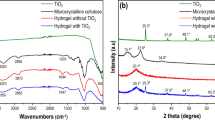
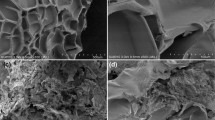
Abstract
Industrial wastewater has become one of the main factors affecting human health, and wastewater purification has become an important subject of academic research. Therefore, we report a Uio-66/cellulose composite hydrogel with the advantages of simple preparation, excellent adsorption performance, and high adsorption efficiency. Cellulose hydrogels have the characteristics of simple preparation and excellent adsorption. As the metal organic framework, Uio-66 has excellent adsorption to dyes. It combined with cellulose hydrogel can improve the adsorption performance of the composite hydrogel. Uio-66 can not only optimize the adsorption performance of cellulose hydrogels, but also improve the adsorption rate of composite hydrogels. By changing the amount of Uio-66, we studied the adsorption of methylene blue by composite hydrogel under different initial concentration, temperature, and pH. At room temperature, when the adding amount of Uio-66 was 10% of the mass of cellulose, the composite hydrogel had the best adsorption performance. The adsorption rate was significantly improved, and the maximum adsorption amount was 764.95 mg g−1, which is much better than the cellulose hydrogel without Uio-66, and the time to reach adsorption equilibrium was also significantly shortened.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data required to reproduce these findings of the present report cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
L. Sun, S.G. Wan, W.S. Luo, Biochars prepared from anaerobic digestion residue, palm bark, and eucalyptus for adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye: characterization, equilibrium, and kinetic studies. Bioresour. Technol. 140, 406–413 (2013)
J.L. Ren, Q.Q. Dai, H.Q. Zhong, X.X. Liu, L. Meng, X.H. Wang, F.X. Xin, Quaternized xylan/cellulose nanocrystal reinforced magnetic hydrogels with high strength. Cellulose 25, 4537–4549 (2018)
E. Yildirir, L. Ballice, Supercritical water gasification of wet sludge from biological treatment of textile and leather industrial wastewater. J. Supercrit. Fluid. 146, 100–106 (2019)
P. Sirajudheen, N.C. Poovathumkuzhi, S. Vigneshwaran, B.M. Chelaveettil, S. Meenakshi, Applications of chitin and chitosan based biomaterials for the adsorptive removal of textile dyes from water-A comprehensive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 273, 118604 (2021)
S. Natarajan, H.C. Bajaj, R.J. Tayade, Recent advances based on the synergetic effect of adsorption for removal of dyes from waste water using photocatalytic process. J. Environ. Sci-China. 65, 201–222 (2018)
S. Varjani, P. Rakholiya, H.Y. Ng, S. You, J.A. Teixeira, Microbial degradation of dyes: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 314, 123728 (2020)
M.W. Cao, Y. Shen, Z.S. Yan, Q. Wei, T. Jiao, Y.T. Shen, Y.C. Han, Y.L. Wang, S.J. Wang, Y.Q. Xia, T.T. Yue, Extraction-like removal of organic dyes from polluted water by the graphene oxide/PNIPAM composite system. Chem. Eng. J. 405, 126647 (2021)
Q. Liu, Y. Li, H. Chen, J. Lu, G. Yu, M. Moslang, Y. Zhou, Superior adsorption capacity of functionalised straw adsorbent for dyes and heavy-metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 382, 121040 (2020)
M.N. Ahamad, M.S. Khan, M. Shahid, M. Ahmad, Metal organic frameworks decorated with free carboxylic acid groups: topology, metal capture and dye adsorption properties. Dalton. Trans. 49, 14690–14705 (2020)
Y.C. Sun, T.T. Wang, C.H. Han, X.T. Lv, L. Bai, X.Y. Sun, P.F. Zhang, Facile synthesis of Fe-modified lignin-based biochar for ultra-fast adsorption of methylene blue: selective adsorption and mechanism studies. Bioresour. Technol. 344, 126186 (2022)
