Abstract
As a natural biopolymer, cellulose has the advantages of good biodegradability, good thermal stability, easy processing and low cost. As a result, cellulose and its derivatives have received widespread attention in various applications, especially in the field of microwave absorption. In this review, the research progress of different structured cellulose-based microwave absorption materials (MAMs) in the last five years is firstly summarized. The processing methods and microstructures of these precursors are highlighted. Typical precursors mainly include cotton, bamboo, wood, agricultural waste, bacterial cellulose and nut shell. Then, their unique advantages in the field of microwave absorption are analyzed. Finally, the challenges and research prospects of cellulose-based MAMs are discussed, and some suggestions are provided based on the development status of MAMs.


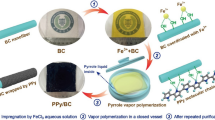
Reproduced with permission from Ref. [38]

Reproduced with permission from Ref. [123]
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
J. Liu, M.H. Wei, H.F. Li, X. Wang, X.Y. Wang, S. Shi, Measurement and mapping of the electromagnetic radiation in the urban environment. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 39, 38–43 (2020)
J.L. Wolff, J.D. Darer, K.L. Larsen, Family caregivers and consumer health information technology. J. Gen. Intern. Med 31, 117–121 (2016)
Y. Li, Z. Liu, Y.F. Zheng, X.S. Guo, W. Yuan, P.F. Zhao, Transverse crack detection of rail base considering wedge-like structure and using a bulk-wave electromagnetic acoustic transducer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Measurement 71, 6002009 (2022)
O. Dasdag, N. Adalier, S. Dasdag, Electromagnetic radiation and Alzheimer’s disease. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 34, 1087–1094 (2020)
N. Wongkasem, Electromagnetic pollution alert: microwave radiation and absorption in human organs and tissues. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 40, 236–253 (2021)
M. Ghazanfarpour, Z.A. Kashani, R. Pakzad, F. Abdi, F.A. Rahnemaei, P.A. Akbari, N. Roozbeh, Effect of electromagnetic field on abortion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Open. Med. 16, 1628–1641 (2021)
S. Zhang, Z. Gao, Z. Sun, B. Cheng, Z. Zhao, Y. Jia, G. Wu, Solid solution strategy for bimetallic metal-polyphenolic networks deriving electromagnetic wave absorbers with regulated heterointerfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 611, 155707 (2023)
X. Han, Y. Huang, J. Wang, G. Zhang, T. Li, P. Liu, Flexible hierarchical ZnO/AgNWs/carbon cloth-based film for efficient microwave absorption, high thermal conductivity and strong electro-thermal effect. Compos. Pt B: Eng. 229, 109458 (2022)
M. Qin, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv. Sci. 9, 2105553 (2022)
N. Gao, W.P. Li, W.S. Wang, D.P. Liu, Y.M. Cui, L. Guo, G.S. Wang, Balancing dielectric loss and magnetic loss in Fe-NiS2/NiS/PVDF composites toward strong microwave reflection loss. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 14416–14424 (2020)
C. Lei, Y. Du, Tunable dielectric loss to enhance microwave absorption properties of flakey FeSiAl /ferrite composites. J. Alloy Compd. 822, 153674 (2020)
D. Chen, F. Luo, L. Gao, W. Zhou, D. Zhu, Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of divalent-doped Na3Zr2Si2PO12 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38, 4440–4445 (2018)
X. Zuo, Y. Zhao, H. Zhang, H. Huang, C. Zhou, T. Cong, J. Muhammad, X. Yang, Y. Zhang, Z. Fan, L. Pan, Surface modification of helical carbon nanocoil (CNC) with N-doped and co-anchored carbon layer for efficient microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 608, 1894–1906 (2022)
L.X. Gai, H.H. Zhao, F.Y. Wang, P. Wang, Y.L. Liu, X.J. Han, Y.C. Du, Advances in core-shell engineering of carbon-based composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 15, 9410–9439 (2022)
H.H. Zhao, X.Z. Xu, D.G. Fan, P. Xu, F.Y. Wang, L.R. Cui, X.J. Han, Y.C. Du, Anchoring porous carbon nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes as a high-performance composite with a unique core-sheath structure for electromagnetic pollution precaution. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 22489–22500 (2021)
