Abstract
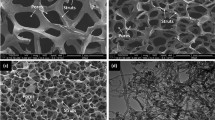
The combined effect of MWCNTs (multi-walled carbon nanotubes) and ENIAg (Electroless Nickel Immersion Silver) surface finish on the formation of interfacial microstructure and shear strength of the Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu (SAC105) solder was investigated in this study. Plain and composite solders (SAC-xCNT; x = 0, 0.01, 0.05 and 0.1 wt%) were successfully synthesized through the powder metallurgy route and afterwards soldered on the ENIAg surface finish and plain Cu substrates. Detailed analysis of the microstructure revealed the formation of the Cu6Sn5 IMC at the SAC solder/Cu substrate interface of the SAC-xCNT/Cu solder interconnects. Whereas, the Ni3Sn4 IMC and (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 IMC appeared at the SAC solder/ENIAg substrate interface of the SAC-xCNT/ENIAg. The MWCNTs-reinforced SAC composite solder interconnects exhibited thinner interfacial IMC layer thicknesses relative to the plain counterparts for both substrates used. Given the prospects of the ENIAg as a reliable surface finish material, the SAC-xCNT/ENIAg exhibited IMC thickness values within the range of 2.98–2.65 µm as compared to the 5.23–3.61 µm demonstrated by the SAC-xCNT/Cu. Overall, the strengthening capacity of the MWCNTs was well-defined in both sample grades, with the SAC-0.05CNT/Cu and SAC-0.05CNT/ENIAg exhibiting the highest shear strength values of 10.23 MPa and 11.14 MPa, respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
T.L. Yang, J.Y. Wu, C.C. Li, S. Yang, C.R. Kao, Low temperature bonding for high temperature applications by using SnBi solders. J. Alloy. Compd. 647, 681–685 (2015)
H.W. Yang, J.Y. Wu, Z.X. Zhu, C.R. Kao, Effects of surface diffusion and reaction-induced volume shrinkage on morphological evolutions of micro joints. Mater. Chem. Phys. 191, 13–19 (2017)
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Hanim, M. Norkhairunnisa, M.T. Suraya, H.M. Yusoff, Influence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on melting temperature and microstructural evolution of Pb-free Sn-5Sb/Cu solder joint. IOP Conf. Series Mater. Sci. Eng. 238(1), 012010 (2017)
C.K. Chung, Y.J. Chen, C.C. Li, C.R. Kao, The critical oxide thickness for Pb-free reflow soldering on Cu substrate. Thin Solid Films 520(16), 5346–5352 (2012)
S. He, R. Gao, Y.A. Shen, J. Li, H. Nishikawa, Wettability, interfacial reactions, and impact strength of Sn–3.0 Ag–0.5 Cu solder/ENIG substrate used for fluxless soldering under formic acid atmosphere. J Mater. Sci. 55(7), 3107–3117 (2020)
E. Wernicki, Z. Gu, Effect of Sn nanoparticle additions on thermal properties of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder paste. Thermochim. Acta 690, 178642 (2020)
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Hanim, O.J. Ojo-Kupoluyi, R. Calin, Impact of different isothermal aging conditions on the IMC layer growth and shear strength of MWCNT-reinforced Sn–5Sb solder composites on Cu substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 808, 151714 (2019)
W. Liu, D.P. Sekulic, Capillary driven molten metal flow over topographically complex substrates. Langmuir 27(11), 6720–6730 (2011)
Z. Gyökér, G. Gergely, D.K. Horváth, E. Bodnár, Z. Gácsi, Role of reinforcement surface treatment on the SnAg3Cu0. 5 microelectronic joints. Appl. Surf. Sci. 475, 982–985 (2019)
Y. Tang, S.M. Luo, K.Q. Wang, G.Y. Li, Effect of Nano-TiO2 particles on growth of interfacial Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn layers in Sn3.0Ag0. 5CuxTiO2 solder joints. J. Alloy. Compd. 684, 299–309 (2016)
J. Shen, Y.C. Chan, Research advances in nano-composite solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 49(3), 223–234 (2009)
V.M.F. Marques, C. Johnston, P.S. Grant, Microstructural evolution at Cu/Sn–Ag–Cu/Cu and Cu/Sn–Ag–Cu/Ni–Au ball grid array interfaces during thermal ageing. J. Alloy. Compd. 613, 387–394 (2014)
A.T. Tan, A.W. Tan, F. Yusof, Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu/SAC305/Cu solder joints under the influence of low ultrasonic power. J. Alloy. Compd. 705, 188–197 (2017)
Q.B. Tao, L. Benabou, T.N. Van, H. Nguyen-Xuan, Isothermal aging and shear creep behavior of a novel lead-free solder joint with small additions of Bi, Sb and Ni. J. Alloy. Compd. 789, 183–192 (2019)
Frear, D. R. (2006). Issues related to the implementation of Pb-free electronic solders in consumer electronics. In Lead-Free Electronic Solders (pp. 319–330). Springer, Boston, MA.