L.P. Sun, Y.H. Mo, L. Zhang, A mini review on bio-electrochemical systems for the treatment of azo dye wastewater: state-of-the-art and future prospects. Chemosphere 294, 133801 (2022)
L.W. Chen, Y.Y. Zhu, Y.M. Cui, R. Dai, Z.H. Shan, H. Chen, Fabrication of starch-based high-performance adsorptive hydrogels using a novel effective pretreatment and adsorption for cationic methylene blue dye: behavior and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 405, 126953 (2021)
Y. Wang, Y. Zheng, G. Zhao, S. Liu, J. Hu, X. Long, Z. Xiao, H. Zhang, F. Jiao, Co-precipitation synthesis of reusable ZnAl-CLDH/ZIF-8 heterojunction for enhanced photodegradation of organic dye. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 28051–28064 (2021)
H. Mirhosseini, T. Shamspur, A. Mostafavi, G. Sargazi, A novel ultrasonic assisted-reverse micelle procedure to synthesize Eu-MOF nanostructure with high sono/sonophotocatalytic activity: a systematic study for brilliant green dye removal. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 22840–22859 (2021)
S. Cui, Z. Ye, C. Qian, J. Liu, J. Jin, Q. Liang, C. Liu, S. Xu, Z. Li, Construction of ternary Ag/AgBr@UIO-66(NH2) heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic performance for the degradation of methyl orange. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 15138–15146 (2018)
N. Peng, D.N. Hu, J. Zeng, Y. Li, L. Liang, C.Y. Chang, Superabsorbent cellulose-clay nanocomposite hydrogels for highly efficient removal of dye in water. Acs. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 7217–7224 (2016)
E. Alipour, S. Norouzi, H. Yousefzadeh, R. Mohammadi, M.S. Amini-Fazl, Synthesis of chitosan-grafted poly-acrylic acid (CTS-g-PAA) hydrogel and its potential application in biosensors for signal enhancing and bioanalysis. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 24812–24824 (2021)
T. Hu, Q.Z. Liu, T.T. Gao, K.J. Dong, G. Wei, J.S. Yao, Facile preparation of tannic acid-poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for methylene blue removal from simulated solution. ACS Omega 3, 7523–7531 (2018)
S.F. He, F. Zhang, S.Z. Cheng, W. Wang, Synthesis of sodium acrylate and acrylamide copolymer/GO hydrogels and their effective adsorption for Pb2+ and Cd2+. Acs. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 3948–3959 (2016)
C.Z. Bai, X.J. Huang, F. Xie, X.P. Xiong, Microcrystalline cellulose surface-modified with acrylamide for reinforcement of hydrogels. Acs. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 12320–12327 (2018)
S. Bhaladhare, D. Das, Cellulose: a fascinating biopolymer for hydrogel synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. B. 10, 1923–1945 (2022)
Y. Chen, Z. Xiang, D. Wang, J. Kang, H. Qi, Effective photocatalytic degradation and physical adsorption of methylene blue using cellulose/GO/TiO2 hydrogels. Rsc. Adv. 10, 23936–23943 (2020)
C. Kuang, P. Tan, A. Bahadur, S. Iqbal, M. Javed, M.A. Qamar, M. Fayyaz, G. Liu, O.M. Alzahrani, E. Alzahrani, A. Farouk, Dye degradation study by incorporating Cu-doped ZnO photocatalyst into polyacrylamide microgel. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 33, 9930–9940 (2022)
M.S. Embaby, S.D. Elwany, W. Setyaningsih, M.R. Saber, The adsorptive properties of UiO-66 towards organic dyes: a record adsorption capacity for the anionic dye Alizarin Red S. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 26, 731–739 (2018)
Z.C. Ji, H.Y. Sun, Y.F. Zhu, D.D. Zhang, L.H. Wang, F.Y. Dai, Y.P. Zhao, L. Chen, Enhanced selective removal of lead ions using a functionalized PAMAM@UiO-66-NH2 nanocomposite: experiment and mechanism. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 328, 111433 (2021)
X. Hou, L. Wu, L. Gu, G. Xu, H. Du, Y. Yuan, Maximizing the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of Z-scheme UiO-66-NH2@Au@CdS by aminated-functionalized linkers. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 5203–5211 (2019)