F. Wang, Y. Liu, H. Zhao, L. Cui, L. Gai, X. Han, Y. Du, Controllable seeding of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes on three-dimensional Co/C foam for enhanced dielectric loss and microwave absorption characteristics. Chem. Eng. J. 450, 138160 (2022)
S. Zhang, Y. Pei, Z. Zhao, C. Guan, G. Wu, Simultaneous manipulation of polarization relaxation and conductivity toward self-repairing reduced graphene oxide based ternary hybrids for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 630, 453–464 (2023)
Y. Yuan, Y.Y. Xiong, J.J. Li, W.L. Yin, Q.Y. Peng, H.B. Lu, Y.B. Li, X.D. He, Large-scale synthesis of hollow carbon fibers with ultra-large diameter by thermally controlled pyrolysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 103, 5629–5637 (2020)
X.D. Zuo, P. Xu, C.Y. Zhang, M.Z. Li, X.Y. Jiang, X.G. Yue, Porous magnetic carbon nanofibers (P-CNF/Fe) for low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption synthesized by electrospinning. Ceram. Int. 45, 4474–4481 (2019)
D.Q. Zhang, H.H. Wang, J.Y. Cheng, C.Y. Han, X.Y. Yang, J.Y. Xu, G.C. Shan, G.P. Zheng, M.S. Cao, Conductive WS2-NS/CNTs hybrids based 3D ultra-thin mesh electromagnetic wave absorbers with excellent absorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 528, 147052 (2020)
X. Yang, S.K. Biswas, J. Han, S. Tanpichai, M.C. Li, C. Chen, S. Zhu, A.K. Das, H. Yano, Surface and Interface Engineering for Nanocellulosic Advanced Materials. Adv. Mater. 33, 2002264(2021)
A.K. Mohanty, S. Vivekanandhan, J.M. Pin, M. Misra, Composites from renewable and sustainable resources: challenges and innovations. Science 362, 536–542 (2018)
N. Gill, A.L. Sharma, V. Gupta, M. Tomar, O.P. Pandey, D.P. Singh, Enhanced microwave absorption and suppressed reflection of polypyrrole-cobalt ferrite-graphene nanocomposite in X-band. J. Alloy Compd. 797, 1190–1197 (2019)
H. Liang, H. Xing, M. Qin, H. Wu, Bamboo-like short carbon fibers@Fe3O4@phenolic resin and honeycomb-like short carbon fibers@Fe3O4@FeO composites as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Compos. Pt A: Appl Sci. Manuf. 135, 105959 (2020)
W.H. Zhou, C. Jiang, X. Duan, J.C. Song, Y. Yuan, N. Chen, Fe3O4/carbonized cellulose micro-nano hybrid for high-performance microwave absorber. Carbohydr. Polym. 245, 116531 (2020)
A.R. Pai, T. Binumol, D.A. Gopakumar, D. Pasquini, B. Seantier, N. Kalarikkal, S. Thomas, Ultra-fast heat dissipating aerogels derived from polyaniline anchored cellulose nanofibers as sustainable microwave absorbers. Carbohydr. Polym. 246, 116663 (2020)
Z. Yang, Y. Zhang, B. Wen, Enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding capability in bamboo fiber@polyaniline composites through microwave reflection cavity design. Compos. Sci. Technol. 178, 41–49 (2019)
A. Anzlovar, E. Zagar, Cellulose structures as a support or template for inorganic nanostructures and their assemblies. Nanomaterials 12, 1837 (2022)
Z. Zhang, J.W. Tan, W.H. Gu, H.Q. Zhao, J. Zheng, B.S. Zhang, G.B. Ji, Cellulose-chitosan framework/polyailine hybrid aerogel toward thermal insulation and microwave absorbing application. Chem. Eng. J. 395, 125190 (2020)
L.Y. Liu, S. Yang, H.Y. Hu, T.L. Zhang, Y. Yuan, Y.B. Li, X.D. He, Lightweight and efficient microwave-absorbing materials based on Loofah-sponge-derived hierarchically porous carbons. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 1228–1238 (2019)
Y. Jiang, X. Xie, Y. Chen, Y.J. Liu, R. Yang, G.X. Sui, Hierarchically structured cellulose aerogels with interconnected MXene networks and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 8679–8687 (2018)
H.Q. Zhao, Y. Cheng, J.N. Ma, Y.N. Zhang, G.B. Ji, Y.W. Du, A sustainable route from biomass cotton to construct lightweight and high-performance microwave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 339, 432–441 (2018)
G. Wang, D.G. Lai, X.H. Xu, Y. Wang, Lightweight, stiff and heat-resistant bamboo-derived carbon scaffolds with gradient aligned microchannels for highly efficient EMI shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 136911 (2022)
