Abstract
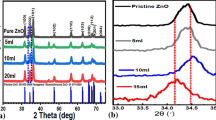
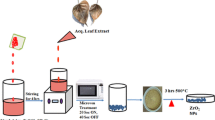
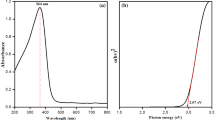
The use of plant extract for the synthesis of nanomaterials has been preferred over conventional growth techniques due to its safety, simple, ecofriendly, cost-effective and biocompatibility properties. The present study includes environmentally friendly approach for synthesis of ZnO–NPs using milky sap of Calotropis procera (CP) parts. The biosynthesized ZnO–NPs were investigated in terms of crystalline, morphology, and optical characterization. The CP has resulted spherical-shaped oriented nanoparticles, hexagonal phase and significantly reduced crystallite size of − 26.1 nm. The photodegradation of malachite green (MG) and methyl blue (MB) dye under the illumination of UV light was investigated using biosynthesized ZnO–NPs. The effect of different volumes of milky sap of CP was considered as a point of care to demonstrate its role towards the enhancement of photodegradation effectiveness of ZnO against two different organic dyes like malachite and methylene blue owing their issues raised for aquaculture and worsen environmental impacts. The degradation of both dyes was followed by pseudo first-order kinetics and highest volume of milky sap of CP has given out high rate constant value. The degradation efficiency of milky sap of CP-assisted ZnO nanostructures was found about 85.3% and 86.3% for MG and MB, respectively. However, we studied the effect of pH of dye solution on the photocatalytic performance of ZnO and it has revealed highly enhanced degradation efficiency. The increased functionality of ZnO was connected to the reduced particle size, optical bandgap, and tunable surface properties with the use of terminal oxygenated groups.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
5. References
H.Y. Zhu, R. Jiang, Y.Q. Fu, Y.J. Guan, J. Yao, L. Xiao, G. Zeng, Effective photocatalytic decolorization of methyl orange utilizing TiO2/ZnO/ chitosan nanocomposite films under simulated solar irradiation. Desalination 286, 41–48 (2012)
N. Mathur, P. Bhatnagar, P. Sharma, Review of the mutagenicity of textile dye products. Univers. J. Environ. Res. Technol. 2, 1–18 (2012)
R. Kumar, G. Kumar, A. Umar, ZnO nano-mushrooms for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Mater. Lett. 97, 100–103 (2013)
M. Arab Chamjangali, G. Bagherian, B. Bahramian, B. Fahimi Rad, Synthesis and application of multiple rods gold–zinc oxide nanostructures in the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Int. J. Enviro. Sci. Technol. 12, 151–160 (2015)
N.Z. Razali, A.H. Abdullah, M. Haron, Degradation of methyl orange mediated by CuO-doped ZnO photocatalysts. Environ. Eng. Manage. J. (EEMJ) 10, 1523–1528 (2011)
N. Tripathy, R. Ahmad, J.E. Song, H.A. Ko, Y.B. Hahn, G. Khang, Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye by ZnO nanoneedle under UV irradiation. Mater. Lett. 136, 171–174 (2014)
F. Tian, Z. Wu, Q. Chen, Y. Yan, G. Cravotto, Z. Wu, Microwaveinduced crystallization of AC/TiO2 for improving the performance of rhodamine B dye degradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 351, 104–112 (2015)
D. Liu, Z. Wu, F. Tian, B.C. Ye, Y. Tong, Synthesis of N and La codoped TiO2/AC photocatalyst by microwave irradiation for the photocatalytic degradation of naphthalene. J. Alloy. Compd. 676, 489–549 (2016)
S. Chidambaram, B. Pari, N. Kasi, S. Muthusamy, ZnO/Ag heterostructures embedded in Fe3O4 nanoparticles for magnetically recoverable photocatalysis. J. Alloy. Compd. 665, 404–410 (2016)
Y. Liu, L. Yu, Y. Hu, C.F. Guo, F.M. Zhang, X.W. Lou, A magnetically separable photocatalyst based on nest-like γ-Fe2O3/ZnO double-shelled hollow structures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 4, 183–187 (2012)
A. Vázquez, D.B. Hernández-Uresti, S. Obregón, Electrophoretic deposition of CdS coatings and their photocatalytic activities in the degradation of tetracycline antibiotic. Appl. Surf. Sci. 386, 412–417 (2016)
D. Pathania, D. Gupta, H. Ala’a, G. Sharma, A. Kumar, M. Naushad, T. Ahamad, S.M. Alshehri, Photocatalytic degradation of highly toxic dyes using chitosan-g-poly (acrylamide)/ZnS in presence of solar irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 329, 61–68 (2016)
