Abstract
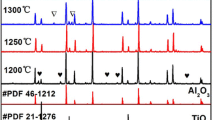
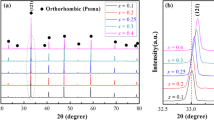
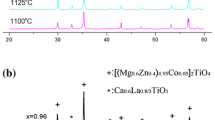
0.8Mg2SiO4–0.2Ca0.9Sm0.2/3Al4x/3Ti1−xO3 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, and 0.25) ceramics with zero τf and high Q × f value were prepared by a traditional solid-state reaction method. The influences of Al content on phase evolution, sintering behavior, microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of ceramics have been systematically investigated. With the increase of x, the exchange of Ti4+ and Al3+ at B site leads to the decrease of dielectric constant and the increase of quality factor Q × f. The τf increases first and then decreases to close to 0 with a rise of x from 0.05 to 0.025. The results show that 0.8Mg2SiO4–0.2Ca0.9Sm0.2/3Al0.8/3Ti0.8O3 samples sintered at 1410 °C for 3 h exhibited excellent microwave dielectric properties: εr = 10.69, Q × f = 70,769 GHz, τf = − 0.66 ppm/°C. Therefore 0.8Mg2SiO4–0.2Ca0.9Sm0.2/3Al4x/3Ti1−xO3 ceramics are considered as potential candidates for microwave dielectric applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon resonable request.
References
M.K. Du, L.G. Li, L.Z. Ni et al., Ultra-high Q Ba (Mg1/3Ta0.675)O3 microwave dielectric ceramics realized by slowly cooling step process and the simulation design for hairpin dielectric filters. Ceram. Int. 47(14), 19716–19726 (2021)
W.C. Lou, M.M. Mao, K.X. Song et al., Low dielectric constant cordierite-based microwave dielectric ceramics for 5G/6G telecommunications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42(6), 2820–2826 (2022)
M.T. Ma, K.X. Song, Y.P. Ji et al., 5G microstrip patch antenna and microwave dielectric properties of cold sintered LiWVO6-K2MoO4 composite ceramics[J]. Ceram. Int. 47(13), 19241–19246 (2021)
W.C. Lou, K.X. Song, F. Hussain et al., Microwave dielectric properties of Mg1.8R0.2Al4Si5O18 (R = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) cordierite ceramics and their application for 5G microstrip patch antenna. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42(5), 2254–2260 (2022)
Y.M. Lai, X.L. Tang, X. Huang et al., Phase composition, crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of Mg2 – xCuxSiO4 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(4), 1508–1516 (2021)
W. Wei, L. Tang, W. Bai et al., Microwave dielectric properties of (1-x)(Mg0.4Zn0.6)2SiO4-xCaTiO3 composite ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(8), 3601–3607 (2014)
Z. Liang, X.N. Liang, G. Wang et al., Microwave dielectric properties and sintering behaviors of Zn1.8SiO3.8 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(1), 1–7 (2021)
G. Dou, D.X. Zhou, M. Guo et al., Low-temperature sintered Mg2SiO4–CaTiO3 ceramics with near-zero temperature coefficient of resonant frequency. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 1431–1438 (2013)
K.H. Yoon, W.S. Kim, E.S. Kim, Dependence of the octahedral bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of Ca1–xSm4x/3TiO3 ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 99(1–3), 112–115 (2003)
M.S. Fu, L. Ni, X.M. Chen, Abnormal variation of microwave dielectric properties in A/B site co-substituted (Ca1 – 0.3xLa0.2x)(Mg1/3Ta2/3)1–xTixO3 complex perovskite ceramic. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33(4), 813–823 (2013)
J. Qu, F. Liu, C. Yuan et al., Microwave dielectric properties of 0.2SrTiO3-0.8Ca0.61Nd0.26Ti1–xAl4x/3O3 ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 191, 15–20 (2015)
Q.Q. Feng, P.Z. Fu et al., Microwave dielectric properties of low-fired (1 – x)Mg2SiO4 –xCa0.9Sr0.1TiO3 ceramics by using nanopowders from high energy ball milling. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 5398–15404 (2017)
]S. He, K.G. Wang, X.J. Zhou, Phase structure and microwave dielectric properties of 0.85(0.74CaTiO3-0.26SmAlO3)-0.15Ca1.15Sm0.85Al 0.85Ti0.15O4 composite ceramics prepared by reaction-sintering process. Ceram. Int. 47(11), 15580–15584 (2021)
A. Zhang, H.Q. Fan, D.W. Hou et al., A novel low-loss (1-x)(Ca0.8Sr0.2)TiO3-xSmAlO3 microwave dielectric ceramics with near-zero temperature coefficient. J. Alloys Compd. 898, 1–8 (2021)
Y.F. Liu, Y.H. Tan, S.G. Liu et al., Dielectric properties, microstructure and phase evolution of non-stoichiometric 0.9Mg2 + xSiO4 + x-0.1CaTiO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Ceram. Int. 47(23), 33798–33804 (2021)
M. Ando, H. Ohsato, I. Kagomiya et al., Quality factor of forsterite for ultrahigh frequency dielectrics depending on synthesis proces. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 47(9), 7729–7731 (2008)
B.J. Li, S.Y. Wang, Y.H. Liao et al., Low loss dielectric material system of (1 x)(Mg0.95Co0.05)2(Ti0.95Sn0.05)O4 – x(Ca0.8Sm0.4/3)TiO3 at microwave frequency with a near-zero temperature coefficient of the resonant frequency. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn 124(3), 208–212 (2016)
H. Chen, Phase evolution and microwave dielectric properties of Ca0.61Nd0.26Ti1–x(Al1/2Nb1/2)xO3 ceramics (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.2). Ceram. Silik. 61(1), 1–5 (2016)
V. Sivasubramanian, V.R.K. Murthy, B. Viswanathan, Microwave dielectric properties of certain simple alkaline earth perovskite compounds as a function of tolerance factor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 36(1), 194–197 (1997)
E.S. Kim, C.J. Jeon, J.S. Kim et al., Effects of crystal structure on microwave dielectric properties of ceramics. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 45, 251–255 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Program for Jiaxing Leading Innovative and Enterpreneurial Teams.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CT contributed to the experimentation, data analysis, collation, and manuscript preparation. YL contributed to the methodology, software, and theorization. XY contributed to the investigation and experimentation. SL and JT contributed to the theorization. WG contributed to the validation. FM contributed to writing, reviewing, and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, C., Liu, Y., Yan, X. et al. Phase composition, crystal structure, and microwave dielectric properties of 0.8Mg2SiO4–0.2Ca0.9Sm0.2/3Al4x/3Ti1−xO3 ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 22119–22126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08981-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08981-5