T. Gao, Y. Ma, L. Ji, Y. Zheng, S. Yan, Y. Li, X. Zhang, Nickel-coated wood-derived porous carbon (Ni/WPC) for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 5, 2328–2338 (2022)
Q. Liu, D. Zhang, T. Fan, J. Gu, Y. Miyamoto, Z. Chen, Amorphous carbon-matrix composites with interconnected carbon nano-ribbon networks for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 46, 461–465 (2008)
Y. Fei, M. Liang, T. Zhou, Y. Chen, H. Zou, Unique carbon nanofiber@Co/C aerogel derived bacterial cellulose embedded zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 167, 575–584 (2020)
X. Qiu, L.X. Wang, H.L. Zhu, Y.K. Guan, Q.T. Zhang, Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on walnut shell-derived nano-porous carbon. Nanoscale 9, 7408–7418 (2017)
X.X. Zhao, J. Yan, Y. Huang, X.D. Liu, L. Ding, M. Zong, P.B. Liu, T.H. Li, Magnetic porous CoNi@C derived from bamboo fiber combined with metal-organic-framework for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 595, 78–87 (2021)
Z.H. Wu, Z.Z. Meng, C. Yao, Y. Deng, G.L. Zhang, Y.B. Wang, Rice husk derived hierarchical porous carbon with lightweight and efficient microwave absorption. Mater. Chem. Phys. 275, 125246 (2022)
N. Sriplai, S. Pinitsoontorn, Bacterial cellulose-based magnetic nanocomposites: a review. Carbohydr. Polym. 254, 117228 (2021)
Y.J. Tan, J. Li, Y. Gao, J. Li, S. Guo, M. Wang, A facile approach to fabricating silver-coated cotton fiber non-woven fabrics for ultrahigh electromagnetic interference shielding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 458, 236–244 (2018)
J. Chen, Z. Zhu, H. Zhang, S. Tian, S. Fu, Wood-derived nanostructured hybrid for efficient flame retarding and electromagnetic shielding. Mater. Des. 204, 109695 (2021)
T. Heinze, Cellulose: structure and properties. Adv. Polym. Sci. 271, 1–52 (2015)
X. Zhang, H.H. Zheng, J. Wu, W. Chen, Y.Q. Chen, G. Xuezhi, H.P. Yang, H.P. Chen, Physicochemical and adsorption properties of biochar from biomass-based pyrolytic polygeneration: effects of biomass species and temperature. Biochar 3, 657–670 (2021)
S. Zhang, B. Cheng, Z. Jia, Z. Zhao, X. Jin, Z. Zhao, G. Wu, The art of framework construction: hollow-structured materials toward high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 5, 1658–1698 (2022)
H.W. Rong, T. Gao, Y.H. Zhang, X.G. Liu, X.F. Zhang, M. Yan, Carbonized fibers with multi-elemental doping and hollow architecture derived from natural cotton for tunable microwave absorption properties. J. Alloy Compd. 884, 161084 (2021)
Y. Wei, H.J. Liu, S.C. Liu, M.M. Zhang, Y.P. Shi, J.W. Zhang, L. Zhang, C.H. Gong, Waste cotton-derived magnetic porous carbon for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Compos. Commun. 9, 70–75 (2018)
X.C. Di, Y. Wang, Y.Q. Fu, X.M. Wu, P. Wang, Wheat flour-derived nanoporous carbon@ZnFe2O4 hierarchical composite as an outstanding microwave absorber. Carbon 173, 174–184 (2021)
Z.J. Liao, M.L. Ma, Z.Y. Tong, Y.X. Bi, K.L. Chung, M.T. Qiao, Y. Ma, A.J. Ma, G.L. Wu, X. Zhong, R.R. Sun, Fabrication of one-dimensional CoFe2/C@MoS2 composites as efficient electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Dalton Trans. 50, 11640–11649 (2021)
Q. Chang, H. Liang, B. Shi, H. Wu, Microstructure induced dielectric loss in lightweight Fe3O4 foam for electromagnetic wave absorption. iScience 25, 103925 (2022)
Y. Wang, X.C. Di, Z. Lu, X.M. Wu, Rational construction of hierarchical Co@C@NPC nanocomposites derived from bimetallic hybrid ZIFs/biomass for boosting the microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 589, 462–471 (2021)
Z.Y. Tong, Y.X. Bi, M.L. Ma, Z.J. Liao, W.B. Huang, K.L. Chung, Y. Ma, G.L. Wu, Y.L. Qu, C.B. Pan, Y.S. Wang, Fabrication of flower-like surface Ni@Co3O4 nanowires anchored on RGO nanosheets for high-performance microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 565, 150483 (2021)
Q. Chang, H. Liang, B. Shi, X. Li, Y. Zhang, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Ethylenediamine-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of NiCo2O4 absorber with controlled morphology and excellent absorbing performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 588, 336–345 (2021)