K. Govindaraju, S. Khaleel Basha, V. Ganesh Kumar, G. Singaravelu, Silver, gold and bimetallic nanoparticles production using single-cell protein (Spirulina platensis) Geitler. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 5115–5122 (2008)
G. Scarano, E. Morelli, Properties of phytochelatin-coated CdS nanocrystallites formed in a marine phytoplanktonic alga (Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Bohlin) in response to Cd. Plant Sci. 165, 803–810 (2003)
M.F. Lengke, M.E. Fleet, G. Southam, Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by filamentous cyanobacteria from a silver (I) nitrate complex. Langmuir 23(5), 2694–2499 (2007)
A. Muthuvel, M. Jothibas, C. Manoharan, S.J. Jayakumar, Synthesis of CeO2-NPs by chemical and biological methods and their photocatalytic, antibacterial and in vitro antioxidant activity. Res. Chem. Intermed. 46, 2705–2729 (2020)
K. Elumalai, S. Velmurugan, Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Azadirachta indica (L.). Appl. Surf. Sci. 345, 329–336 (2015)
B. Siripireddy, B.K. Mandal, Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Eucalyptus globulus and their photocatalytic and antioxidant activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 785–797 (2017)
K. Elumalai, S. Velmurugan, S. Ravi, V. Kathiravan, S. Ashokkumar, Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera leaf extract and evaluation of its antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 143, 158–164 (2015)
D. Suresh, P.C. Nethravathi, H. Rajanaika, H. Nagabhushana, S.C. Sharma, Green synthesis of multifunctional zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using Cassia fistula plant extract and their photodegradative, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 31, 446–454 (2015)
H. Çolak, E. Karaköse, Green synthesis and characterization of nanostructured ZnO thin films using Citrus aurantifolia (lemon) peel extract by spin-coating method. J. Alloys Compd. 690, 658–662 (2017)
S.K. Chaudhuri, L. Malodia, Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea: characterization and its evaluation on tree seedling growth in nursery stage. Appl. Nanosci. 7, 501–512 (2017)
S. Ambika, M. Sundrarajan, Green biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Vitex negundo L. extract: spectroscopic investigation of interaction between ZnO nanoparticles and human serum albumin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 149, 143–148 (2015)
P. Mishra, P. Singh, H.P. Nagaswarupa, S.C. Sharma, Y.S. Vidya, S.C. Prashantha, H. Nagabhushana, K.S. Anantharaju, S. Sharma, L. Renuka, Caralluma fimbriata extract induced green synthesis, structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanostructure modified with Gd. J. Alloys Compd. 685, 656–669 (2016)
M. Ramesh, M. Anbuvannan, G. Viruthagiri, Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochim Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 136, 864–870 (2015)
D. Sharma, M.I. Sabela, S. Kanchi, P.S. Mdluli, G. Singh, T.A. Stenström, K. Bisetty, Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Jacaranda mimosifolia flowers extract: synergistic antibacterial activity and molecular simulated facet specific adsorption studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 162, 199–207 (2016)
R. Dobrucka, J. Długaszewska, Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles using Trifolium pratense flower extract. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 23, 517–523 (2016)
S.P. Hinge, A.B. Pandit, Solar-assisted synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using lime juice: a green approach. Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci Nanotechnol. 8, 045006–045020 (2017)
D. Suresh, R.M. Shobharani, P.C. Nethravathi, M.A. Pavan Kumar, H. Nagabhushana, S.C. Sharma, Artocarpus gomezianus aided green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: luminescence, photocatalytic and antioxidant properties. Spectrochim Acta–Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 141, 128–134 (2015)