X. Tianliang, L. Yingchao, L. Weizun, J. Meiting, Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by MOFs based materials: a review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 32, 2975–2984 (2021)
C. Zhao, G. Wu, Research progress on the mechanism and applications of MOFs composite materials for catalytic degradation of organic pollutants in the solution. Chem. Ind. Eng. 38, 1775–1784 (2019)
D.X. Zhao, C. Cai, Cerium-based UiO-66 metal-organic framework for synergistic dye adsorption and photodegradation: a discussion of the mechanism. Dyes Pigments 185, 108957 (2021)
L.Y. Wang, H. Xu, J.K. Gao, J.M. Yao, Q.C. Zhang, Recent progress in metal-organic frameworks-based hydrogels and aerogels and their applications. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 398, 213016 (2019)
M.R.M. Shafiee, J. Parhizkar, S. Radfar, Removal of Rhodamine B by g-C3N4/Co3O4/MWCNT composite stabilized in hydrogel via the synergy of adsorption and photocatalysis under visible light. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 12475–12486 (2019)
J.H. Cavka, S. Jakobsen, U. Olsbye, N. Guillou, C. Lamberti, S. Bordiga, K.P. Lillerud, A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 13850–13851 (2008)
X.L. Zhao, S.L. Liu, Z. Tang, H.Y. Niu, Y.Q. Cai, W. Meng, F.C. Wu, J.P. Giesy, Synthesis of magnetic metal-organic framework (MOF) for efficient removal of organic dyes from water. Sci Rep-Uk. 5, 11849 (2015)
Y.H. Teow, L.M. Kam, A.W. Mohammad, Synthesis of cellulose hydrogel for copper (II) ions adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 4588–4597 (2018)
N. Harada, Y. Mitsukami, H. Uyama, Preparation and characterization of water-swellable hydrogel-forming porous cellulose beads. Polymer 215, 123381 (2021)
C.Y. Li, Y.Y. Yan, Q.Z. Zhang, Z.B. Zhang, L.H. Huang, J.X. Zhang, Y.Q. Xiong, S.Z. Tan, Adsorption of Cd2+ and Ni2+ from Aqueous Single Metal Solutions on Graphene Oxide-Chitosan-Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogels (vol 35, pg 4481, 2019). Langmuir 35, 9323–9333 (2019)
C. Wang, J. Liu, Q. Li, S. Chen, Self-healing hydrogel toward metal ion rapid removal via available solar-driven fashion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 58, 17067–17074 (2019)
H.J. Dai, Y. Chen, L. Ma, Y.H. Zhang, B. Cui, Direct regeneration of hydrogels based on lemon peel and its isolated microcrystalline cellulose: characterization and application for methylene blue adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 191, 129–138 (2021)
B. Gao, H.R. Yu, J.Y. Wen, H.J. Zeng, T. Liang, F. Zuo, C.J. Cheng, Super-adsorbent poly(acrylic acid)/laponite hydrogel with ultrahigh mechanical property for adsorption of methylene blue. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 106346 (2021)
V.V. Tran, D. Park, Y.C. Lee, Hydrogel applications for adsorption of contaminants in water and wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 24569–24599 (2018)
Z.F. Akl, E.G. Zaki, S.M. ElSaeed, Green hydrogel-biochar composite for enhanced adsorption of uranium. ACS Omega 6, 34193–34205 (2021)
C.S. Fonseca, C. Rosa, T.J. Lopes, G. Rosa, Sewage sludge in phenol and methylene blue adsorption: a miniproject for teaching sustainability. J. Chem. Educ. 97, 1087–1092 (2020)
C.L. Jiang, X.H. Wang, B.X. Hou, C. Hao, X. Li, J.B. Wu, Construction of a lignosulfonate-lysine hydrogel for the adsorption of heavy metal ions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 3050–3060 (2020)
S. Park, Y. Oh, J. Yun, E. Yoo, D. Jung, K.K. Oh, S.H. Lee, Cellulose/biopolymer/Fe3O4 hydrogel microbeads for dye and protein adsorption. Cellulose 27, 2757–2773 (2020)