W. Huang, Z. Tong, Y. Bi, M. Ma, Z. Liao, G. Wu, Y. Ma, S. Guo, X. Jiang, X. Liu, Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of coralloid core-shell structure NiS/Ni3S4@PPy@MoS2 nanowires. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 599, 262–270 (2021)
D.W. Liu, Y.C. Du, P. Xu, F.Y. Wang, Y.H. Wang, L.R. Cui, H.H. Zhao, X.J. Han, Rationally designed hierarchical N-doped carbon nanotubes wrapping waxberry-like Ni@C microspheres for efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 5086–5096 (2021)
D. Liu, L. Yang, F. Wang, H. Zhang, J. Liu, T. Lv, H. Zhao, Y. Du, Hierarchical carbon nanotubes@Ni/C foams for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 196, 867–876 (2022)
H. Liang, H. Xing, Z. Ma, H. Wu, Tailoring high-electroconductivity carbon cloth coated by nickel cobaltate/nickel oxide: a case of transition from microwave shielding to absorption. Carbon 183, 138–149 (2021)
R.D. Guo, D. Su, F. Chen, Y.Z. Cheng, X. Wang, R.Z. Gong, H. Luo, Hollow beaded Fe3C/N-doped carbon fibers toward broadband microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 3084–3094 (2022)
W. Li, Z.L. Zhang, Y.Y. Lv, Z. Wu, L. Yang, W.X. Zou, Y.H. Zou, Ultralight coral-like hierarchical Fe/CNTs/Porous carbon composite derived from biomass with tunable microwave absorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 571, 151349 (2022)
J.Y. Fang, P. Li, Y.D. Liu, Y.G. Min, Cobalt magnetic particles and carbon composite microtubes as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 2474–2482 (2021)
M.L. Ma, Y.X. Bi, Z.Y. Tong, Y.Y. Liu, P. Lyu, R.Z. Wang, Y. Ma, G.L. Wu, Z.J. Liao, Y. Chen, Recent progress of MOF-derived porous carbon materials for microwave absorption. RSC Adv. 11, 16572–16591 (2021)
Y. Bi, M. Ma, Z. Jiao, Y. Ma, D. Hou, G. Geng, W. Feng, A. Ma, M. Qiao, Y. Liu, Enhancing electromagnetic wave absorption performance of one-dimensional C@Co/N-doped C@PPy composite fibers. Carbon 197, 152–162 (2022)
H. Zhao, F. Wang, L. Cui, X. Xu, X. Han, Y. Du, Composition optimization and microstructure design in MOFs-derived magnetic carbon-based microwave absorbers: a review. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 208 (2021)
M.L. Yang, Y. Yuan, Y. Li, X.X. Sun, S.S. Wang, L. Liang, Y.H. Ning, J.J. Li, W.L. Yin, R.C. Che, Y.B. Li, Dramatically enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of hierarchical CNT/Co/C fiber derived from cotton and metal-organic-framework. Carbon 161, 517–527 (2020)
X. Li, E.B. Cui, Z. Xiang, L.Z. Yu, J. Xiong, F. Pan, W. Lu, Fe@NPC@CF nanocomposites derived from Fe-MOFs/biomass cotton for lightweight and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption applications. J. Alloy Compd. 819, 152952 (2020)
M. Zhu, X.X. Yan, H.L. Xu, Y.J. Xu, L. Kong, Highly conductive and flexible bilayered MXene/cellulose paper sheet for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Ceram. Int. 47, 17234–17244 (2021)
Z. Xiang, Y. Shi, X. Zhu, L. Cai, W. Lu, Flexible and waterproof 2D/1D/0D construction of MXene-based nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption, EMI shielding, and photothermal conversion. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 150 (2021)
S.J. Wang, D.S. Li, Y. Zhou, L. Jiang, Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/Ni Chain/ZnO array hybrid nanostructures on cotton fabric for durable self-cleaning and enhanced microwave absorption. ACS Nano 14, 8634–8645 (2020)
Y.Y. Shi, L.J. Yu, K. Li, S.Z. Li, Y.B. Dong, Y.F. Zhu, Y.Q. Fu, F.B. Meng, Well-matched impedance of polypyrrole-loaded cotton non-woven fabric/polydimethylsiloxane composite for extraordinary microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 197, 108246 (2020)
Y. Bi, M. Ma, Z. Liao, Z. Tong, Y. Chen, R. Wang, Y. Ma, G. Wu, One-dimensional Ni@Co/C@PPy composites for superior electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 605, 483–492 (2022)
D. Lan, H. Zhou, H. Wu, A polymer sponge with dual absorption of mechanical and electromagnetic energy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 633, 92–101 (2022)
W. Gu, J. Lv, B. Quan, X. Liang, B. Zhang, G. Ji, Achieving MOF-derived one-dimensional porous ZnO/C nanofiber with lightweight and enhanced microwave response by an electrospinning method. J. Alloy Compd. 806, 983–991 (2019)
