Abstract
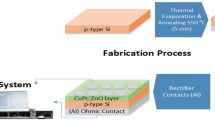
In this work, the fabrication and characterization of a strontium-doped CuO/Si photodetector by chemical spray pyrolysis are demonstrated. The structural, electrical, and optical properties of CuO film and strontium-doped CuO film doped at doping concentrations of 3% and 6% are studied. The X-ray diffraction studies reveal that the deposited CuO film is crystalline with a monoclinic structure, and a new Cu4O3 phase was observed when the film was doped with strontium. The optical energy gap decreases from 2.5 to 2.25 eV after doping with Sr at 6%. The scanning electron microscopy investigation shows that the grain size decreases from 150 to 75 nm after doping with 6% strontium. The DC electrical conductivity of the film decreased after doping, and the activation energy was determined and found to be 0.52 and 0.75 eV for Sr dopant at 3% and 6%, respectively. The current–voltage characteristics of CuO/Si and CuO:Sr/Si heterojunction photodetectors under dark and light conditions are studied as a function of doping concentration. The photodetectors show rectification characteristics. The figures of merit of the photodetectors are measured. The responsivity (Rλ) of the photodetectors increases from 0.9 to 1.7 and 2.85 A/W at 650 nm after doping with strontium at doping concentrations of 3 and 6%, respectively. The maximum external quantum efficiency (EQE) and specific detectivity (D*) were 2.79 × 102% and 2.66 × 1012 Jones, respectively, for a CuO:Sr/Si photodetector doped with 3%.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
(Not applicable).
References
A. Alhattab, H. Alhattab, I. Takano, Investigation of structure and optical properties for copper oxide thin films on plastic substrate by helicon plasma DC magnetron sputtering technique. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–9 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4357486
A.N. Hussain, K.I. Hassoon, M.A. Hassan, Effect of annealing on copper oxide thin films and its application in solar cells. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1530/1/012140
G. Papadimitropoulos, N. Vourdas, V.E. Vamvakas, D. Davazoglou, Deposition and characterization of copper oxide thin films. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 10(1), 182–185 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/10/1/045
B.N. Roy, T. Wright, Electrical conductivity in polycrystalline copper oxide thin films. Cryst. Res. Technol. 31(8), 1039–1044 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.2170310812
C.R. Dhas, D. Alexander, A.J. Christy, K. Jeyadheepa, A.M.E. Raj, C.S. Raja, Preparation and characterization of CuO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique for ethanol gas sensing application. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 7(8), 671–684 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3923/ajaps.2014.671.684
Ş Baturay, A. Tombak, D. Batibay, Ocak, n-type conductivity of CuO thin films by metal doping. Appl. Surf. Sci. 477, 91–95 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.004
G. Li, M. Jing, Z. Chen, B. He, M. Zhou, Z. Hou, Self-assembly of porous CuO nanospheres decorated on reduced graphene oxide with enhanced lithium storage performance. RSC Adv. 7(17), 10376–10384 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra28724g
K. Kumar, A. Chowdhury, Facile synthesis of CuO nanorods obtained without any template and/or surfactant. Ceram. Int. 43(16), 13943–13947 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.07.125
H.J. Song, M.H. Seo, K.W. Choi, M.S. Jo, J.Y. Yoo, J.B. Yoon, High-performance copper oxide visible-light photodetector via grain-structure model. Sci. Rep. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43667-9
Z.M. Sadiq, M.A. Hassan, K.I. Hassoon, Preparation and characterization of CuO nanostructured thin films by chemical bath deposition. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2322/1/012088
H. Kidowaki, T. Oku, T. Akiyama, A. Suzuki, B. Jeyadevan, J. Cuya, Fabrication and characterization of CuO-based solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. Res. 1, 138 (2012)
J. Meng, Z. Yang, L. Chen, H. Qin, F. Cui, Y. Jiang, X. Zeng, Energy storage performance of CuO as a cathode material for aqueous zinc ion battery. Mater. Today Energy (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2019.100370
H. Zhang, K. Wang, L. Wang, H. Xie, W. Yu, Mesoporous CuO with full spectrum absorption for photothermal conversion in direct absorption solar collectors. Sol. Energy 201, 628–637 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.03.047
N.S. Sadeq, M.A. Hassan, Z.G. Mohammadsalih, Preparation and study of properties of CdO: Al thin films prepared by chemical spraying. Int. J. Thin Film Sci. Technol. 11(1), 101–110 (2022). https://doi.org/10.18576/ijtfst/110113