H.Y. Jing, H.J. Guo, L.X. Wang, J. Wei, L.Y. Xu, Y.D. Han, Influence of Ag-modified graphene nanosheets addition into Sn–Ag–Cu solders on the formation and growth of intermetallic compound layers. J. Alloy. Compd. 702, 669–678 (2017)
A.K. Gain, Y.C. Chan, The influence of a small amount of Al and Ni nano-particles on the microstructure, kinetics and hardness of Sn–Ag–Cu solder on OSP-Cu pads. Intermetallics 29, 48–55 (2012)
L.C. Tsao, S.Y. Chang, C.I. Lee, W.H. Sun, C.H. Huang, Effects of nano-Al2O3 additions on microstructure development and hardness of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu solder. Mater. Design 31(10), 4831–4835 (2010)
Y. Tang, G.Y. Li, Y.C. Pan, Effects of TiO2 nanoparticles addition on microstructure, microhardness and tensile properties of Sn–3.0 Ag–0.5 Cu–xTiO2 composite solder. Mater. Des. 55, 574–582 (2014)
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Hanim, R. Calin, R.A. Ilyas, Microstructure evolution and hardness of MWCNT-reinforced Sn-5Sb/Cu composite solder joints under different thermal aging conditions. Microelectron Reliab 110, 113681 (2020)
A.K. Gain, Y.C. Chan, Growth mechanism of intermetallic compounds and damping properties of Sn–Ag–Cu-1 wt% nano-ZrO2 composite solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(5), 945–955 (2014)
A. Aqel, K.M.M.A. El-Nour, R.A.A. Ammar, A. Al-Warthan, Carbon nanotubes, science and technology part (I) structure, synthesis and characterisation. Arab. J. Chem. 5(1), 1–23 (2012)
L. Xu, L. Wang, H. Jing, X. Liu, J. Wei, Y. Han, Effects of graphene nanosheets on interfacial reaction of Sn–Ag–Cu solder joints. J. Alloy. Compd. 650, 475–481 (2015)
X. Hu, Y.C. Chan, K. Zhang, K.C. Yung, Effect of graphene doping on microstructural and mechanical properties of Sn–8Zn–3Bi solder joints together with electromigration analysis. J. Alloy. Compd. 580, 162–171 (2013)
D. Ma, P. Wu, Effects of coupled stressing and solid-state aging on the mechanical properties of graphene nanosheets reinforced Sn–58Bi–0.7 Zn solder joint. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 651, 499–506 (2016)
J.W. Yoon, S.B. Jung, Effect of surface finish on interfacial reactions of Cu/Sn–Ag–Cu/Cu (ENIG) sandwich solder joints. J. Alloy. Compd. 448(1–2), 177–184 (2008)
Ourdjini, A., Hanim, M. A., Koh, S. J., Aisha, I. S., Tan, K. S., & Chin, Y. T. (2006, November). Effect of solder volume on interfacial reactions between eutectic Sn-Pb and Sn-Ag-Cu solders and Ni (P)-Au surface finish. In 2006 Thirty-First IEEE/CPMT International Electronics Manufacturing Technology Symposium (pp. 437–442). IEEE.
D.J. Lee, H.S. Lee, Major factors to the solder joint strength of ENIG layer in FC BGA package. Microelectron. Reliab. 46(7), 1119–1127 (2006)
Lentz, T., & Assembly, F. C. T. (2018). How does Surface Finish affect solder paste performance. In Proceedings of SMTA International.
M.A. Hanim, N.M. Kamil, C.K. Wei, T.T. Dele-Afolabi, O.S. Azlina, Microstructural and shear strength properties of RHA-reinforced Sn–0.7 Cu composite solder joints on bare Cu and ENIAg surface finish. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(11), 8316–8328 (2020)
S.F.M. Amli, M.A.A.M. Salleh, R.M. Said, N.R.A. Razak, J.A. Wahab, M.I.I. Ramli, Effect of surface finish on the wettability and electrical resistivity of Sn-3.0 Ag-0.5 Cu solder. IOP Conf. Series Mater. Sci. Eng. 701(1), 012029 (2019)
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Hanim, M. Norkhairunnisa, H.M. Yusoff, M.T. Suraya, Investigating the effect of isothermal aging on the morphology and shear strength of Sn-5Sb solder reinforced with carbon nanotubes. J. Alloy. Compd. 649, 368–374 (2015)
Q.V. Bui, S.B. Jung, Effect of Pd thickness on wettability and interfacial reaction of Sn-10 Ag-Ce solders on ENEPIG surface finish. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25(1), 423–430 (2014)
A.S. Zuruzi, C.H. Chiu, S.K. Lahiri, K.N. Tu, Roughness evolution of Cu 6 Sn 5 intermetallic during soldering. J. Appl. Phys. 86(9), 4916–4921 (1999)
Y.Y. Chen, J.G. Duh, B.S. Chiou, The effect of substrate surface roughness on the wettability of Sn-Bi solders. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 11(4), 279–283 (2000)
K. Maslinda, A.S. Anasyida, M.S. Nurulakmal, Effect of Al addition to bulk microstructure, IMC formation, wetting and mechanical properties of low-Ag SAC solder. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(1), 489–502 (2016)
Fahim, A., Ahmed, S., Suhling, J. C., & Lall, P. (2018, May). Mechanical characterization of intermetallic compounds in SAC solder joints at elevated temperatures. In 2018 17th IEEE Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (ITherm) (pp. 1081–1090). IEEE.