Y. Qiu, H. Yang, B. Wen, L. Ma, Y. Lin, Facile synthesis of nickel/carbon nanotubes hybrid derived from metal organic framework as a lightweight, strong and efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 590, 561–570 (2021)
Z. Liao, M. Ma, Z. Tong, R. Wang, Y. Bi, Y. Chen, K.L. Chung, Y. Ma, Fabrication of ZnFe2O4/C@PPy composites with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 602, 602–611 (2021)
Y.X. Bi, M.L. Ma, Y.Y. Liu, Z.Y. Tong, R.Z. Wang, K.L. Chung, A.J. Ma, G.L. Wu, Y. Ma, C.P. He, P. Liu, L.Y. Hu, Microwave absorption enhancement of 2-dimensional CoZn/C@MoS2@PPy composites derived from metal-organic framework. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 600, 209–218 (2021)
Z.J. Liao, M.L. Ma, Z.Y. Tong, R.Z. Wang, Y.X. Bi, Y. Chen, K.L. Chung, Y. Ma, Fabrication of ZnFe2O4/C@PPy composites with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 602, 602–611 (2021)
M. Ma, W. Li, Z. Tong, Y. Yang, Y. Ma, Z. Cui, R. Wang, P. Lyu, Huang, 1D flower-like Fe3O4@SiO2@MnO2 nanochains inducing RGO self-assembly into aerogels for high-efficient microwave absorption. Mater. Des. 188, 108462 (2020)
S. Feng, J.C. Deng, L.J. Yu, Y.B. Dong, Y.F. Zhu, Y.Q. Fu, Development of lightweight polypyrrole/cellulose aerogel composite with adjustable dielectric properties for controllable microwave absorption performance. Cellulose 27, 10213–10224 (2020)
Y.Y. Wang, Z.H. Zhou, J.L. Zhu, W.J. Sun, D.X. Yan, K. Dai, Z.M. Li, Low-temperature carbonized carbon nanotube/cellulose aerogel for efficient microwave absorption. Compos. Pt B: Eng. 220, 108985 (2021)
X. Zhang, J. Qiao, F.L. Wang, L.F. Lv, D.M. Xu, Y.Y. Jiang, P. Cui, Q. Wang, W. Liu, J.R. Liu, Tailoring electromagnetic absorption performances of TiO2/Co/carbon nanofibers through tuning graphitization degrees. Ceram. Int. 46, 4754–4761 (2020)
X. Li, L. Wang, W.B. You, L.S. Xing, L.T. Yang, X.F. Yu, J. Zhang, Y.S. Li, R.C. Che, Enhanced polarization from flexible hierarchical MnO2 arrays on cotton cloth with excellent microwave absorption. Nanoscale 11, 13269–13281 (2019)
S. Gupta, C. Chang, A.K. Anbalagan, C.H. Lee, N.H. Tai, Reduced graphene oxide/zinc oxide coated wearable electrically conductive cotton textile for high microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 188, 107994 (2020)
L. Yang, Z. Lou, X. Han, J. Liu, Z. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Wu, C. Yuan, Y. Li, Fabrication of a novel magnetic reconstituted bamboo with mildew resistance properties. Mater. Today Commun. 23, 101086 (2020)
S.H. Park, N.J. Wistara, F. Febrianto, M. Lee, Evaluation of sembilang bamboo (Dendrocalamus giganteus) charcoal for potential utilization. BioResources 15, 6–19 (2020)
X. Pang, M. Cao, J. Qin, X. Li, X. Yang, Synthesis of bamboo-derived porous carbon: exploring structure change, pore formation and supercapacitor application. J. Porous Mater. 29, 559–569 (2022)
H. Chen, Y. Zheng, X. Zhu, W. Hong, Y. Tong, Y. Lu, G. Pei, Y. Pang, Z. Shen, C. Guan, Bamboo-derived porous carbons for Zn-ion hybrid supercapacitors. Mater. Res. Bull. 139, 111281 (2021)
S.C. Abbas, C. Lin, Z. Hua, Q. Deng, H. Huang, Y. Ni, S. Cao, X. Ma, Bamboo-derived carbon material inherently doped with SiC and nitrogen for flexible supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 133738 (2022)
X.N. Pang, L.D. Ye, X.J. Li, B.H. Yan, J.L. Zhang, X. Yang, Magnetic core-shell structure in-situ encapsulated in bamboo-derived carbon skeleton for efficient microwave absorption. J. Alloy Compd. 888, 161510 (2021)
X. Zhang, Y.Y. Dong, F. Pan, Z. Xiang, X.J. Zhu, W. Lu, Electrostatic self-assembly construction of 2D MoS2 wrapped hollow Fe3O4 nanoflowers@1D carbon tube hybrids for self-cleaning highperformance microwave absorbers. Carbon 177, 332–343 (2021)
Z.Y. Tong, Z.J. Liao, Y.Y. Liu, M.L. Ma, Y.X. Bi, W.B. Huang, Y. Ma, M.T. Qiao, G.L. Wu, Hierarchical Fe3O4/Fe@C@MoS2 core-shell nanofibers for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 179, 646–654 (2021)
