D. Guo, W. Kong, J. Feng, X. Li, X. Fan, Microwave absorption properties of SrxBa3–xCo2Fe24O41 hexaferrites in the range of 0.1–18 GHz. J. Alloys Compd. 751, 80–85 (2018)
S. Shooshtary Veisi, M. Yousefi, M.M. Amini, A.R. Shakeri, M. Bagherzadeh, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Cu/Zr doped M-type Ba/Sr hexaferrites prepared via sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.189
D. Guo, W. Kong, J. Feng, X. Li, X. Fan, Synthesis, electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of Ba3Co2Fe24O41 hexaferrites for GHz application. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 228, 213–217 (2018)
F. Song, X. Shen, J. Xiang, Y. Zhu, Characterization and magnetic properties of BaxSr1–xFe12O19 (x = 0–1) ferrite hollow fibers via gel-precursor transformation process. J. Alloys Compd. 507, 297–301 (2010)
N. Raghuram, T.S. Rao, K.C.B. Naidu, Investigations on functional properties of hydrothermally synthesized Ba1–xSrxFe12O19 (x = 0.0–0.8) Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 94, 136–150 (2019)
M. Cernea, S.-G. Sandu, C. Galassi, R. Radu, V. Kuncser, Magnetic properties of BaxSr1−xFe12O19 (x = 0.05–0.35) ferrites prepared by different methods. J. Alloys Compd. 561, 121–128 (2013)
J. Luo, S. Pan, L. Cheng, P. Lin, Y. He, J. Chang, Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of Er-Ho-Fe alloys. J. Rare Earths 36, 715–720 (2018)
W. Yang, Y. Zhang, G. Qiao, Y. Lai, S. Liu, C. Wang, J. Yang et al., Tunable magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Sm1.5Y0.5Fe17-xSix and their composites. Acta Mater. 145, 331–336 (2018)
C. Chen, L. Pan, S. Jiang, S. Yin, X. Li, J. Zhang, J. Yang et al., Electrical conductivity, dielectric and microwave absorption properties of graphene nanosheets/magnesia composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38, 1639–1646 (2018)
X. Jilei, P. Shunkang, C. Lichun, L. Peihao, Y. Qingrong, F. Yulong, Effect of Dy content on microwave absorption properties of Pr2Fe17 alloy. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 46, 2060–2064 (2017)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1978)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751–767 (1976)
N.S. Kumar, R.P. Suvarna, K.C.B. Naidu, G.R. Kumar, S. Ramesh, Structural and functional properties of sol-gel synthesized and microwave heated Pb0.8Co0.2-zLazTiO3 (z = 0.05–0.2) nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 44, 19408–19420 (2018)
N.S. Kumar, R.P. Suvarna, K.C.B. Naidu, Sol–gel synthesized and microwave heated Pb0.8-yLayCo0.2TiO3 (y = 0.2–0.8) nanoparticles: structural, morphological and dielectric properties. Ceram. Int. 44, 18189–18199 (2018)
N.S. Kumar, R.P. Suvarna, K.C.B. Naidu, Grain and grain boundary conduction mechanism in sol-gel synthesized and microwave heated Pb0.8–yLayCo0.2TiO3 (y = 0.2–0.8) nanofibers. Mater. Chem. Phys. 223, 241–248 (2019)
N. Velhal, G. Kulkarni, D. Mahadik, P. Chowdhury, H. Barshilia, V. Puri, Effect of Ba2+ ion on structural, magnetic and microwave properties of screen printed BaxSr1-x Fe12O19 thick films. J. Alloys Compd. 682, 730–737 (2016)
P. Laokul, V. Amornkitbamrung, S. Seraphin, S. Maensiri, Characterization and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline CuFe2O4, NiFe2O4, ZnFe2O4 powders prepared by the Aloe vera extract solution. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, 101–108 (2011)
K.C.B. Naidu, V.N. Reddy, T.S. Sarmash, D. Kothandan, T. Subbarao, N.S. Kumar, Structural, morphological, electrical, impedance and ferroelectric properties of BaO–ZnO–TiO2 ternary system. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-0225-0
