Abstract
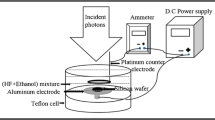
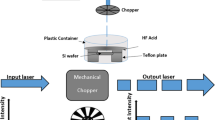
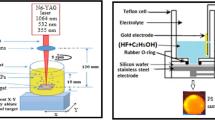
The present paper discusses the creation of mud-like porous silicon structures (mud PSi) with various sizes; formed by laser–assisted etching pathway in Hydroxide potassium KOH solution. The influence of different laser power density (LPD) (from 250 to 400mW/cm2) was studied for mud-like structure as PSi substrates formation through employing short wavelength 405 nm laser diode. Morphological and optical features of the mud PSi dimensions and plasmonics Ag nanoparticles, surface and morphology of the formed layer were examined via the analysis field of emission scanning electron microscopy images, photoluminescence spectra, and (XRD) outcomes. The results showed fine-regulated mud PSi layers later adjusting the laser power density under the same KOH concentration and etching period. The mud PSi dimensions and density of mud regions within the created layer at 350 mW/cm2 laser power density exposed unique properties; due to the maximal heat accumulation process within the layer and non-limited possibility of dissolution the individual muds due to the localized hydrothermal etching process. The muds were used to create and adjust the plasmonic aspects of Ag nanoparticles. The sizes distributions of hotspot junctions and plasmonic Ag nanoparticles dimensions and their unique surface areas and showed fine adjusting structures later controlling the LPD.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this paper are available upon request by contact with the contact corresponding author.
References
Z.H. Xiong, S. Yuan, Z.M. Jiang, J. Qin, C.W. Peil, S. Liao, X.M. Ding, X.Y. Hou, W. Xun, Photoluminescence studies of porous silicon microcavities. J. Lumin. 80, 137–140 (1998)
R.A. Ismail, K.S. Khashan, A.M. Alwan, Study of the effect of incorporation of CdS nanoparticles on the porous silicon photodetector. Silicon 9, 321–326 (2017)
A. Stephen, K. Hashmi, G.J. Hutchings, Gold catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 7896–7936 (2006)
Y. Abdi, J. Derakhshandeh, P. Hashemi, S. Mohajerzadeh, F. Karbassian et al., Light-emitting nano-porous silicon structures fabricated using a plasma hydrogenation technique. Mater. Sci. Engi. B 124, 483–487 (2005)
M.A. Alwan, F.J. Muslim, A.C. Aseel, Controllable synthetization of Au nanoparticles by laser enhanced wet KOH etching process. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1963, 012009 (2021)
X. Guo, S. Xu, L. Zhao, W. Lu, F. Zhang, D.G. Evans et al., One-step hydrothermal crystallization of a layered double hydroxide/alumina bilayer film on aluminum and its corrosion resist lance properties. Langmuir 25(17), 9894–7 (2009)
J. Wang, D. Li, Q. Liu, X. Yin, Y. Zhang, X. Jing et al., Fabrication of hydrophobic surface with hierarchical structure on Mg alloy and its corrosion resistance. Electrochim. Acta. 55(22), 6897–6906 (2010)
L. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Lei, J. He, R. Lv, N. Li et al., A facile approach to fabricate super hydropho bie Zn surface and its effect on corrosion resistance. Corros. Sci. 85, 174–182 (2014)
J. Ou, W. Hu, M. Xue, F. Wang, W. Li, Super hydrophobic surfaces on light alloy substrates fabricated by a versatile process and their corrosion protection. ACS App.l Mater. Interfaces 5(8), 3101–3107 (2013)
R. Gao, Q. Liu, J. Wang, X. Zhang, W. Yang, J. Liu et al., Fabrication of fibrous szaibelyite with hierarchical structure super hydrophobic coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy for corrosion protection. Chem. Eng. J. 241, 352–359 (2014)
Y. Fan, Z. Chen, J. Liang, Y. Wang, H. Chen, Preparation of superhydrophobic films on copper substrate for corrosion protection. Surf. Coat. Technol. 244, 1–8 (2014)