T. Zhang, D.C. Zhao, L.J. Wang, R. Meng, H. Zhao, P.Y. Zhou, L. Xia, B. Zhong, H.T. Wang, G.W. Wen, A facile precursor pyrolysis route to bio-carbon/ferrite porous architecture with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption in S-band. J. Alloy Compd. 819, 153269 (2020)
Z. Lou, X. Han, J. Liu, Q. Ma, H. Yan, C. Yuan, L. Yang, H. Han, F. Weng, Y. Li, Nano-Fe3O4/bamboo bundles/phenolic resin oriented recombination ternary composite with enhanced multiple functions. Compos. Pt B: Eng. 226, 109335 (2021)
F. Yuan, S. Wei, L. Zhichao, W. Qiuyi, Z. Yihan, L. Yanjun, An industrial feasible and sustainable method for preparing fiberized bamboo-derived magnetic biomass carbon. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 26137–26150 (2021)
Y.K. Lahsmin, H. Heryanto, S. Ilyas, A.N. Fahri, B. Abdullah, D. Tahir, Optical properties determined from infrared spectroscopy and structural properties from diffraction spectroscopy of composites Fe/CNs/PVA for electromagnetic wave absorption. Opt. Mater. 111, 110639 (2021)
Z.C. Lou, Q.Y. Wang, U.I. Kara, R.S. Mamtani, X.D. Zhou, H.Y. Bian, Z.H. Yang, Y.J. Li, H.L. Lv, S. Adera, X.G. Wang, Biomass-derived carbon heterostructures enable environmentally adaptive wideband electromagnetic wave absorbers. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 11 (2022)
Z. Wu, H. Zheng, G. Zhang, Y. Deng, Z. Meng, H.U. Wahab, Synthesis of diameter-fluctuating silicon carbide nanowires for excellent microwave absorption. Mater. Chem. Phys. 244, 122648 (2020)
H. Xia, Z. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Deng, D. Zhang, P. Du, S. Zhang, X. Lu, Novel Fe–Mn–O nanosheets/wood carbon hybrid with tunable surface properties as a superior catalyst for fenton-like oxidation. Appl. Catal. B: Environ 259, 118058 (2019)
S. Yin, Y. Huang, C. Deng, Y. Jiao, W.B. Wu, F. Seidi, H.N. Xiao, Hierarchically porous biochar derived from orthometric integration of wooden and bacterial celluloses for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 218, 109184 (2022)
M. Cheng, W. Ren, H. Li, X. Liu, S. Bandaru, J. Zhang, X. Zhang, Multiscale collaborative coupling of wood-derived porous carbon modified by three-dimensional conductive magnetic networks for electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Pt B: Eng 224, 109169 (2021)
Q. Chang, H. Liang, B. Shi, H. Wu, Sodium oxalate-induced hydrothermal synthesis of wood-texture-column-like NiCo2O4 with broad bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 600, 49–57 (2021)
G.Y. Qin, X.X. Huang, X. Yan, Y.F. He, Y.H. Liu, L. Xia, B. Zhong, Carbonized wood with ordered channels decorated by NiCo2O4 for lightweight and high-performance microwave absorber. J. Adv. Ceram. 11, 105–119 (2022)
M. Zhu, X.X. Yan, H.L. Xu, Y.J. Xu, L. Kong, Ultralight, compressible, and anisotropic MXene@Wood nanocomposite aerogel with excellent electromagnetic wave shielding and absorbing properties at different directions. Carbon 182, 806–814 (2021)
Z. Zhao, X. Zhou, K. Kou, H.J.C. Wu, PVP-assisted transformation of ZIF-67 into cobalt layered double hydroxide/carbon fiber as electromagnetic wave absorber. Carbon 173, 80–90 (2021)
L.L. Xu, Y. Xiong, B.K. Dang, Z.N. Ye, C.D. Jin, Q.F. Sun, X.H. Yu, In-situ anchoring of Fe3O4/ZIF-67 dodecahedrons in highly compressible wood aerogel with excellent microwave absorption properties. Mater. Des. 182, 108006 (2019)
Y. Xiong, L.L. Xu, C.X. Yang, Q.F. Sun, X.J. Xu, Implanting FeCo/C nanocages with tunable electromagnetic parameters in anisotropic wood carbon aerogels for efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 18863–18871 (2020)
J.B. Xi, E.Z. Zhou, Y.J. Liu, W.W. Gao, J. Ying, Z.C. Chen, C. Gao, Wood-based straightway channel structure for high performance microwave absorption. Carbon 124, 492–498 (2017)
Y.F. Pan, M.Y. Dai, Q. Guo, D.W. Yin, S.R. Zhuo, N.G. Hu, X.F. Yu, Y.A. Hao, J.T. Huang, Multilayer wood/Cu-Fe3O4@Graphene/Ni composites for absorption-dominated electromagnetic shielding. Compos. Interfaces 29, 711–712 (2022)
S. Dong, P.T. Hu, X.T. Li, C.Q. Hong, X.H. Zhang, J.C. Han, NiCo2S4 nanosheets on 3D wood-derived carbon for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 398, 125588 (2020)
