Abstract
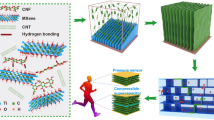
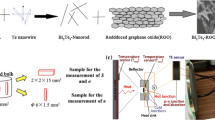
Boron Nitride Aerogels/PEDOT: PSS composite film with good thermoelectric properties were prepared by a simple preparation process. Boron nitride aerogels with a width of less than 1 μm and thickness of approximately 15 nm were prepared by a combination of freeze-drying and high-temperature tubular furnace heating. Then, boron nitride aerogels material was impregnated in a certain amount of 3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene monomer polymer: polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT: PSS) solution by ultrasonic vibration and magnetic stirring to produce a composite film. The output voltage of the flexible Boron Nitride Aerogels/PEDOT: PSS/Au piezoelectric sensor increases with an increase in the bending angle. When the bending angle is greater than 90°, the output voltage reaches 4.03 V. For the sake of broaden the application prospect of nanocomposite films, flexible wearable thermoelectric devices were prepared. Using the human body as a heat source, the output voltage of flexible thin-film thermoelectric devices can reach 233.6 mV. According to the formula calculation, the Seebeck coefficient is 18.54 mV/K and the thermoelectric power factor is 28.86 μW/mK2. With improvements in the energy collection capacity of wearable energy devices, we believe that more work will be done in the future to realize the coordinated development of functionality, comfort and health on the basis of improving energy conversion efficiency.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
T.M. Tritt, M.A. Subramanian, Thermoelectric materials, phenomena, and applications: a bird’s eye view. MRS Bull. 31, 188–198 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2006.44
W. Lei, D. Wang, G. Zhu, J. Li, F. Pan, Thermoelectric properties of conducting polyaniline/graphite composites. Mater. Lett. 65, 1086–1088 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.01.014
E.S. Toberer, A.F. May, G.J. Snyder, Zintl chemistry for designing high efficiency thermoelectric materials†‡. Chem. Mater. 22, 624–634 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm901956r
G.J. Snyder, E.S. Toberer, Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat. Mater. 7, 105–114 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2090
J. Li, Q. Tan, J.F. Li, D.W. Liu, F. Li, Z.Y. Li, M. Zou, K. Wang, BiSbTe-based nanocomposites with high ZT: the effect of SiC nanodispersion on thermoelectric properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 4317–4323 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201300146
Y. Li, G. Wang, M. Akbari-Saatlu, M. Procek, H.H. Radamson, Si and SiGe nanowire for micro-thermoelectric generator: a review of the current state of the art. Front. Mater. 8, 611078 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2021.611078
G.S. Hegde, A.N. Prabhu, Y.H. Gao, Y.K. Kuo, V.R. Reddy, Potential thermoelectric materials of indium and tellurium co-doped bismuth selenide single crystals grown by melt growth technique. J. Alloys Compd. 866, 158814 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158814
Z.N. Kayani, Z. Bashir, M. Mohsin, S. Riaz, S. Naseem, Sol-gel synthesized boron nitride (BN) thin films for antibacterial and magnetic applications. Optik 243, 167502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167502
J. Wang, Y. Wu, Y. Xue, D. Liu, X. Wang, X. Hu, Y. Bando, W. Lei, Super-compatible functional boron nitride nanosheets/polymer films with excellent mechanical properties and ultra-high thermal conductivity for thermal management. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 1363–1369 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tc04860b
R.Y. Tay, X. Wang, S.H. Tsang, G.C. Loh, R.S. Singh, H. Li, G. Mallick, E.H.T. Teo, A systematic study of the atmospheric pressure growth of large-area hexagonal crystalline boron nitride film. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 1650–1657 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tc32011a
K. Behera, M. Kumari, Y.H. Chang, F.C. Chiu, Chitosan/boron nitride nanobiocomposite films with improved properties for active food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 186, 135–144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.022
