Abstract
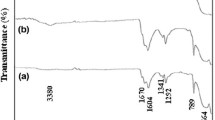
The present study portrays structural, magnetic, electrical, optical and electronic characteristics of polycrystalline pristine and aliovalent Sm3+ modified Tin oxide (SnO2) nanocrystals [Sn(1−x)SmxO2 nanocrystals, where x = 0, x = 0.05, and x = 0.10] were synthesized using conventional sol–gel route. X-ray diffractogram showed rutile-type tetragonal crystallinity [space group P42/mnm] for all the samples. Microstructural investigations depicted well-interlinked grains and it was observed that average grain size increases with Sm3+ substitution in the crystal framework of SnO2. HRTEM images also confirmed the tetragonal rutile symmetry for all the compositions. FTIR spectra validated the phase pure synthesis and formation of Sm3+ substituted SnO2 nanocrystals as bend at 470 cm−1 attributed to the Sn/Sm–O vibrations. Magnetic measurements depicted that Sm3+ modified compositions showed room temperature magnetism with low coercivity and retentivity, while pristine SnO2 nanocrystals illustrated diamagnetism at higher magnetic field and defect-assisted ferromagnetism at low fields. The maximum value of dielectric constant (ε′) was observed for pure SnO2, and dielectric constant (ε′) decreases with increasing Sm3+ concentration. I-V curves showed non-linear behavior for all the samples and the maximum resistance was found for pure SnO2 nanocrystals. The incorporation of aliovalent rare-earth Sm3+ ion in SnO2 crystal matrix induces ferromagnetism in the system, which makes it dilute magnetic semiconductor for magneto-or spin electronics.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Hamrouni, M. Noomen, P. Francesco, D.P. Agatino, H. Ammar, P. Leonardo, Sol–gel synthesis and photocatalytic activity of ZnO–SnO2 nanocomposites. J. Mol Catal. A: Chem. 390, 133–141 (2014)
G. Elango, M. Selvaraj, Efficacy of SnO2 nanoparticles toward photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J. Photochem. Photobio. 155, 34–38 (2016)
D.L. Kamble, S.H. Namdev, L.P. Vithoba, S.P. Pramod, D.K. Laxman, Characterization and NO2 gas sensing properties of spray pyrolyzed SnO2 thin films. J. Anal. Appl. Pyro. 127, 38–46 (2017)
D. Singh, V.S. Kundu, A.S. Maan, Structural, morphological and gas sensing study of zinc doped tin oxide nanoparticles synthesized via hydrothermal technique. J. Mol. Struct. 1115, 250–257 (2016)
S. Begum, T.B. Devi, M. Ahmaruzzaman, Surfactant mediated facile fabrication of SnO2 quantum dots and their degradation behavior of humic acid. Mater. Lett. 185, 123–126 (2016)
G. Madhu, V.C. Bose, A.S. Aiswaryaraj, K. Maniammal, V. Biju, Defect dependent antioxidant activity of nanostructured nickel oxide synthesized through a novel chemical method. Coll. Surf. A: Phys. Eng. Asp. 429, 44–50 (2013)
Y. Masuda, O. Tatsuki, K. Kazumi, Environmentally friendly tin oxide coating through aqueous solution process. Adv. Mater. Sci. Env. Ene. Tech. Cera. Transac. 236, 13–23 (2012)
N.L. Carreño, V.F. Humberto, P.M. Adeilton, V. Antoninho, M.P. Fenelon, F.P. Luiz, R.L. Edson, L. Elson, Selective synthesis of vinyl ketone over SnO2 nanoparticle catalysts doped with rare earths. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 207, 91–96 (2004)
Y. Xiao, H. Gaoyi, W. Jihuai, J.Y. Lin, Efficient bifacial perovskite solar cell based on a highly transparent poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) as the p-type hole-transporting material. J. Power Sour. 306, 171–177 (2016)
