Abstract
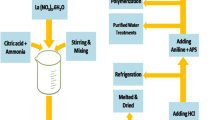
From the past few decades, ferrite is well-known noble material due to its prominent properties like structural, electrical and magnetic properties. With these advantages, ferrites have been used as a substance to incorporate various kinds of functional materials. Among all the ferrites, MnFe2O4-based polyaniline nanocomposites have attracted a great deal of interest due to their enhanced performance due to low cost, strong environmental stability and intriguing electroactivity. In the present work, MnFe2O4 is prepared by sole-gel auto-combustion method and MnFe2O4@PANI nanocomposites were synthesised by mechanical mixing method with various wt% (from 10 to 50%). The as-prepared nanocomposites were characterised by the XRD, and TEM and VSM are used to study the properties like structural and magnetic behaviour of the ferrite-mixed PANI composite. In the 8 GHz–12 GHz range, the complex permittivity and permeability of composite samples were calculated. The values of permittivity were observed to increase as ferrite volume concentration increased, while permittivity decreased as PANI increased. As a result, polyaniline-based nanocomposites specifically demonstrate that they can be used as EMI shielding materials. These nanocomposites are used in microwave absorbers in X band applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.M. Grant Williams, T. Prakash, J. Kennedy, S.V. Chong, S. Rubanov, Spin-dependent tunnelling in magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 229–233 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.04.017
T. Prakash, G.V.M. Williams, J. Kennedy, S. Rubanov, High spin-dependent tunneling magnetoresistance in magnetite powders made by arc-discharge. J. Appl. Phys. 120, 123905 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4963293
K. Thanigai Arul, E. Manikandan, P.P. Murmu, J. Kennedy, M. Henini, Enhanced magnetic properties of polymer-magnetic nanostructures synthesized by ultrasonication. J. Alloys Compd. 720, 395–400 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.146
J. Kruželák, A. Kvasničáková, K. Hložeková, I. Hudec, Progress in polymers and polymer composites used as efficient materials for EMI shielding. Nanoscale Adv. 3, 123–172 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NA00760A
Y. Cao, G.M. Treacy, P. Smith, A.J. Heeger, Optical-quality transparent conductive polyaniline films. Synth. Met. 55, 3526–3531 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-6779(93)90470-H
T.A. Ezquerra, F. Kremer, M. Mohammadi, J. Ruhe, G. Wegner, B. Wessling, AC conductivity measurements in polymeric insulator conductor systems. Synth. Met. 28, 83–88 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-6779(89)90503-1
T. Taka, EMI shielding measurements on poly(3-octyl thiophene) blends. Synth. Met. 41, 1177–1180 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-6779(91)91582-U
T. Mokela, J. Sten, A. Hujanen, H. Isotalo, High frequency polyaniline shields. Synth. Met. 101, 707 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0379-6779(98)01095-9
S.H. Kim, S.H. Jang, S.W. Byun, J.Y. Lee, J.S. Joo, S.H. Jeong, Electrical properties and EMI shielding characteristics of polypyrrole–nylon 6 composite fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 87, 1969–1974 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.11566
Y. Yang, M.C. Gupta, K.L. Dudley, R.W. Lawrence, Conductive carbon nanofiber-polymer foam structures. Adv. Mater. 17, 1999–2003 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200500615
Y. Liu, E. Xuehua Liu, B.W. Xinyu, Z. Jia, Q. Chi, Wu. Guanglei, Synthesis of MnxOy@C hybrid composites for optimal electromagnetic wave absorption capacity and wideband absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 103, 157–164 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.06.034
M. Chang, Z. Jia, S. He, J. Zhou, S. Zhang, M. Tian, B. Wang, Wu. Guanglei, Two-dimensional interface engineering of NiS/MoS2/Ti3C2Tx heterostructures for promoting electromagnetic wave absorption capability. Compos. B. Eng. 225, 109306 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109306
Oh. Kyung Wha, Dong Jun Kim, Seong Hun Kim, Adhesion improvement of electroless copper plated layer on PET film: Effect of pretreatment conditions. Polymer (Korea) 25, 302–310 (2001)
J. Joo, A.J. Epstein, Electromagnetic radiation shielding by intrinsically conducting polymers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 2278 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.112717
H.H. Kuhn, A.D. Child, W.C. Kimbrell, Toward real applications of conductive polymers. Synth. Met. 71, 2139–2142 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-6779(94)03198-F
F. Tabatabaie, M.H. Fathi, A. Saatchi, A. Ghasemi, Microwave absorption properties of Mn- and Ti-doped strontium hexaferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 470, 332–335 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.02.094
