Abstract
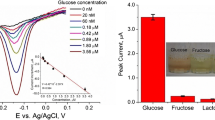
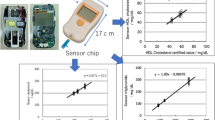
In this work, three specialized oxidases for glucose, lactate and cholesterol are absorbed on carbon microspheres (CSs), which can produce hydrogen peroxide during their substrate-specific enzymatic activity. Electrochemiluminescent (ECL) is generated by the electrochemical reaction between luminol and hydrogen peroxide on an ECL biosensor array, whose light signals are collected by a CCD camera. Under optimum conditions, calibration curves are constructed for glucose, lactate, cholesterol concentrations and ECL intensities. The detection limits of the different biosensors are found to be 12 μM for glucose, 3 μM for lactate and 19 μM for cholesterol. Furthermore, the resulting ECL biosensor array is expected to be an alternative analytical tool in clinical analysis because of its good stability, acceptable precision and reproducibility.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
M. Thapa, R. Sung, Y.S. Heo, Biosensors 11, 507 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120507
Z. Zhou, L. Xu, S. Wu, B. Su, Analyst 139, 4934–4939 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an00687a
Y. Yao, J. Chen, Y. Guo, T. Lv, Z. Chen, N. Li, S. Cao, B. Chen, T. Chen, Biosens. Bioelectron. 179, 113078 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113078
H. Chen, X. Tan, J. Zhang, Q. Lu, X. Ou, Y. Ruo, S. Chen, RSC Adv. 4, 61759–61766 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra09616a
Y. Yao, H. Li, D. Wang, C. Liu, C. Zhang, Analyst 142, 3715–3724 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7an01008g
M. Budiyanto, A.R. Purnomo, W.B. Sabtiawan, Suhariningsih, M. Yasin, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1417, 012005 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1417/1/012005
J. Luo, H. Yang, B.L. Song, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 225–245 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0190-7
A.A. Abdul-Hamead, F.M. Othman, M.A. Fakhri, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 15523–15532 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06102-2
X. Chen, B. Su, X. Song, Q. Chen, X. Chen, X. Wang, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 30, 665–676 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2010.12.004
Q. Wang, S. Liu, Z. Tang, J. Mater. Chem. B 9, 8174–8184 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tb01521d
S. Kurbanoglu, C. Erkmen, B. Uslu, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 124, 115809 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115809
Q. Cao, B. Liang, C. Yu, L. Fang, T. Tu, J. Wei, X. Ye, J. Electroanal. Chem. 873, 114358 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114358
M. Besharati, M.A. Tabrizi, F. Molaabasi, R. Saber, M. Shamsipur, J. Hamedi, S. Hosseinkhani, Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 69, 41–50 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2078
M. Wang, F. Liu, D. Chen, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 32, 23445–23456 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06832-3
M. Bonet-San-Emeterio, N. Felipe Montiel, M. Del Valle, Nanomaterials 11, 2094 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082094
D. Wang, C. Liu, Y. Liang, Y. Su, Q. Shang, C. Zhang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 165, B361–B369 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0551809jes
X. Ma, W. Gao, F. Du, F. Yuan, J. Yu, Y. Guan, N. Sojic, G. Xu, Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 2936–2945 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00230
Y. Zhao, L. Bouffier, G. Xu, G. Loget, N. Sojic, Chem. Sci. 13, 2528–2550 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1sc06987j
Q. Han, C. Wang, Z. Li, J. Wu, P.K. Liu, F. Mo, Y. Fu, Anal. Chem. 92, 3324–3331 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05262
N. Liao, J.L. Liu, Y.Q. Chai, R. Yuan, Y. Zhuo, Anal. Chem. 92, 3940–3948 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05433
M.M. Chen, C.H. Xu, W. Zhao, H.Y. Chen, J.J. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202117401 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202117401
R. Yang, Y. Liu, H. Ye, B. Qiu, Z. Lin, L. Guo, Electroanalysis 28, 1783–1786 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201600125
C. Ma, Y. Cao, X. Gou, J.J. Zhu, Anal. Chem. 92, 431–454 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04947
T.H. Fereja, F. Du, C. Wang, D. Snizhko, Y. Guan, G. Xu, J. Anal. Test. 4, 76–91 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-020-00128-x
Y. Xiao, L. Xu, L.W. Qi, Talanta 165, 577–583 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.019
T. Chen, L. Pan, T. Lu, C. Fu, D.H.C. Chua, Z. Sun, J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 1263–1267 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta14037g
L. Guo, S. Chen, Y.L. Yu, J.H. Wang, Anal. Chem. 93, 16240–16247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04126
C. Yang, N. Gao, Y. Liu, H. Zhao, J. Jing, X. Zhang, New J. Chem. 45, 19515–19520 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ03826E
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grants No. 2008085QB68), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Provincial Department of Education (No. KJ2021A0521) and National Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (Grants No. 202010373008, 202010373022 and 202110373006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC: Methodology, Investigation, Data Curation. FD & ZH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-Original Draft. HL: Investigation. HG: Data Curation, Visualization. GL: Validation, Resources, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Dai, F., Liu, H. et al. Visualization analysis of glucose, lactate and cholesterol based on an electrochemiluminescent biosensor array. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 415 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09852-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09852-3