Abstract
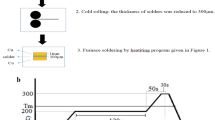
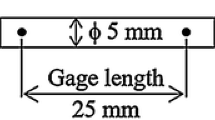
Nowadays, the development and improvement of physical and mechanical properties of lead-free solders have become a topic of interest for researchers, because the use of lead-containing solders has been banned. In this paper, Sn-5 wt% Sb-0.7 wt% Cu (SSC507) solder is microalloyed by germanium. Alloys were prepared by vacuum induction melting, and their thickness was reduced by rolling to 1 mm and then 300 μm, respectively. Then the physical properties (i.e., microstructure, wetting and thermal behavior) and the mechanical properties (i.e., microhardness, tensile and fractography) of the alloys were investigated. The results indicated that the addition of germanium to the base solder composition resulted in fine-graining and uniform distribution of intermetallic phases in the structure. Germanium additive significantly improved wettability properties by reducing the surface tension of the alloys. The addition of germanium has increased the microhardness of the alloys and, by modifying the microstructure, has improved the yield strength and the ultimate tensile strength of the alloys.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
H.B. Lee, Y.W. Kim, S.H. Kim, S.H. Park, J.P. Choi, C. Aranas, A modular solder system with hierarchical morphology and backward compatibility. Small 14(33), 1–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201801349
P. Svec, D. Janiˇ, Interface between Sn–Sb–Cu solder and copper substrate. Mater. Sci. Eng. 528, 5955–5960 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.04.008
A.R. Geranmayeh, Power law indentation creep of Sn-5 % Sb. J. Mater. Sci. 40, 3361–3366 (2005)
S. Chen, A. Zi, W. Gierlotka, C. Yang, C. wang, S. Lin, C. Hsu, Phase equilibria of Sn–Sb–Cu system. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132(2–3), 703–715 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.11.088
A.A. El-Daly, Y. Swilem, A.E. Hammad, Creep properties of Sn–Sb based lead-free solder alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 471, 98–104 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.03.097
K. Suganuma, S. Kim, K. Kim, High-temperature lead-free solders: properties and possibilities. JOM 61, 64 (2009)
M. Dias, T.A. Costa, B.L. Silva, J.E. Spinelli, N. Cheung, Microelectronics reliability a comparative analysis of microstructural features, tensile properties and wettability of hypoperitectic and peritectic Sn-Sb solder alloys. Microelectron. Reliab. 81, 150–158 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2017.12.029
D. Zhou, A.S.M.A. Haseeb, A. Andriyana, Mechanical performance of advanced multicomponent lead-free solder alloy under thermal aging. Mater. Today Commun. 33, 104430 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104430
C. Zhang, S. Liu, G. Qian, J. Zhou, F. Xue, Effect of Sb content on properties of Sn—Bi solders effect of Sb content on properties of Sn—Bi solders. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63046-6
P. Sungkhaphaitoon, T. Plookphol, The effects of antimony addition on the microstructural, mechanical, and thermal properties of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 49(2), 652–660 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4439-5
E.A. Eid, E. El-Khawas, A.S. Abd-Elrahman, Impact of Sb additives on solidification performance, microstructure enhancement and tensile characteristics of Sn-6.5Zn-0.3Cu Pb-free solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(7), 6507–6518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00956-3
Y. Yuan, X. Chen, Z. Zhou, Y. Li, B. Xu, D. Lio, B. Yang, Theoretical study on Sn–Sb-based lead-free solder by ab initio molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mater. Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.137
S.H. Kim, S. Yeon, J. Kim, J. Lee, S. Park, J. Choi, C. Aranas, Y. Son, Fine microstructured In-Sn-Bi solder for adhesion on a flexible PET substrate: its effect on superplasticity and toughness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(18), 17090–17099 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b04159
R. Xu, Y. Liu, F. Sun, Effect of isothermal aging on the microstructure, shear behavior and hardness of the Sn58Bi/Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Cu solder joints. Results Phys. 15, 102701 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102701
S. Tikale, K.N. Prabhu, Performance and reliability of Al2O3 nanoparticles doped multicomponent Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-Ni-Ge solder alloy. Microelectron. Reliab. 113(September), 113933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2020.113933
L. Yang, S. Ma, G. Mu, Improvements of microstructure and hardness of lead-free solders doped with Mo nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 304, 130654 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130654
M. Sarkar, F. Gulshan, A.R.M.H. Rashid, M. Hasanuzzaman, A review of TiO2-nanoparticle reinforced lead-free solder composites used in electronic components soldering, in Reference module in materials science and materials engineering. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2022)