L. Yang, S. Quan, C. Liu, H. Xiong, Effect of Mo nanoparticles on the growth behavior of the intermetallic compounds layer in Sn30Ag05Cu/cu solder joints. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 20(4), 2573–2577 (2020)
L. Yang, S. Quan, C. Liu, G. Shi, Aging resistance of the Sn-Ag-Cu solder joints doped with Mo nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 253, 191–194 (2019)
M.R. Adawiyah, O.S. Azlina, Comparative study on the isothermal aging of bare Cu and ENImAg surface finish for Sn-Ag-Cu solder joints. J. Alloy. Compd. 740, 958–966 (2018)
D. Ma, P. Wu, Improved microstructure and mechanical properties for Sn58Bi0.7Zn solder joint by addition of graphene nanosheets. J. Alloy. Compd. 671, 127–136 (2016)
Y. Gu, X. Zhao, Y. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Z. Li, Effect of nano-Fe2O3 additions on wettability and interfacial intermetallic growth of low-Ag content Sn–Ag–Cu solders on Cu substrates. J. Alloy. Compd. 627, 39–47 (2015)
Y.H. Lee, H.T. Lee, Shear strength and interfacial microstructure of Sn–Ag–xNi/Cu single shear lap solder joints. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 444(1–2), 75–83 (2007)
L. Zhang, N. Jiang, P. He, S.J. Zhong, Properties and microstructure evolution of Sn–Cu–Ni/Cu joints bearing carbon nanotubes and graphene nanosheets for solar cell. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(23), 21758–21766 (2020)
X.D. Liu, Y.D. Han, H.Y. Jing, J. Wei, L.Y. Xu, Effect of graphene nanosheets reinforcement on the performance of Sn Ag Cu lead-free solder. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 562, 25–32 (2013)
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Hanim, M. Norkhairunnisa, H.M. Yusoff, M.T. Suraya, Growth kinetics of intermetallic layer in lead-free Sn–5Sb solder reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(10), 8249–8259 (2015)
E.T. Thostenson, Z. Ren, T.W. Chou, Advances in the science and technology of carbon nanotubes and their composites: a review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 61(13), 1899–1912 (2001)
S. Xu, Y.C. Chan, K. Zhang, K.C. Yung, Interfacial intermetallic growth and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes reinforced Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu solder joint under current stressing. J. Alloy. Compd. 595, 92–102 (2014)
J.M. Kim, M.H. Jeong, S. Yoo, C.W. Lee, Y.B. Park, Effects of surface finishes and loading speeds on shear strength of Sn–3.0 Ag–0.5 Cu solder joints. Microelectron. Eng. 89, 55–57 (2012)
B. Ali, M.F.M. Sabri, I. Jauhari, N.L. Sukiman, Impact toughness, hardness and shear strength of Fe and Bi added Sn-1Ag-0.5 Cu lead-free solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 63, 224–230 (2016)
R.D. Wang, S.M. Zhang, Q. Hu, F.W. Zhang, Effect of boron on microstructure and properties of Sn-1.0Ag-0.5 Cu low-silver lead-free solder. Mater. Sci. Forum. 898, 908–916 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (KPT) and Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) for providing necessary resources in completing this study. This research was fully funded by the Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) Research Grant (UPM-GRANT Putra, UPM/GP-IPB/2020/9688700), and the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (KPT) Research Grant (FRGS/2012/5524194).
Funding
This research was fully funded by the Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) Research Grant (UPM-GRANT Putra, UPM/GP-IPB/2020/9688700), and the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (KPT) Research Grant (FRGS/2012/5524194).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by [KV], [AHMA] and [TTDA]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [TTDA] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dele-Afolabi, T.T., Hanim, M.A.A., Vidyatharran, K. et al. Interfacial microstructure evolution and shear strength of MWCNTs-reinforced Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu (SAC105) composite solder interconnects on plain Cu and ENIAg surface finish. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 8233–8246 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07974-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07974-8