U. Naresh, R.J. Kumar, K.C.B. Naidu, Hydrothermal synthesis of barium copper ferrite nanoparticles: nanofiber formation, optical, and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 236, 121807 (2019)
T. Ramaprasad, R.J. Kumar, U. Naresh, M. Prakash, D. Kothandan, K.C.B. Naidu, Effect of pH value on structural and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by low temperature hydrothermal technique. Mater. Res. Express 5, 095025 (2018)
I. Zouaria, Z. Sassib, L. Seveyratb, N. Abdelmoulaa, L. Lebrunb, H. Khemakhem, Structural, dielectric, piezoelectric, ferroelectric and electro-caloric properties of Ba1−xCaxTi0.975(Nb0.5Yb0.5)0.025O3 lead-free ceramics. Ceram. Int. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.242
Guo-Long Tan, Wei Li, Ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism of M-type lead hexaferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 1812–1817 (2015)
U. Naresh, R.J. Kumar, K.C.B. Naidu, Optical, magnetic and ferroelectric properties of Ba0.2Cu0.8-xLaxFe2O4 (x = 0.2–0.6) nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45, 7515–7523 (2019)
M.N. Ashiq, R.B. Qureshi, M.A. Malana, M.F. Ehsan, Synthesis, structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of zirconium copper doped M-type calcium strontium hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 617, 437–443 (2014)
C. Sudakar, G.N. Subbanna, T.R.N. Kutty, Wet chemical synthesis of multicomponent hexaferrites by gel-to-crystallite conversion and their magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 263, 253–268 (2003)
C. Caizer, Nanoparticle size effect on some magnetic properties, handbook of nanoparticles (Springer, Berlin, 2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13188-7-24-1
Tahseen H. Mubarak, Olfat A. Mahmood, Zahraa J. Hamakhan, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Ba2Mg2Fe28O46 (Mg2X) hexaferrites. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 13, 6369–6379 (2018)
J. Geshev, A.D.C. Viegas, J.E. Schm, Negative remanent magnetization of fine particles with competing cubic and uniaxial anisotropies. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 1488–1492 (1998)
Y. Chen, Y. Zhang, R. Keil, M. Zopf, F. Ding, O.G. Schmidt, Temperature-dependent coercive field measured by a quantum dot strain gauge. Nano Lett. 17, 7864–7868 (2017)
H.H. Wu, J. Wang, S.G. Cao, L.Q. Chen, T.Y. Zhang, The unusual temperature dependence of the switching behavior in a ferroelectric single crystal with dislocations. Smart Mater. Struct. 23, 025004 (2014)
E.C. Stoner, E.P. Wohlfarth, A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 240, 599–642 (1948)
J.S. Lee, J.M. Cha, H.Y. Yoon, J.-K. Lee, Y.K. Kim, Magnetic multi-granule nanoclusters: a model system that exhibits universal size effect of magnetic coercivity. Sci. Rep. 5, 12135 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12135
K.C.B. Naidu, W. Madhuri, Ceramic nanoparticle synthesis at lower temperatures for LTCC and MMIC technology (Magn, IEEE Trans, 2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tmag.2018.2855663
Acknowledgements
The authors express their thanks to Prof. T. Subba Rao, S.K.University, Anantapur, A.P., for helping sample preparation and characterization. In addition, the authors thank Varadaraja Perumal, IISC-Bangalore for providing FESEM pictures and PSA data to us on time.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghuram, N., Rao, T.S. & Naidu, K.C.B. Magnetic properties of hydrothermally synthesized Ba1–xSrxFe12O19 (x = 0.0–0.8) nanomaterials. Appl. Phys. A 125, 839 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3143-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3143-2