R. Yuvakkumar, J. Suresh, A.J. Nathanael, M. Sundrarajan, S.I. Hong, Novel green synthetic strategy to prepare ZnO nanocrystals using rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum L.) peel extract and its antibacterial applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 41, 17–27 (2014)
A.G. Millar, M. Morris, (1987) Plants of Dhofar; The Southern Region of Oman, Traditional, Economic and Medicinal Uses. The office of the Advisor for Conservation of the Environment, Diwan of Royal Court Sultanate of Oman, https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X91000302
A.M. Greiss, Elhamy, anatomical identification of plant remains and other materials from (1) El-Omari excavation at Helwan from the first dynasty. Bull Inst. Egypt. 36, 227–235 (1955)
B.A. Ebbell, Contribution to the earliest history of leprosy. Int. J. Leprosy. 3, 257–263 (1935)
A.O. Prakash, R.B. Gupta, R. Mathur, Effect of oral administration of forty two indigenous lants extracts on early and late pregnancy in albino rats. Probe 27, 315–323 (1978)
S.M.H. Ayoub, D.G.I. Kingston, Screening of plants used in Sudan folk medicine for anticancer activity. Fitoterapia 52, 281–284 (1981)
S.N. Nandal, D.S. Bhatti, Preliminary screening of some weeds and shrubs for their neomatocidal activity against Meloidogyne javanica. Indian J. Nematol. 13, 123–127 (1983)
N. Mascolo, R. Sharma, S.C. Jain, F. Capasso, Ethnopharmacology of calotropis procera flowers. J. Ethnopharmacol. 22, 211–221 (1988)
A. Muthuvel, M. Jothibas, V. Mohana, C. Manoharan, Green synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Calotropis procera flower extract and their photocatalytic degradation and antibacterial activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 119, 108086 (2020)
R.P. Mali, P.S. Rao, R. Jadhav, A review on pharmacological activities of Calotropis procera. J. Drug. Deliv. Ther. 9, 947–951 (2019)
M. Khatami, M.S. Nejad, S. Salari, P.G.N. Almani, Plant-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Trifolium resupinatum seed exudate and their antifungal efficacy on Neofusicoccum parvum and Rhizoctonia solani. IET Nanobiotechnol. 10, 237–243 (2016)
L. Shiri, S. Rahmati, Z. Ramezani Nejadv, M. Kazemi, Synthesis and characterization of bromine source immobilized on diethylenetriamine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: a novel, versatile and highly efficient reusable catalyst for organic synthesis. Appl. Organo. Chem. 31, 3687 (2017)
F. Ullah, S. Nasar Shah, W. Zaman, M. Zafar, M. Ahmad, A. Ayaz, A. Sohail, S. Saqib, Using palynomorphological characteristics for the identification of species of Alsinoideae (Caryophyllaceae): a systematic approach. Grana 58, 174–184 (2019)
S. Hemmati, M. Baghayeri, S. Kazemi, H. Veisi, Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using oak leaf extract and their application for electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Appl. Organo. Chem. 32, e4537 (2018)
B.C. Gibb, R.G. Chapman, J.C. Sherman, Synthesis of hydroxyl-footed cavitands. J. Org. Chem. 61, 1505 (1996)
M.G. Demissie, F.K. Sabir, G.D. Edossa, B.A. Gonfa, Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Lippia adoensis (koseret) and evaluation of its antibacterial activity. J Chem (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7459042
S.W. Yun, Y. Shim, S.G. Cho, Sintering behaviour and electrical characteristics of ZnO varistors prepared by pechini process. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 35, 498–504 (1998)
J.H. Ryu, C.S. Lim, K.H. Auh, Synthesis of ZnWO 4 nanopowders by polymerized complex method. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 39, 321–326 (2002)
R. Radhakrishnan, F.L.A. Khan, A. Muthu, A. Manokaran, J.S. Savarenathan, K. Kasinathan, Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles mediated by aqueous leaf extracts of Leucas aspera and Morinda tinctoria. Lett. Appl. Nanobiosci. 10, 2706–2714 (2021)
A. Pugazhendhi, S.S. Kumar, M. Manikandan, M. Saravanani, Photocatalytic properties and antimicrobial efficacy of Fe doped CuO nanoparticles against the pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Microb. Pathog. 122, 84–89 (2018)
P.A. Luque-Morales, A. Lopez-Peraza, O.J. Nava-Olivas, G. Amaya-Parra, Y.A. Baez-Lopez, V.M. Orozco-Carmona, H.E. Garrafa-Galvez, M.D.J. Chinchillas-Chinchillas, ZnO semiconductor nanoparticles and their application in photocatalytic degradation of various organic dyes. Materials 14, 7537 (2021)