J.H. Ren, Y.T. Huang, K.W. Li, J. Shen, W.Y. Zeng, C.M. Sheng, J.J. Shao, Y.B. Han, Q. Zhang, Preparation of rare-earth thulium doped tin-oxide thin films and their applications in thin film transistors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 493, 63–69 (2019)
J.H. Ren, K.W. Li, J. Shen, C.M. Sheng, Y.T. Huang, Q. Zhang, Effects of rare-earth erbium doping on the electrical performance of tin-oxide thin film transistors. J. Alloys Comp. 791, 11–18 (2019)
J. Yue, X. Yaoming, L. Yanping, H. Gaoyi, Y. Zhang, H. Wenjing, Enhanced photovoltaic performances of the dye-sensitized solar cell by utilizing rare-earth modified tin oxide compact layer. Org. Elect. 43, 121–129 (2017)
K.D.A. Kumar, S. Valanarasu, A. Kathalingam, K. Jeyadheepan, Nd3+ Doping effect on the optical and electrical properties of SnO2 thin films prepared by nebulizer spray pyrolysis for opto-electronic application. Mater. Res. Bull. 101, 264–271 (2018)
T. P. Wai, Y. Yin, X. Zhang, Z. Li, Preparation and characterization of rare earth-doped Ti/SnO2-Sb-Mn electrodes for the electrocatalytic performance. J. Nano. (2020).
J. Fernández, G.R. Sara, B. Rolindes, C. Concepción, Rare-earth-doped wide-bandgap tin-oxide nanocrystals: pumping mechanisms and spectroscopy. Opt. Comp. Mater. XV 10528, 1052805 (2018)
M.K. Sohal, K. Manreet, M. Aman, G. Sahil, S.V. Nahirniak, T.A. Dontsova, S.C. Ravi, Rare earth-tuned oxygen vacancies in gadolinium-doped tin oxide for selective detection of volatile organic compounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electr. 31, 8446–8455 (2020)
M. Ferrari, J. I. Mackenzie, T. Stefano, Fiber lasers and glass photonics: materials through applications II, In Soc. of Ph.-Opt. Instr. Engi. (SPIE) Conference Series, 11357 (2020)
G. Singh, T. Rengasamy, R.C. Singh, Effect of crystallite size, Raman surface modes and surface basicity on the gas sensing behavior of terbium-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Cer. Inter. 42, 4323–4332 (2016)
L.P. Singh, N.P. Singh, S.K. Srivastava, Terbium doped SnO2 nanoparticles as white emitters and SnO2: 5Tb/Fe3O4 magnetic luminescent nanohybrids for hyperthermia application and biocompatibility with HeLa cancer cells. Dal. Transac. 44, 6457–6465 (2015)
C.H. Kwak, T.H. Kim, S.Y. Jeong, J.W. Yoon, J.S. Kim, J.H. Lee, Humidity-independent oxide semiconductor chemiresistors using terbium-doped SnO2 yolk–shell spheres for real-time breath analysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 10, 18886–18894 (2018)
N. T. Tayade, S. Dhawankar, P. R. Arjuwadkar, Perspective of distortion and vulnerability in structure by using the cds-zns composite approach in rietveld refinement (2017)
O. Hyung-Suk, H.N. Nong, T. Reier, M. Gliech, P. Strasser, Oxide-supported irnanodendrites with high activity and durability for the oxygen evolution reaction in acid PEM water electrolyzers. Chem. Sci. 6, 3321–3328 (2015)
D. Sharma, S. Tripathi, R.S. Panwar, G. Dhillon, A.K. Bhatia, D. Vashisht, S.K. Mehta, N. Kumar, Crystal chemistry and physicochemical investigation of aliovalent substituted SnO2 nanoparticles. Vacuum 184, 109925 (2021)
S. Das, V. Jayaraman, SnO2: a comprehensive review on structures and gas sensors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 66, 112–255 (2014)
B.A. Hamad, First-principle calculations of structural and electronic properties of rutile-phase dioxides (MO2), M = Ti, V, Ru, Ir and Sn. Euro. Phys. J. B 70, 163–169 (2009)
K.S. Abdel-Aal, A.S. Abdel-Rahman, Graphene influence on the structure, magnetic, and optical properties of rare-earth perovskite. J. Nanopar. Res. 22, 1–10 (2020)
