Abstract
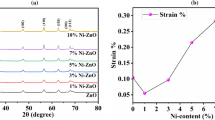
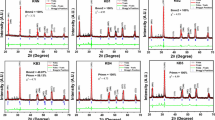
0.90Al2O3–0.10TiO2 doped with x mol% ZnO (x = 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5) microwave dielectric ceramics, have been prepared by the conventional solid-state method with various sintering temperatures. A relationship between phase composition and microwave dielectric properties was systematically discussed for millimeter-wave applications. The formation of Al2TiO5 impurity phase was inhibited by ZnO addition without annealing treatment. The existence of Al2TiO5 impurity phase deteriorated seriously the microwave dielectric properties, especially quality factor (Q × f) and temperature coefficient (τ f ). Due to the liquid sintering effect, the addition of ZnO could reduce the sintering temperature to 1300 °C. To a large extend, ZnO additive improved the density of 0.90 Al2O3–0.10 TiO2 ceramics, and ultimately enhanced the microwave dielectric properties. The ZnAl2O4 impurity phase could also enhance the Q × f value and permittivity (ε r ) of 0.90Al2O3–0.10TiO2 ceramics. Excellent microwave dielectric properties was achieved for 0.4 mol% ZnO doped 0.90Al2O3–0.10TiO2 ceramics sintered at 1300 °C for 4 h: ε r = 12.4, Q × f = 159,000 GHz, τ f = −0.2 ppm/°C.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.J. Cava, J. Mater. Chem. 11(1), 54 (2001)
M.T. Sebastian, Dielectric Materials for Wireless Communication, 1st edn. (Elsevier Science, San Diego, 2008), pp. 16–24
W. Wersing, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1(5), 715 (1996)
Z.F. Wang, B.Y. Huang, L.X. Wang, Z.X. Fu, Q.T. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci-Mater. Electron. 26(6), 4273 (2015)
B.Y. Huang, Z.F. Wang, T. Chen, L.X. Wang, Z.X. Fu, Q.T. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci-Mater. Electron. 26(5), 3375 (2015)
H. Ohsato, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 113(1323), 703 (2005)
M. Kono, H. Takagi, T. Tatekawa, H. Tamura, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26(10), 1909 (2006)
N.M. Alford, S.J. Penn, J. Appl. Phys. 80(10), 5895 (1996)
S.B. Narang, S. Bahel, J. Ceram. Process. Res. 11(3), 316 (2010)
C.L. Huang, J.J. Wang, C.Y. Huang, Mater. Lett. 59(28), 3746 (2005)
D.X. Zhou, R.G. Sun, S.P. Gong, Y.X. Hu, Ceram. Int. 37(7), 2377 (2011)
J. Dhanya, A.N. Unnimaya, R. Ratheesh, J. Mater. Sci-Mater. Electron. 25(10), 4617 (2014)
K.X. Song, S.Y. Wu, X.M. Chen, Mater. Lett. 61(16), 3357 (2007)
G. Ramesh et al., Optoelectron. Adv. Mat. 7(11–12), 965 (2013)
W.C. Tzou et al., Mater. Res. Bull. 38(6), 981 (2003)
C.F. Yang et al., Mater. Lett. 57(19), 2945 (2003)
Z. Qilong, Y. Hui, W. Huanping, J Zhejiang Univ Eng Sci. 40(8), 1450 (2006)
H. Erkalfa, Z. Misirli, T. Baykara, Ceram. Int. 24(2), 81 (1998)
D.W. Kim, B. Park, J.H. Chung, K. Sun. Hong, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 39(5R), 2696 (2000)
C.L. Huang, J.J. Wang, C.Y. Huang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90(5), 1487 (2007)
J. Molla, R. Heidinger, A. Ibarra, J. Nucl. Mater. 212, 1029 (1994)
Y. Ohishi, Y. Miyauchi, H. Ohsato, K. Kakimoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43(6A), L749 (2004)
B. Hakki, P. Coleman, IRE Trans. MTT. 8(4), 402 (1960)
W.E. Courtney, IEEE Trans. MTT. 18(8), 476 (1970)
E.M. Levin, H.F. McMurdie, Phase Diagrams for Ceramists, 1975 Supplement, 2nd edn. (American Ceramic Society, New York, 1975), p. 135
K.P. Surendran, N. Santha, P. Mohanan, M.T. Sebastian, Eur. Phys. J. B 41(3), 301 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), the Opening Project of State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure (Project No. SKL201309SIC), as well as Science and Technology Projects of Guangdong Province (Project No. 2011A091103002). College Industrialization Project of Jiangsu Province (JHB2012-12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Huang, B., Chen, T. et al. Effects of ZnO additive on crystalline phase and microwave dielectric properties of 0.90Al2O3–0.10TiO2 ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 2687–2692 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-4078-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-4078-9