V.J. Angadi, B. Rudraswamy, S. Matteppanavar, B. Angadi, S.E. Vinodini, K. Sadhana, K. Praveena, Effect of Zn2+ Substituted on Structural and Magnetic Properties of Manganese Ferrite Synthesized via Combustion Route. Adv. Sci. Lett. 22, 790–796 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2016.6952
K. Praveena, K.B.R. Varma, Improved magneto-electric response in Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–MnFe2O4 composites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater Electron. 25, 111–116 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1557-8
K. Praveena K, K.B.R. Varma, Enhanced electric field tunable magnetic properties of lead-free Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–MnFe2O4 multiferroic composites, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 5403–5409 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2320-5
H. Ibrahim Sharifi, S.A. Shokrollahi, Ferrite-based magnetic nanofluids used in hyperthermia applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 903–915 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.10.017
V.J. Angadi, B. Rudraswamy, K. Sadhana, K. Praveena, Structural and magnetic properties of manganese zinc ferrite nanoparticles prepared by solution combustion method using mixture of fuels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 409, 111–115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.02.096
K. Sadhana, R. Sandhya, K. Praveena, DC-Bias-Superposition Characteristics of Ni0.4Zn0.2Mn0.4Fe2O4 Nanopowders Synthesized by Auto-Combustion. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 15, 4552–4557 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2015.9809
K. Praveena, H.W. Chen, H.L. Liu, K. Sadhana, S.R. Murthy, Enhanced magnetic domain relaxation frequency and low power losses in Zn2+ substituted manganese ferrites potential for high frequency applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 420, 129–142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.07.011
V. Jagadeesha Angadi, B. Rudraswamy, K. Sadhana, K. Praveena, Effect of Sm3+-Gd3+ co-doping on dielectric properties of Mn-Zn ferrites synthesized via combustion route. Mater. Today: Proc. 3, 2178–2186 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2016.04.124
S. Yunus, A. Attout, P. Bertrand, Controlled aniline polymerization strategies for polyaniline micro- and nano self-assembling into practical electronic devices. Langmuir 25, 1851–1854 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/la803034q
Q. Lu, X.H. Wang, Water dispersed conducting polyaniline nanofibers for high-capacity rechargeable lithium-oxygen battery. ACS Macro Lett. 2, 92–95 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/mz3005605
S. Virji, J. Huang, R.B. Kaner, B.H. Weiller, P.N.G. Sensors, Examination of response mechanisms. Nano Lett. 4, 491–496 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl035122e
H. Ding, X.-M. Liu, M. Wan, Fu. Shao-Yun, Electromagnetic functionalized cage-like polyaniline composite nanostructures. Phys. Chem. B 112, 9289–9294 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp8016997
J.C. Aphesteguy, A. Damiani, D. DiGiovanni, S.E. Jacobo, Microwave absorption behavior of a polyaniline magnetic composite in the X-band. J. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 407, 3168–3171 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.12.055
J.R. Capadona, O. Van Den Berg, L.A. Capadona, M. Schroeter, S.J. Rowan, D.J. Tyler, C. Weder, A versatile approach for the processing of polymer nanocomposites with self-assembled nanofibre templates. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 765–769 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.379
Y. Wang, X. Jing, Intrinsically conducting polymers for electromagnetic interference shielding. Polym. Adv. Technol. 16, 344–351 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.589
S. Fauveaux, J.L. Miane, Broadband electromagnetic shields using polyaniline composites. Electromagnetics 23, 617–627 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1080/02726340390244734
H.M. Xiao, X.M. Liu, S.Y. Fu, Synthesis, magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of core-shell structured MnFe2O4/TiO2 nanocomposites. Compo. Sci. Tech. 66, 2003–2008 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.01.001
S.H. Hosseini, S.H. Mohseni, A. Asadnia, H. Kerdari, Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of polyaniline/MnFe2O4 nanocomposite. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 4682–4687 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.11.198
B. Birsoz, A. Baykal, H. Sozeri, M.S. Toprak, Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole–BaFe12O19 nanocomposite. J. Alloys Compd. 493, 481–485 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.12.135
T. Giannakopoulou, L. Kompotiatis, A. Kontogeorgakos, G. Kordas, Microwave behavior of ferrites prepared via sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 246, 360–365 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00106-3