M.A. Debeila, M.C. Raphulu, E. Mokoena, M. Avalos, V. Petranovskii, N.J. Coville, M.S. Scurrell, The influence of gold on the optical properties of sol–gel derived titania. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 396, 70–76 (2005)
T. Saad Algarni, N.A. Abduh, A. Al Kahtani, A. Aouissi, Photocatalytic degradation of some dyes under solar light irradiation using ZnO nanoparticles synthesized from Rosmarinus officinalis extract. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 15, 460–473 (2022)
S. Chen, W. Zhao, W. Liu, S.J. Zhang, Prepartion, characterization and activity evaluation of p-n junction photocatalyst p-NiO/n-ZnO. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 50, 387–396 (2009)
M.A. Bhatti, A.A. Shah, K.F. Almani, A. Tahira, S.E. Chalangar, A. dad Chandio, O. Nur, M. Willander, Z.H. Ibupoto, Efficient photo catalysts based on silver doped ZnO nanorods for the photo degradation of methyl orange. Ceramics Int. 45, 23289–23297 (2019)
M.A. Bhatti, A. Tahira, K.F. Almani, A.L. Bhatti, B. Waryani, A. Nafady, Z.H. Ibupoto, Enzymes and phytochemicals from neem extract robustly tuned the photocatalytic activity of ZnO for the degradation of malachite green (MG) in aqueous media. Res. Chem. Intermed. 47, 1581–1599 (2021)
Z. Zhao, Y. Zheng, Sci. China, Ser. D Earth Sci. 52, 1295–1318 (2009)
K. Sharma, R.K. Vyas, A.K. Dalai, Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of methylene blue degradation using reactive adsorption and its comparison with adsorption. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 62, 3651–3662 (2017)
T.H. Han, M.M. Khan, S. Kalathil, J. Lee, M.H. Cho, imultaneous enhancement of methylene blue degradation and power generation in a microbial fuel cell by gold nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 8174–8181 (2013)
A.N. Rao, B. Sivasankar, V. Sadasiva, Kinetic study on the photocatalytic degradation of salicylic acid using ZnO catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 166, 1357–1361 (2009)
N. Sobana, M. Swaminathan, The effect of operational parameters on the photocatalytic degradation of acid red 18 by ZnO. Sep. Purif. Technol. 56, 101–107 (2007)
I.K. Konstantinou, T.A. Albanis, TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: a review. Appl. Catal. B 49, 1–14 (2004)
M.A. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla, R. Hamzavi, Kinetic study on photocatalytic degradation of CI Acid Yellow 23 by ZnO photocatalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 133, 226–232 (2006)
R. Comparelli, E. Fanizza, M.L. Curri, P.D. Cozzoli, G. Mascolo, A. Agostiano, UV-induced photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes by organic-capped ZnO nanocrystals immobilized onto substrates. Appl. Catal. B 60, 1–11 (2005)
H. Li, S. Yin, Y. Wang, T. Sato, Efficient persistent photocatalytic decomposition of nitrogen monoxide over a fluorescence-assisted CaAl2O4: (Eu, Nd)/(Ta, N)-codoped TiO2/Fe2O3. Appl. Catal. B 132, 487–492 (2013)
B. Palanisamy, C.M. Babu, B. Sundaravel, S. Anandan, V. Murugesan, Sol– gel synthesis of mesoporous mixed Fe2O3/TiO2 photocatalyst: application for degradation of 4-chlorophenol. J Hazard Mater 252, 233–242 (2013)
J.C. Sin, J. Quek, S.M. Lam, H. Zeng, H. Lin, H. Li, K.O. Tham, A.R. Mohamed, J.W. Lim, Punica granatum mediated green synthesis of cauliflower-like ZnO and decorated with bovine bone-derived hydroxyapatite for expeditious visible light photocatalytic antibacterial, antibiofilm and antioxidant activities. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 105736 (2021)
S.M. Lam, J.C. Sin, H. Zeng, H. Lin, H. Li, Y.Y. Chai, M.K. Choong, A.R. Mohamed, Green synthesis of Fe-ZnO nanoparticles with improved sunlight photocatalytic performance for polyethylene film deterioration and bacterial inactivation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 123, 105574 (2021)
Y.H. Chin, J.C. Sin, S.M. Lam, H. Zeng, H. Lin, H. Li, L. Huang, A.R. Mohamed, 3-D/3-D Z-Scheme heterojunction composite formed by marimo-like Bi2WO6 and mammillaria-like ZnO for expeditious sunlight photodegradation of dimethyl phthalate. Catalysts 12, 1427 (2022)