C. Ji, Y. Liu, Y.Y. Li, X.L. Su, J. Xu, L.L. Lu, Facile preparation and excellent microwave absorption properties of cobalt-iron/porous carbon composite materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 527, 167776 (2021)
P.T. Hu, S. Dong, X.T. Li, J.M. Chen, X.H. Zhang, P. Hu, S.S. Zhang, A low-cost strategy to synthesize MnO nanorods anchored on 3D biomass-derived carbon with superior microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 9219–9228 (2019)
S. Dong, W.K. Tang, P.T. Hu, X.G. Zhao, X.H. Zhang, J.C. Han, P. Hu, Achieving excellent electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities by construction of MnO nanorods on porous carbon composites derived from natural wood via a simple route. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng 7, 11795–11805 (2019)
Z.C. Lou, Y.J. Li, H. Han, H.H. Ma, L. Wang, J.B. Cai, L.T. Yang, C.L. Yuan, J. Zou, Synthesis of porous 3D Fe/C Composites from waste wood with tunable and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng 6, 15598–15607 (2018)
Z.C. Lou, H. Han, M. Zhou, J.Q. Han, J.B. Cai, C.X. Huang, J. Zou, X.Y. Zhou, H.J. Zhou, Z.B. Sun, Synthesis of magnetic Wood with excellent and tunable Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Properties by a facile Vacuum/Pressure impregnation method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 1000–1008 (2018)
C. Ji, Y. Liu, J. Xu, Y. Li, Y. Shang, X. Su, Enhanced microwave absorption properties of biomass-derived carbon decorated with transition metal alloy at improved graphitization degree. J. Alloy Compd. 890, 161834 (2022)
J.Y. Fang, Y.S. Shang, Z. Chen, W. Wei, Y. Hu, X.G. Yue, Z.H. Jiang, Rice husk-based hierarchically porous carbon and magnetic particles composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave attenuation. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 4695–4705 (2017)
L. Zahid, M. Jusoh, R.B. Ahmad, T. Sabapathy, M.F. Malek, M.R. Kamarudin, M.N. Yasin, M.N. Osman, FEMC performance of pyramidal microwave absorber using sugarcane baggasse and rubber tire dust at 1 GHz to 18 GHz frequencies. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J 34, 162–171 (2019)
M.A. Aslam, W. Ding, S.U. Rehman, A. Hassan, Y.C. Bian, Q.C. Liu, Z.G. Sheng, Low cost 3D bio-carbon foams obtained from wheat straw with broadened bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 543, 148785 (2021)
S. Zhang, Q. Zhang, S. Zhu, H. Zhang, X. Liu, Porous carbons derived from desilication treatment and mixed alkali activation of rice husk char for supercapacitors. Energy Sour. Part A: Recov. Util. Environ. Eff 43, 282–290 (2019)
Y. Zhao, Y. Zhang, C. Yang, L. Cheng, Ultralight and flexible SiC nanoparticle-decorated carbon nanofiber mats for broad-band microwave absorption. Carbon 171, 474–483 (2021)
Z.D. Chen, Z.Y. Wu, J.J. Su, J.P. Li, B. Gao, J.J. Fu, X.M. Zhang, K.F. Huo, P.K. Chu, Large-scale and low-cost synthesis of in situ generated SiC/C nano-composites from rice husks for advanced electromagnetic wave absorption applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 406, 126641 (2021)
Q.S. Li, J.J. Zhu, S.N. Wang, F. Huang, Q.C. Liu, X.K. Kong, Microwave absorption on a bare biomass derived holey silica-hybridized carbon absorbent. Carbon 161, 639–646 (2020)
X.F. Shu, B. Fang, W.J. Wu, Y.A. Song, Z.J. Zhao, Acicular or octahedral Fe3O4/rice husk-based activated carbon composites through graphitization synthesis as superior electromagnetic wave absorbers. Compos. Pt A: Appl Sci. Manuf 151, 106635 (2021)
Y. Liu, Z. Chen, W.H. Xie, S.K. Song, Y. Zhang, L.J. Dong, In-situ growth and graphitization synthesis of porous Fe3O4/Carbon fiber composites derived from biomass as lightweight microwave absorber. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng 7, 5318–5328 (2019)
G.J. Gou, F.B. Meng, H.G. Wang, M. Jiang, W. Wei, Z.W. Zhou, Wheat straw-derived magnetic carbon foams: in-situ preparation and tunable high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res 12, 1423–1429 (2019)
P.F. Yin, L.M. Zhang, Y.Y. Jiang, Y. Zhang, J. Wang, X. Feng, J.W. Dai, Y.T. Tang, Recycling of waste straw in sorghum for preparation of biochar/(Fe,Ni) hybrid aimed at significant electromagnetic absorbing of low-frequency band. J. Mater. Res. Technol-JMRT 9, 14212–14222 (2020)