S. Sugimoto, K. Haga, T. Kagotani, K. Inomata, Microwave absorption properties of Ba M-type ferrite prepared by a modified coprecipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 290–291, 1188–1191 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2004.11.381
K.H. Wu, T.H. Ting, M.C. Lia, W.D. Ho, Sol–gel auto-combustion synthesis of SiO2-doped NiZn ferrite by using various fuels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 298, 25–32 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.03.008
K. Praveena, S. Srinath, The effect of Sb on the electrical and magnetic properties of Ni-Zn ferrites prepared by sol–gel autocombustion method. J. Electroceram. 31, 168–175 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-013-9840-x
K. Praveena, M. Penchal Reddy, M. Bououdina, R. Sandhya, K. Sadhana, Effect of Ni–Zr codoping on dielectric and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 via sol–gel route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 382, 172–178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.01.050
K. Sadhana, S.R. Murthy, K. Praveena, Effect of Sm3+ on dielectric and magnetic properties of Y3Fe5O12 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater Electron. 25, 5130–5136 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2282-7
H. Chyi Ching, W. Tsung Yung, W. Jun, T. Jih Sheng, Development of a novel combustion synthesis method for synthesizing of ceramic oxide powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 111, 49–56 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2004.03.023
J. Livage, C. Sanchez, M. Henry, S. Doeuff, The chemistry of the sol-gel process. Solid State Ion. 32–33, 633–638 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(89)90338-X
W.B. Weir, Automatic measurement of complex dielectric constant and permeability at microwave frequencies. Proc. IEEE 62, 33–36 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1974.9382
A.M. Nicolson, G.F. Ross, Measurement of the intrinsic properties of materials by time-domain techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 19, 377–382 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.1970.4313932
K. Manjunatha, V. Jagadeesha Angadi, R. Rajaramakrishna, U. Mahaboob Pasha, Role of 5 mol% Mg-Ni on the Structural and Magnetic Properties of Cobalt Chromates Crystallites Prepared by Solution Combustion Technique. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 2861–2866 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05549-4
Z. Wang, X. Wang, N. Zhao, J. He, S. Wang, Wu. Guanglei, Y. Cheng, the desirable dielectric properties and high thermal conductivity of epoxy composites with the cobweb-structured SiCnw–SiO2–NH2 hybrids. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 32, 20973–20984 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06543-9
J. Liu, Z. Jia, W. Zhou, X. Liu, C. Zhang, Xu. Binghui, Wu. Guanglei, Self-assembled MoS2/magnetic ferrite CuFe2O4 nanocomposite for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 429, 132253 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132253
D.A. Dimitrov, G.M. Wysin, Magnetic properties of spherical fcc clusters with radial surface anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 51, 11947 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.51.11947
V.P. Shilov, J.C. Bacri, F. Gazeau, F. Gendron, R. Perzynski, Y.L. Raikher, Ferromagnetic resonance in ferrite nanoparticles with uniaxial surface anisotropy. J. Appl. Phys. 85, 6642–6647 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.370173
N.E. Kazantseva, J. Vilcˇa´kova, V. Krˇesa´lek, P. Sa´ha, I. Sapurina, J. Stejskald, Magnetic behaviour of composites containing polyaniline-coated manganese–zinc ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 269, 30–37 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(03)00557-2
L. Li, J. Jiang, Xu. Feng, Novel polyaniline-LiNi0.5La0.02Fe1.98O4 nanocomposites prepared via an in situ polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 42, 2221–2227 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2006.06.024
J. Wang, Z. Jia, X. Liu, J. Dou, B. Xu, B. Wang, Guanglei, Construction of 1D heterostructure NiCo@C/ZnO nanorod with enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-021-00704-5
X. Huang, X. Liu, Z. Jia, B. Wang, Wu. Xiaomeng, Wu. Guanglei, Synthesis of 3D cerium oxide/porous carbon for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00304-2
Acknowledgements
Taif University Researchers Supporting Project Number (TURSP-2020/45) Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Praveena, K., Jagadeesha Gowda, G.V., El-Denglawey, A. et al. Manganese ferrite—polyaniline nanocomposites for microwave absorbers in X band. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 5678–5685 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07753-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07753-5