S. K. Abdel-Aal, A. I. Beskrovnyi, A. M. Ionov, R. N. Mozhchil, A. S. Abdel-Rahman, structure investigation by neutron diffraction and x‐ray diffraction of graphene nanocomposite CuO–rGO prepared by low‐cost method. Phys. State Solidi (a). 2100138 (2021)
S. K. Abdel-Aal, M. F. Kandeel, A. F. El-Sherif, A. S. Abdel-Rahman, Synthesis, characterization, and optical properties of new organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites [(NH3)2(CH2)3] CuCl4 and [(NH3)2 (CH2)4] CuCl2Br2. Phys. State Solid (a). 2100036 (2021)
N. Hussain, S. Zulfiqar, T. Khan, R. Khan, S.A. Khattak, S. Ali, G. Khan, Investigation of structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of SnO2 nanorods and nanospheres. Mater. Chem. Phys. 241, 122382 (2020)
M.A. Gondal, Q.A. Drmosh, T.A. Saleh, Preparation and characterization of SnO2 nanoparticles using high power pulsed laser. Appl. Sur. Sci. 256, 7067–7070 (2010)
L. Tan, L. Wang, Y. Wang, Hydrothermal synthesis of nanostructures with different morphologies and their optical properties. J. Nano. 2011 (2011)
N.M. Shaalan, D. Hamad, A.Y. Abdel-Latief, M.A. Abdel-Rahim, Preparation of quantum size of tin oxide: structural and physical characterization. Prog. Nat. Sci: Mater. Int. 26, 145–151 (2016)
S.E. Thamarai, S.M. Sundar, Effect of Mn doping on structural, optical and magnetic properties of SnO2 nanoparticles by solvothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 5021–15032 (2017)
S. Tazikeh, A. Akbari, A. Talebi, E. Talebi, Synthesis and characterization of tin oxide nanoparticles via the co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 32, 98–101 (2014)
V.B. Kamble, A.M. Umarji, Achieving selectivity from the synergistic effect of Cr and Pt activated SnO2 thin film gas sensors. Sens. Act. B: Chem. 236, 208–217 (2016)
S.K. Abdel-Aal, A.S. Abdel-Rahman, W.M. Gamal, M. Abdel-Kader, H.S. Ayoub, A.F. El-Sherif, M.F. Kandeel, S. Bozhko, E.E. Yakimov, E.B. Yakimov, Crystal structure, vibrational spectroscopy and optical properties of a one-dimensional organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite of [NH3CH2CH(NH3)CH2] BiCl5. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B: Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mat. 75, 880–886 (2019)
D. Sharma, N. Kumar, T. Mehrotra, N. Pervaiz, L. Agrawal, S. Tripathi, A. Jha, T. Poullikkas, R. Kumar, L. Ledwani, In vitro and in silico molecular docking studies of Rheum emodi-derived diamagnetic SnO2 nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effects against breast cancer. New J. Chem. 45, 1695–1711 (2021)
C. Wang, Q. Wu, H.L. Ge, T. Shang, J.Z. Jiang, Magnetic stability of SnO2 nanosheets. NANO 23, 075704 (2012)
G. Feng, S.F. Wang, K.L. Meng, G.J. Zhou, X. Dong, D.R. Yuan, Photoluminescence properties of SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol− gel method. The Jour. of Phy. Chem. B 108, 8119–8123 (2004)
X.L. Wang, Z.X. Dai, Z. Zeng, Search for ferromagnetism in SnO2 doped with transition metals (V, Mn, Fe, and Co). J. Phys. Cond. Mat. 20, 045214 (2008)
V. Agrahari, M.C. Mathpal, M. Kumar, A. Agarwal, Investigations of optoelectronic properties in DMS SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Alloys. Comp. 622, 48–53 (2015)
A. Dieguez, A. Romano-Rodrıguez, A. Vila, J.R. Morante, The complete Raman spectrum of nanometric SnO2 particles. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 1550–1557 (2001)
D. Varshney, K. Verma, Effect of stirring time on size and dielectric properties of SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Str. 1034, 216–222 (2013)
A. Ahmed, M.N. Siddique, T. Ali, P. Tripathi, Defect assisted improved room temperature ferromagnetism in Ce doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci 483, 463–471 (2019)