Y. Fang, I.S. Merenkov, X. Li, J. Xu, S. Lin, M.L. Kosinova, X. Wang, Vertically aligned 2D carbon doped boron nitride nanofilms for photoelectrochemical water oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 1–7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA04593D
T. Wang, D. Ou, H. Liu, S. Jiang, W. Huang, X. Fang, X. Chen, M. Lu, Thermally conductive boron nitride nanosheet composite paper as a flexible printed circuit board. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 1, 1705–1712 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b00160
T. Lan, W. Zhang, Y. Wang, S. Liu, C. Liu, L. Tong, X. Liu, Dielectric films with good dielectric breakdown strength based on poly (arylene ether nitrile) enhanced by nano boron nitride and graphene oxide via noncovalent interaction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 151, 109906 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109906
Z. Zhang, L. Weng, K. Guo, L. Guan, X. Wang, Z. Wu, Durable and highly sensitive flexible sensors for wearable electronic devices with PDMS-MXene/TPU composite films. Ceram. Int. 48, 4977–4985 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.11.035
Y. Li, K. Zhang, Q. Geng, M. Nie, Q. Wang, Z. Huang, Z. Wu, L. Pi, Helically intersected conductive network design for wearable electronic devices: from theory to application. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 13, 11480–11488 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c22086
M.S. Josephine, L. Lakshmanan, N. Resmi R, P. Visu, R. Ganesan, R. Jothikumar, Monitoring and sensing COVID-19 symptoms as a precaution using electronic wearable devices. IJPCC. 16, 341–350 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPCC-06-2020-0067
J.L. González, A. Rubio, F. Moll, Human powered piezoelectric batteries to supply power to wearable electronic devices. Int. J. Soc. Mater. Eng. Resour. 10, 34–40 (2002). https://doi.org/10.5188/ijsmer.10.34
F. Lin, Y. Qiu, X. Zhang, Z. Duanmu, Q. Lu, B. Huang, L. Tang, B. Lu, One-pot mechanochemical assembly of lignocellulose nanofiber/graphite nanocomposites for wearable electronic devices. Chem. Eng. J. 437, 135286 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135286
J. Dong, D. Gerlach, P. Koutsogiannis, P. Rudolf, G. Portale, Boosting the thermoelectric properties of PEDOT: PSS via low-impact deposition of tin oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Electron. Mater. 7, 2001284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.202001284
A. Hong-Ju, K. Seil, K. Kwang Ho, L. Joo-Yul, Preparation and characterization of thermoelectric PEDOT/Te nanorod array composite films. Materials 15, 148 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010148
T. Liu, Y.L. Li, J.Y. He, Y. Hu, C.M. Wang, K.S. Zhang, X.J. Huang, L.T. Kong, J.H. Liu, Porous boron nitride nanoribbons with large width as superior adsorbents for rapid removal of cadmium and copper ions from water. New. J. Chem. 43, 3280–3290 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ05299A
J. Xiangqian, B. Chuncheng, L. Ling, H. Jiandong, C. Zhao, L. Xinyu, C. Weiping, L. Xiaowei, Synthesis of high porosity and high adsorption performance BNNRs aerogels with long straight and their application for water cleaning. Diam. Relat. Mater. 120, 108649 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108649
J.R. Grandusky, R.V. Randive, T.C. Jordan, L.J. Schowalter, Fabrication of high performance UVC LEDs on aluminum-nitride semiconductor substrates and their potential application in point-of-use water disinfection systems, springer series in materials. Science 227, 171–192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24100-5-7
S. Nakamura, High-power InGaN-based blue laser diodes with a long lifetime. J. Cryst. Growth. 195, 242–247 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(98)00624-1
E. Ehsan-o-llah, A. Hojjat, R. Alimorad, N. Amideddin, M.S. Saeid, Preparation and thermal properties of oil-based nanofluid from multi-walled carbon nanotubes and engine oil as nano-lubricant. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 46, 142–147 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2013.05.003