A. Mehtab, J. Ahmed, S.M. Alshehri, Y. Mao, T. Ahmad, Rare earth doped metal oxide nanoparticles for photocatalysis: a perspective. Nanotechnology 33(14), 142001 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ac43e7
U. Alam, A. Khan, D. Ali, D. Bahnemann, M. Muneer, Comparative photocatalytic activity of sol–gel derived rare earth metal (La, Nd, Sm and Dy)-doped ZnO photocatalysts for degradation of dyes. RSC Adv. 8(31), 17582–17594 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01638K
D.S. Murali, A. Subrahmanyam, Synthesis of low resistive p type Cu4O3 thin films by DC reactive magnetron sputtering and conversion of Cu4O3 into CuO by laser irradiation. J. Phys. D (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/49/37/375102
M.A. Cruz Almazán, E. Vigueras Santiago, R. López, S. Hernández López, V.H. Castrejón Sánchez, A. Esparza, C. Encarnación Gómez, Cu4O3 thin films deposited by non-reactive rf-magnetron sputtering from a copper oxide target. Rev. Mex. Fís. (2021). https://doi.org/10.31349/RevMexFis.67.495
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges Wiss Göttingen 26, 98 (1918)
J.I. Langford, A.J.C. Wilson, “Scherrer after sixty years: a survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size.” J. Appl. Cryst. 11, 102 (1978)
R.A. Ismail, A.M. Mousa, M.A. Hassan, Critical methanol to ethanol volume ratio effect on the electrodeposition of DLC films. Optik 179, 29–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.10.170
S. Gao, W. Li, J. Dai, Q. Wang, Z. Suo, Effect of transition metals doping on electronic structure and optical properties of β-Ga2O3. Mater. Res. Exp. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abde10
M. Jawad, R. Ismail, Preparation of nanocrystalline Cu2O thin film by pulsed laser deposition. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 22, 1244–1247 (2011)
S.S. Hamd, A. Ramizy, R.A. Ismail, Preparation of novel B4C nanostructure/Si photodetectors by laser ablation in liquid. Sci. Rep. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20685-8
R.A. Ismail, N.F. Habubi, M.M. Abbod, Preparation of high-sensitivity In2S3/Si heterojunction photodetector by chemical spray pyrolysis. Opt. Quant. Electron 48(10), 455 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-016-0725-5
C. Zhang, B. Wang, R. Luo, C. Wu, S. Chen, J. Hu, C. Xie, L. Luo, Enhanced light trapping in conformal CuO/Si microholes array heterojunction for self-powered broadband photodetection. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 42(6), 883–886 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2021.3072042
R.A. Ismail, Characteristics of p-Cu2O/n-Si heterojunction photodiode made by rapid thermal oxidation. JSTS: J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 9(1), 51–54 (2009). https://doi.org/10.5573/JSTS.2009.9.1.051
M.S. Jo, H.J. Song, B.J. Kim, Y.K. Shin, S.H. Kim, X. Tian, S.M. Kim, M.H. Seo, J.B. Yoon, Aligned CuO nanowire array for a high performance visible light photodetector. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 2284 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-06031-y
Q. Hong, Y. Cao, J. Xu, H. Lu, J. He, J.L. Sun, Self-powered Ultrafast Broadband Photodetector based on p–n heterojunctions of CuO/Si Nanowire array. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(23), 20887–20894 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am5054338
M.A. Jabr, A.M. Ali, R.A. Ismail, Preparation of high-performance p-CuO/n-Si heterojunction photodetector by laser-assisted chemical bath deposition: effect of laser wavelength. Ceram. Int. 49(7), 11442–11451 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.11.343
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the department of Applied Sciences, University of Technology–Iraq for their logistic support.
Funding
No fund has been received for this research study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RAI and MAH conceived the presented idea. RAI and MAH supervised the finding of this work. MAH and RAI discussed the results and contributed equally to the final manuscript. MAH, MHM, and RAI conducted the experiments. RAI and MHM provided critical feedback and helped shape the research, analysis, and manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
(Not applicable)
Consent to participate
(Not applicable)
Consent for publication
(Not applicable)
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M.A., Mohsin, M.H. & Ismail, R.A. Preparation of high-responsivity strontium–doped CuO/Si heterojunction photodetector by spray pyrolysis. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 912 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10348-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10348-3