P.P. Sahay, R.K. Mishra, S.N. Pandey, S. Jha, M. Shamsuddin, Structural, dielectric and photoluminescence properties of co-precipitated Zn-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 479–486 (2013)
N. Hussain, S. Zulfiqar, T. Khan, R. Khan, S.A. Khattak, S. Ali, G. Khan, Investigation of structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of SnO2 nanorods and nanospheres. Mat. Chem. Phys. 241, 122382 (2020)
J.R. Macdonald, Impedance Spectroscopy: Emphasizing Solid Materials and Systems (Wiley, Hoboken, 1987)
J.G. Han, Z.Y. Zhu, S. Ray, A.K. Azad, W.L. Zhang, M.X. He, S.H. Li, Y.P. Zhao, Optical and dielectric properties of ZnO tetrapod structures at terahertz frequencies. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 031107 (2006)
S.M. Zhou, Y.S. Feng, L.D. Zhang, A physical evaporation synthetic route to large-scale GaN nanowires and their dielectric properties. Chem. Phys. Lett. 69, 610 (2003)
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121 (1951)
K. Dutta, S.K. De, Optical and diode like current–voltage characteristics of SnO2–polypyrrole nanocomposites. Jour. of Phy. D: App. Phy. 40, 734 (2007)
P.M.R.M. Bharathi, T. Amutha, M. Rameshbabu, K. Prabha, Synthesis and investigation of Ce doped tinoxide (SnO2) nanoparticles. IRJET 4, 334 (2017)
M. Veerabhadrayya, R.A. Kumari, G. Nagaraju, Y.T. Ravikiran, B. Chethan, Structural, optical and electrical properties of Ce doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by surfactant assisted gel combustion method. J. Nano. Elec. Phys. 12, 04017 (2020)
P.G. Li, X. Guo, X.F. Wang, W.H. Tang, Synthesis, photoluminescence and dielectric properties of O-deficient SnO2 nanowires. J. Alloys. Comp. 479, 74 (2009)
F. Gu, S.F. Wang, M.K. Lü, G.J. Zhou, D. Xu, D.R. Yuan, Photoluminescence properties of SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol−gel method. J. Phys. Chem. B. 108, 8119 (2004)
K. Vanheusden, W.L. Warren, C.H. Seager, D.R. Tallant, J.A. Voigt, B.E. Gnade, Mechanisms behind green photoluminescence in ZnO phosphor powders. J. App. Phys. 79, 7983 (1996)
M.B. Reddy, S. Sailaja, P. Giridhar, C.N. Raju, B.S. Reddy, Spectroscopic investigations of Sm3+ Ions Doped B2O3-Bi2O3-ZnO-Li2O glasses. Ferroelectr. Lett. Sect. 38, 40 (2011)
L.P. Singh, M. Niraj Luwang, S.K. Srivastava, Luminescence and photocatalytic studies of Sm3+ ion doped SnO2 nanoparticles. New J. of Chem. 38, 115–121 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Chitkara University, Punjab for support and institutional facilities. A special thanks to Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Facility, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India, for characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Formal analysis and conceptualization: GD. Methodology: MC. Data analysis and investigation: NK. Writing (original draft): AK
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors hereby declare that we have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. All procedures performed in studies were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional or national research committee or comparable ethical standards.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Kumar, N., Chitkara, M. et al. Physicochemical investigations of structurally enriched Sm3+ substituted SnO2 nanocrystals. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 5283–5296 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07716-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07716-w