J. Li, N. Zhang, H. Zhao, Z. Li, B. Tian, Y. Du, Cornstalk-derived macroporous carbon materials with enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 25758–25768 (2020)
J. Yu, Y. Li, G. Duan, P. Wen, W. Zhou, Bio-templated fabrication of chain-spherical V2O5/C composites from dandelion fiber for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Vacuum 195, 110683 (2022)
Q. Zheng, M. Yu, W. Wang, S. Liu, X. Liang, C. Wang, Y. Dai, X. Gao, Hierarchically porous carbon/α-Fe@Fe3C absorbers derived from luffa sponge with efficient microwave absorption. ChemistrySelect 5, 15075–15083 (2020)
W.X. Li, F. Guo, X.Q. Wei, Y.E. Du, Y.Q. Chen, Preparation of Ni/C porous fibers derived from jute fibers for high-performance microwave absorption. RSC Adv. 10, 36644–36653 (2020)
G.H. Li, L. Wang, Y. Deng, Q.F. Wei, Research progress of the biosynthetic strains and pathways of bacterial cellulose. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 49, kuab071 (2022)
A. Fillat, J. Martinez, C. Valls, O. Cusola, M.B. Roncero, T. Vidal, S.V. Valenzuela, P. Diaz, F.I.J. Pastor, Bacterial cellulose for increasing barrier properties of paper products. Cellulose 25, 6093–6105 (2018)
Z.J. Xu, M. He, Y.M. Zhou, S.X. Nie, Y.J. Wang, Y. Huo, Y.F. Kang, R.L. Wang, R. Xu, H. Peng, X. Chen, Spider web-like carbonized bacterial cellulose/MoSe2 nanocomposite with enhanced microwave attenuation performance and tunable absorption bands. Nano Res. 14, 738–746 (2021)
A.K. Sonker, K. Rathore, A.K. Teotia, A. Kumar, V. Verma, Rapid synthesis of high strength cellulose-poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) biocompatible composite films via microwave crosslinking. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 136, 47393 (2019)
L.L. Liang, Z.Q. Zhang, F. Song, W. Zhang, H. Li, J.J. Gu, Q.L. Liu, D. Zhang, Ultralight, flexible carbon hybrid aerogels from bacterial cellulose for strong microwave absorption. Carbon 162, 283–291 (2020)
H. Geng, X. Zhang, W. Xie, P. Zhao, G. Wang, J. Liao, L. Dong, Lightweight and broadband 2D MoS2 nanosheets/3D carbon nanofibers hybrid aerogel for high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 609, 33–42 (2022)
B. Du, D.Y. Zhang, J.J. Qian, M. Cai, C. He, P. Zhou, A.Z. Shui, Multifunctional carbon nanofiber-SiC nanowire aerogel films with superior microwave absorbing performance. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 4, 1281–1291 (2021)
Z.J. Li, H. Lin, S.Q. Ding, H.L. Ling, T. Wang, Z.Q. Miao, M. Zhang, A. Meng, Q.D. Li, Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 167, 148–159 (2020)
P.P. Zhou, X.K. Wang, L.X. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Song, X. Qiu, M.X. Yu, Q.T. Zhang, Walnut shell-derived nanoporous carbon@Fe3O4 composites for outstanding microwave absorption performance. J. Alloy Compd. 805, 1071–1080 (2019)
L.X. Wang, P.P. Zhou, Y. Guo, J. Zhang, X. Qiu, Y.K. Guan, M.X. Yu, H.L. Zhu, Q.T. Zhang, The effect of ZnCl2 activation on microwave absorbing performance in walnut shell-derived nano-porous carbon. RSC Adv. 9, 9718–9728 (2019)
Q. Huang, C. Bao, Q. Wang, C. Dong, H. Guan, Tuning the microwave absorption capacity of TiP2O7 by composited with biomass carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 515, 145974 (2020)
Funding
This work is financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant Nos. ZR2021ME019, ZR2019BB063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZJ contributed to conceptualization, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing. JH contributed to editing. MM contributed to supervision, writing—reviewing and Investigation. XH contributed to investigation. YM contributed to editing. AM contributed to conceptualization. FW contributed to conceptualization. JZ contributed to conceptualization. YL contributed to conceptualization, resources, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, Z., Hu, J., Ma, M. et al. Research progress of cellulose-derived carbon-based composites for microwave absorption. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 536 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09811-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09811-4