L. Chang-Gun, H. Yu-Jin, C. Young-Min, L. Jae-Keun, C. Cheol, O. Je-Myung, A study on the tribological characteristics of graphite nano lubricants. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Man. 10, 85–90 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-009-0013-4
R. Harichandran, P. Paulraj, S. Maha Pon Raja, J. Kalyana Raman, Effect of h-BN solid nanolubricant on the performance of R134a-polyolester oil-based vapour compression refrigeration system. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 41, 140 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1645-7
D.H. Cho, J.S. Kim, S.H. Kwon, C. Lee, Y.Z. Lee, Evaluation of hexagonal boron nitride nano-sheets as a lubricant additive in water. Wear 302, 981–986 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2012.12.059
H. Jinkun, M. Xiaomei, F. Haiyan, S. Yao, G. Qian, C. Xuejiang, Z. Jianmei, Y. Yali, N. Jinfang, Z. Yun, Tyndall-effect-enhanced supersensitive naked-eye determination of mercury (II) ions with silver nanoparticles. Sensor. Actuat. B 344, 130218 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130218
T. Li, Z. Cui, J. Sun, C. Jiang, G. Li, Generation of bulk nanobubbles by self-developed venturi-type circulation hydrodynamic cavitation device. Langmuir 37, 12952–12960 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02010
S. Alok K, Y. Abhimanyu, I. Arindam, R. R. Bala, Superior performance of ultrathin metal organic framework nanosheets for antiwear and antifriction testing. Coll. Surf. A 613, 126100 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.126100
J. Wang, D. Liu, Q. Li, C. Chen, Z. Chen, P. Song, J. Hao, Y. Li, S. Fakhrhoseini, M. Naebe, X. Wang, W. Lei, Lightweight, superelastic yet thermoconductive boron nitride nanocomposite aerogel for thermal energy regulation. ACS Nano. 13, 7860–7870 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b02182
G. Swati, K. Vaibhav, White graphene based composite proton exchange membrane: improved durability and proton conductivity. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 43, 21683–21689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.05.051
Q. Weng, X. Wang, C. Zhi, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, Boron nitride porous microbelts for hydrogen storage. ACS Nano. 7, 1558–1565 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn305320v
K. Jasuja, K. Ayinde, C.L. Wilson, S.K. Behura, M.A. Ikenbbery, D. Moore, Introduction of protonated sites on exfoliated, large-area sheets of hexagonal boron nitride. ACS Nano. 12, 9931–9939 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b03651
Y. Li, Z. Li, J. Zhai, L. Zhao, J. Chen, F. Meng, Synthesis, microstructure and thermal stability of graphene nanoplatelets coated by hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). Mater. Chem. Phys. 221, 477–482 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.09.079
Y. Song, B. Li, S. Yang, G. Ding, C. Zhang, X. Xie, Ultralight boron nitride aerogels via template-assisted chemical vapor deposition. Sci. Rep. 5, 10337 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10337
J. Wang, Y. Xia, J. Fang, Z. Zhang, B. Xu, J. Wang, L. Ai, W. Song, K.N. Hui, X. Fan, Y. Li, Solution-processed transparent conducting electrodes for flexible organic solar cells with 16.61% efficiency. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 44 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00566-3
T. Liu, Y. Li, J. He, K. Zhang, Y. Hu, X. Chen, C. Wang, X. Huang, L. Kong, J. Liu, Few-layered boron nitride nanosheets as superior adsorbents for the rapid removal of lead ions from water. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 5366–5380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-03240-7
J. Pan, J. Wang, Boron nitride aerogels consisting of varied superstructures. Nanoscale Adv. 2, 149–155 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9na00702d
R.U. Heredia, K. Sachin, N. Sina, W. Julia, S. Sotoudeh, M. Zeynep, R. Rahim, Printed low-cost PEDOT:PSS/PVA polymer composite for radiation sterilization monitoring. ACS Sens. 7, 960–971 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.1c02105