Y.H. Chin, J.C. Sin, S.M. Lam, H. Zeng, H. Lin, H. Li, A.R. Mohamed, 0-D/3-D heterojunction composite constructed by decorating transition metal oxide nanoparticle on peony-like ZnO hierarchical microstructure for improved photodegradation of palm oil mill effluent. Optik 260, 169098 (2022)
S.M. Lam, K.C. Chew, J.C. Sin, H. Zeng, H. Lin, H. Li, J.W. Lim, A.R. Mohamed, Ameliorated photodegradation performance of polyethylene and polystyrene films incorporated with ZnO-PVP catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10, 107594 (2022)
K. Elumalai, S. Velmurugan, Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Azadirachta indica (L.) Appl. Surf. Sci. 345, 329–336 (2015)
J. Osuntokun, D.C. Onwudiwe, E.E. Ebenso, Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using aqueous Brassica oleracea L. var. italica and the photocatalytic activity. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 12, 444–457 (2019)
M.H. Kahsay, Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Becium grandiflorum for antimicrobial activity and adsorption of methylene blue. Appl Water Sci 11, 45 (2021)
M.J. Haque, M.M. Bellah, M.R. Hassan, S. Rahman, Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by two different methods & comparison of their structural, antibacterial, photocatalytic and optical properties. Nano Express 1, 0007 (2020)
Y.C. Liu, J. Li, J. Ahn, J. Pu, E.J. Rupa, Y. Huo, D.C. Yang, Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by one-pot green synthesis using fruit extract of Amomum longiligulare and its activity as a photocatalyst. Optik 218, 165245 (2020)
M.P. Kumar, D. Suresh, H. Nagabhushana, S.C. Sharma, Beta vulgaris aided green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their luminescence, photocatalytic and antioxidant properties. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 109 (2015)
J.K. Park, E.J. Rupa, M.H. Arif, J.F. Li, G. Anandapadmanaban, J.P. Kang, M. Kim, J.C. Ahn, R. Akter, D.C. Yang, S.C. Kang, Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Gynostemma pentaphyllum extracts and assessment of photocatalytic properties through malachite green dye decolorization under UV illumination-A Green Approach. Optik 239, 166249 (2021)
F.M. Albarakaty, M.I. Alzaban, N.K. Alharbi, F.S. Bagrwan, A.R. Abd El-Aziz, M.A. Mahmoud, Zinc oxide nanoparticles, biosynthesis, characterization and their potent photocatalytic degradation, and antioxidant activities. J. King Saud University-Science 35, 102434 (2023)
A. El Golli, M. Fendrich, N. Bazzanella, C. Dridi, A. Miotello, M. Orlandi, Wastewater remediation with ZnO photocatalysts: green synthesis and solar concentration as an economically and environmentally viable route to application. J. Environ. Manage. 286, 112226 (2021)
S.M. Rao, S. Kotteeswaran, A.M. Visagamani, Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from camellia sinensis: organic dye degradation and antibacterial activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 134, 108956 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their sincere appreciations to Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R79), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, for partial funding of this work.
Funding
King Saud University, RSP2023R79, Ayman Nafady
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MAB, did synthesis of ZnO nanostructures and evaluate the partial photocatalytic properties. AT, did XRD analysis. AAH, did analysis of obtained photodegradation results. UA, did optical bandgap analysis. AN, partially supervised the work and edit the draft of manuscript. BV, did the SEM analysis and edit the draft of paper. ZHI, supervised the work and wrote the first draft of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest in the presented research work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatti, M.A., Tahira, A., Hullio, A.A. et al. Oxygenated terminals of milky sap of Calotropis procera transformed 1D ZnO structure to 0D nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of malachite green and methylene blue. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 929 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10290-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10290-4