D. Kundu, S.K. Mondal, T. Banerjee, Development of beta-cyclodextrin-cellulose/hemicellulose-based hydrogels for the removal of Cd(II) and Ni(II): synthesis, kinetics, and adsorption aspects. J. Chem. Eng. Data 64, 2601–2617 (2019)
J.M. Wu, Z.X. Feng, C.H. Dong, P. Zhu, J.H. Qiu, L.X. Zhu, Synthesis of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/poly(acrylic acid) microgels via visible-light-triggered polymerization as a self-sedimentary cationic basic dye adsorbent. Langmuir 38, 3711–3719 (2022)
X.W. Peng, L.X. Zhong, J.L. Ren, R.C. Sun, Highly effective adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by macroporous xylan-rich hemicelluloses-based hydrogel. J. Agr. Food Chem. 60, 3909–3916 (2012)
Z.H. Liu, Q. Wang, X.J. Huang, X.R. Qian, Surface functionalization of graphene oxide with hyperbranched polyamide-amine and microcrystalline cellulose for efficient adsorption of heavy metal ions. ACS Omega 7, 10944–10954 (2022)
J.P. Yang, K.L. Wang, Z.X. Lv, W.J. Li, K.M. Luo, Z. Cao, Facile preparation and dye adsorption performance of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid)/molybdenum disulfide composite hydrogels. ACS Omega 6, 28285–28296 (2021)
Y.F. Yan, H. Han, Y.J. Dai, H. Zhu, W.H. Liu, X. Tang, W. Gan, H. Li, Nb2CTx MXene nanosheets for dye adsorption. ACS. Appl. Nano Mater. 4, 11763–11769 (2021)
S.K. Lahiri, L. Liu, Fabrication of a nanoporous silica hydrogel by cross-linking of SiO2-H3BO3-hexadecyltrimethoxysilane for excellent adsorption of azo dyes from wastewater. Langmuir 37, 8753–8764 (2021)
A. M. Aljeboree, N. D. Radia, L. S. Jasim, A. A. Alwarthan, M. M. Khadhim, A. Washeel Salman and A. F. Alkaim, Synthesis of a new nanocomposite with the core TiO2/hydrogel: Brilliant green dye adsorption, isotherms, kinetics, and DFT studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 109, 475–485 (2022)
S. Sharma, G. Sharma, A. Kumar, T. S. AlGarni, M. Naushad, Z. A. ALOthman and F. J. Stadler, Adsorption of cationic dyes onto carrageenan and itaconic acid-based superabsorbent hydrogel: Synthesis, characterization and isotherm analysis. J Hazard Mater. 421, 126729 (2022)
N. Kumar, H. Mittal, V. Parashar, S.S. Ray, J.C. Ngila, Efficient removal of rhodamine 6G dye from aqueous solution using nickel sulphide incorporated polyacrylamide grafted gum karaya bionanocomposite hydrogel. Rsc. Adv. 6, 21929–21939 (2016)
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support of Shandong Institute of Inorganic Nonmetallic Materials.
Funding
We are thankful for the financial support from the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) and Qinglan Project of Jiangsu Province of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lixi Wang conceived and designed the experiments, and supervised the complete study. Jianlin Huang prepared the samples, performed the experiments, and collected the data. All the authors analyzed the data, wrote the manuscript, and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of the present article declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome. We confirm that we have given due consideration to the protection of intellectual property associated with this work and there are no impediments to publication, including the timing of publication, concerning intellectual property.
Ethical approval
This manuscript does not contain any stuff which needed ethical approval and the research does not involve human participants and/or animals.
Informed consent
There is no ‘informed consent’ applicable to this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Ren, Q., Wang, L. et al. Rapid preparation and adsorption properties of Uio-66/cellulose composite hydrogels. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1080 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10332-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10332-x