M. Guzinski, J.M. Jarvis, F. Perez, B.D. Pendley, E. Lindner, R.D. Marco, G.A. Crespo, R.G. Acres, R. Walker, J. Bishop, PEDOT(PSS) as solid contact for ion-selective electrodes: the influence of the PEDOT(PSS) film thickness on the equilibration times. Anal. Chem. 89, 3508–3516 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04625
S.V. Selvaganesh, J. Mathiyarasu, K.L.N. Phani, V. Yegnaraman, Chemical synthesis of PEDOT-Au nanocomposite. Nanoscale. Res. Lett. 2, 546–549 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-007-9100-6
S. Harish, J. Mathiyarasu, K. Phani, V. Yegnaraman, Synthesis of conducting polymer supported Pd nanoparticles in aqueous medium and catalytic activity towards 4-nitrophenol reduction. Catal. Lett. 128, 197–202 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-008-9732-x
S. Sakamoto, M. Okumura, Z. Zhao, Y. Furukawa, Raman spectral changes of PEDOT–PSS in polymer light-emitting diodes upon operation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 412, 395–398 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2005.07.040
M. Stavytska-Barba, A.M. Kelley, Surface-enhanced Raman study of the interaction of PEDOT–PSS with plasmonically active nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 6822–6830 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp100135x
K.J. Moreno, I. Moggio, E. Arias, I. Llarena, S.E. Moya, R.F. Ziolo, H. Barrientos, Silver nanoparticles functionalized in situ with the conjugated polymer (PEDOT:PSS). J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 3987–3992 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2009.215
M. Deepa, A. Kharkwal, A.G. Joshi, A.K. Srivastava, Charge transport and electrochemical response of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxypyrrole) films improved by noble-metal nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 115, 7321–7331 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp201055y
M. Namboothiry, T. Zimmerman, F.M. Coldren, J. Liu, K. Kim, D.L. Carroll, Electrochromic properties of conducting polymer metal nanoparticles composites. Synth. Met. 157, 580–584 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2007.06.006
X.J. Lv, J.W. Sun, B. Hu, M. Ouyang, Z.Y. Fu, P.J. Wang, G.F. Bian, C. Zhang, Effective process to achieve enhanced electrochromic performances based on poly(4,4’,4″-tris[4-(2-bithienyl)pheny]amine)/ZnO nanorod composites. Nanotechnology 24, 265705 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/26/265705
Z. Lu, C. Qi, C. Li, G. Shi, Electrochemical fabrication of p-poly(3-methylthiophene)/n-silicon solar cells. Sol. Energy. Mater. Sol. Cells. 91, 1811–1815 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2007.06.010
L. Xu, J. Zhao, C. Cui, R. Liu, J. Liu, H. Wang, Electrosynthesis and characterization of an electrochromic material from poly(1,4-bis(2-thienyl)-benzene) and its application in electrochromic devices. Electrochim. Acta. 56, 2815–2822 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.12.062
J.S. Lee, Y.J. Choi, H.H. Park, J.C. Pyun, Electrochromic properties of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanocomposite film containing SiO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 122, 3080–3085 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34130
S. Xu, M. Hong, X.L. Shi, Y. Wang, L. Ge, Y. Bai, L. Wang, M. Dargusch, J. Zou, Z.G. Chen, High-performance PEDOT:PSS flexible thermoelectric materials and their devices by triple post-treatments. Chem. Mater. 31, 5238–5244 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b01500
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang province, China (No. YQ2021F012). National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62074046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing. WC: Conceptualization, Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Resources. LL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition. PG: Conceptualization, Validation, Resources. CB: Validation, Writing—original draft. JH: Validation, Formal analysis. NS: Methodology, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Chen, W., Li, L. et al. Thermoelectric properties of boron nitride aerogels/PEDOT: PSS composite films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 197 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09760-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09760-y