E.A. Eid, A.M. Deghady, A.N. Fouda, Materials science & engineering A enhanced microstructural, thermal and tensile characteristics of heat treated Sn-5.0Sb-0.3Cu (SSC-503) Pb-free solder alloy under high pressure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 743(August 2018), 726–732 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.137
X. Zhang, Effects of germanium on the microstructural, mechanical and thermal properties of Sn-0.7Cu solder alloy. Mater. Res. Express. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aae95d
M. Hasnine, N. Vahora, Microstructural and mechanical behavior of SnCu–Ge solder alloy subjected to high temperature storage. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(11), 8904–8913 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8908-4
P. Sebo, P. Svec, D. Janickovic, E. Illekova, Influence of Sb and Cu in Sn-Sb-Cu alloys on wetting of Cu and Cu-solder-Cu joint strength. Kovov. Mater. 48(1), 353 (2010)
K. Kanlayasiri, R. Kongchayasukawat, Property alterations of Sn-0.6Cu-0.05Ni-Ge lead-free solder by Ag, Bi, In and Sb addition. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(6), 1166–1175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64754-5
S.-W. Chen, C.-C. Chen, W. Gierlotka, A.-R. Zi, P.-Y. Chen, H.-J. Wu, Phase equilibria of the Sn-Sb binary system. J. Electron. Mater. 37(7), 992–1002 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-008-0464-x
S. Chen, A. Zi, P. Chen, H. Wu, Y. Chen, C. Wang, Interfacial reactions in the Sn–Sb/Ag and Sn–Sb/Cu couples. Mater. Chem. Phys. 111(1), 17–19 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.04.018
Y.-T. Chen, C.-C. Chen, Interfacial reactions in Sn–Sb/Ni couples. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 43(2), 295–300 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2011.08.003
T. Kobayashi, K. Kobayashi, K. Mitsui, I. Shohji, Comparison of Sn-5Sb and Sn-10Sb alloys in tensile and fatigue properties using miniature size specimens. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 1 (2018)
K. Kobayashi, I. Shohji, S. Koyama, H. Hokazono, Fracture behaviors of miniature size specimens of Sn-5Sb lead-free solder under tensile and fatigue conditions. Procedia Eng. 184, 238–245 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.04.091
K. Kobayashi, I. Shohji, H. Hokazono, Tensile and fatigue properties of miniature size specimens of Sn-5Sb lead-free solder. Thermec 879, 2377–2382 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.879.2377
M. Hasnine, B. Tolla, M. Karasawa, Effect of Ge addition on wettability, copper dissolution, microstructural and mechanical behavior of SnCu–Ge solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(21), 16106–16119 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7511-4
K. Habu, N. Takeda, H. Watanabe, H. Ooki, J.Abe, T.Saito, Y. Tanigochi, K. Takayama, “Development of Lead-free solder Alloys of the Ge doped Sn-Ag-Bi system,” pp. 606–609, 1999.
X. Zhang, X. Hu, X. Jiang, Y. Li, Effects of germanium on the microstructural, mechanical and thermal properties of Sn-0.7Cu solder alloy. Mater. Res. Express (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aae95d
S. Liu, L. Ma, C. Zhen, Y. Wang, D. Li, F. Guo, Microstructural evolution of intermetallic compounds between crystalline/amorphous Cobalt-Phosphorous coatings and lead-free solders. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 19, 2916–2929 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.06.035
S.H.A. Jaffery, M. Sabri, S. Rozali, S. Hasan, M. Mahdavifard, D.A. Al-Zubiady, B.R. Ravuri, Oxidation and wetting characteristics of lead-free Sn-0.7Cu solder alloys with the addition of Fe and Bi. Microelectron. Reliab. 139, 114802 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2022.114802
S. Tikale, K.N. Prabhu, Performance and reliability of Al2O3 nanoparticles doped multicomponent Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-Ni-Ge solder alloy. Microelectron. Reliab. 113, 113933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2020.113933
M. Hasnine, B. Tolla, M. Karasawa, Effect of Ge addition on wettability, copper dissolution, microstructural and mechanical behavior of SnCu–Ge solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7511-4
G.E. Dieter, D.J. Bacon, D. Bacon, Mechanical metallurgy (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988)
A. El-Daly, A.Z. Mohamad, A. Fawzy, A. El-Taher, Creep behavior of near-peritectic Sn–5Sb solders containing small amount of Ag and Cu. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 1055–1062 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.11.001
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by HP and HN-M. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HP and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pooshgan, H., Naffakh-Moosavy, H. The effect of Ge on the microstructure, thermal behavior, and mechanical properties of lead-free Sn-5Sb-0.7Cu solder alloy. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09496-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09496-9