Z. Wang, J. Gong, J. Ma, J. Xu, In situ growth of hierarchical bochmite on 2024 aluminum alloy surface as superhydrophobic materials. RSC Adv. 4(28), 143–214 (2014)
A.S. Ruqaya, S.M. Mohammed, Illumination effects on the physical properties of porous silicon prepared by PECE. Appl. Nanosci. 8, 1279 (2018)
R.B. Rashid, A.M. Alwan, A.B. Dheyab, Morphological and electrical properties of gold nanoparticles/macroPorous silicon for CO2 gas. Iraqi J. Sci. 59(1A), 57–66 (2018)
L.A. Wali, K.K. Hasan, A.M. Alwan, An investigation of efficient detection of ultra-low concentration of penicillins in milk using AuNPs/PSi hybrid structure. Plasmonics 15(4), 985–993 (2020)
A.M. Alwan, R.B. Rashid, A.B. Dheyab, Morphological and electrical properties of gold nanoparticles/macroporous silicon for CO2. Iraqi J. Sci. (IJS) (2018). https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2018.59.1A.8
A.A. Jabbar, A.M. Alwan, M.Q. Zayer, A.J. Bohan, Efficient single cell monitoring of pathogenic bacteria using bimetallic nanostructures embedded in gradient porous silicon. Mater. Chem. Phys. 241, 122359 (2020)
A.M. Alwan, Calculation of energy band gap of porous silicon based on the carrier transport mechanisms. Eng. & Tech. 25, 1143–1148 (2007)
M.S. Detlef, Scherrer grain-size analysis adapted to grazingincidence scattering with area detectors. J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 1030–1034 (2009)
A.H. Duaa, M.A. Alwan, F.J. Muslim, An investigation of structural properties of monometallic (Ag, Pd) and bimetallic (Ag@ Pd) nanoparticles growth on macro porous silicon. Int. J. Nanoelectron. & Mater. 11, 461–472 (2018)
C. Zhai, Y. Li, Y. Peng, T. Xu, Detection of chlorpyrifos in apples using gold nanoparticles based on surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Int. J. Agric. & Biol. Eng. 8, 113–120 (2015)
Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, H. Wang, B. Ye, Detection of pesticides on navel orange skin by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with Ag nanostructures. Int. J. Agric. & Biol. Eng. 9(2), 179–185 (2016)
A. Virga, P. Rivolo, E. Descrovi, A. Chiolerio, G. Digregorio, F. Frascella, SERS active Ag nanoparticles in mesoporous silicon: detection of organic molecules and peptide–antibody assays. J. Raman Spectrosc. 43, 730–736 (2012)
S. Devarajan, B. Vimalan, S. Sampath, Phase transfer of Au–Ag alloy nanoparticles from aqueousmedium to an organic solvent: effect of aging of surfactant on the formation of Ag-rich alloy compositions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 278, 126–132 (2004)
M.A. Alwan, A.B. Dheyab, A.J. Allaa, Study of the influence of incorporation of gold nanoparticles on the modified porous silicon sensor for petroleum gas detection. Engi. Technol. J. 8, 811–815 (2017)
Z. Irena, R. Krzysztof, K. Małgorzata, The effect of isopropyl alcohol concentration on the etching process of Si-substrates in KOH solutions. Sens. Actuators A 171, 436–445 (2011)
M.A. Gosalvez, Y. Xing, K. Sato, Analytical solution of the continuous cellular automaton for anisotropic etching. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 17, 410–431 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Department of Applied Sciences/University of Technology and Razi metallurgical research center, Iran, for using the SEM(MIRA3 TESCAN) and the EDS analyses.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
We, the authors, all participated in the implementation of the experiments, the management of the data, and the preparation of the report for this research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shlaga, R.A., Alwan, A.M. & Mohammed, M.S. The role of laser irradiation in the modulation of an efficient mud-like structure as PSi layer for nanophotonic sensors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 208 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09579-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09579-7