Abstract
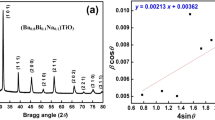
In the present report, an attempt has been made to develop (via synthesis and characterization) a lead-free multifunctional material by introducing Ni in BaTiO3 of a composition of (Ba0.5Ni0.5)TiO3 for the temperature sensor and bandwidth applications. The phase analysis using X-ray diffraction data reveals the mono-phase nature of the developed system in the tetragonal crystal symmetry. The variation of structural parameters such as lattice constant, unit volume, change in tetragonality ratio from 1.0082 to c/a = 1.5792, are evidence of structural distortion generated in the unit cell of BaTiO3 on the addition of nickel at its Ba-site of the parent compound. This distortion significantly affects the dielectric, ferroelectric, impedance, and conductivity characteristics of barium titanate. The electron microscopic studies of the material show the compactness and uniform distribution of grains almost the same size over the surface of the pellet sample. The frequency-temperature-dependent studies of the material exhibit that ferroelectric-paraelectric phase transition temperature (Tc) of BaTiO3 (~ 120 °C) has been diffused or shifted, and hence no phase transition or dielectric anomaly is observed in the experimental temperature range (30–500 °C) in Ni-rich barium titanate (i.e., Ba0.5Ni0.5)TiO3. The relative permittivity even at 450 °C is found to be in the order of 103 with conductivity in the order of 10–4 Ω cm−1. However, room temperature hysteresis loop provides the saturation polarization of (Ps = 3.1416 μC/cm2), remnant polarization (Pr = 0.8478 μC/cm2) and coercive field (EC = 87.76 kV/cm). The analysis of various electrical data (parameters), such as relative permittivity, loss tangent, impedance as a function of temperature and frequency has provided dielectric relaxation and conduction mechanism in the material. Based on the above parameters, it may be concluded that the material can be a suitable candidate for multifunctional applications like temperature sensors, bandwidth, etc.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
V. Buscaglia, M.T. Buscaglia, G. Canu, BaTiO3-based ceramics: fundamentals properties and applications, encyclopedia of materials: technical ceramics and glasses. Mater. Sci. 3, 311–344 (2021)
A.C. Ianculescu, C.A.V. Maria Crisan, M. Raileanu, B.S. Vasile, M. Calugaru, D. Crisan, N. Dragan, L. Curecheriu, L. Mitoseriu, Formation mechanism and characteristics of lanthanum-doped BaTiO3 powders and ceramics prepared by the sol–gel process. Mater. Charact. 106, 195–207 (2015)
B.C. Das, A.K.M. Akther, A.A. Hossain, Rietveld refined structure, ferroelectric, magnetic and magnetoelectric response of Gd- substituted Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite and Ca, Zr co-doped BaTiO3 multiferroic composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 867, 159068 (2021)
W. Eerenstein, N. Mathur, J.F. Scoot, Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442, 759–765 (2006)
N.A. Hill, Why are there so few magnetic ferroelectrics? J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6694–6709 (2000)
G. Catalan, J.F. Scoot, Physics and application of bismuth ferrite. Adv. Mater. 21, 1–9 (2009)
D. Khomskii, Classifying multiferroics: mechanism and effects. Physics 2, 20 (2009)
J. Rodel, K.G. Webber, R. Dittmer, W. Jo, M. Kimura, D. Damjanovic, Transferring lead–free piezoelectric ceramics into application. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 1659–1681 (2015)
A. Rani, J. Kolte, P. Gopalan, Phase formation, microstructure, electrical and magnetic properties of Mn substituted barium titnate. Ceram. Int. 41, 14057–14063 (2015)
N.V. Dang, T.D. Thanh, L.V. Hong, V.D. Lam, T.L. Phan, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of polycrystalline BaTi1−xFexO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 043914 (2011)
T.L. Phan, P. Zhang, D. Grinting, S.C. Yu, N.X. Nghia, N.V. Dang, V.D. Lam, Influences of annealing temperature on structural characterization and magnetic properties of Mn-doped BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 013909 (2012)
I.N. Apostolova, A.T. Apostolova, S. Golrokh Bahoosh, J.M. Wesselinowa, Orign of ferromagnetism in transition metal dped BaTiO3. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 203904 (2013)
F. Maldonado, S. Jácome, A. Stashans, Co-doping of Ni and Fe in tetragonal BaTiO3. Comput. Condens. Matter 13, 49–54 (2017)
S.K. Das, R.N. Mishra, B.K. Roul, Magnetic and ferroelectric properties of Ni doped BaTiO3. Solid State Commun. 191, 19–24 (2014)
M. Acosta, N. Novak, V. Rojas, S. Patel, R. Vaish, J. Koruza, G.A. Rossetti Jr., J. Rödel, BaTiO3-based piezoelectrics: fundamentals, current status, and perspectives. Appl. Phys. Rev. 4, 041305 (2017)
M.M. Yuan, L. Cheng, Q. Xu, W.W. Wu, S. Bai, L. Gu, Z. Wang, J. Lu, H.P. Li, Y. Qin, T. Jing, Z.L. Wang, Biocompatible nanogenerators through high piezoelectric coefficient 0.5Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3–0.5(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 nanowires for in-vivo applications. Adv. Mater. 26, 7432–7437 (2014)
L. Cheng, M. Yuan, L. Gu, Z. Wang, Y. Qin, T. Jing, Z.L. Wang, Wireless, power-free and implantable nanosystem for resistance-based biodetection. Nano Energy 15, 598–606 (2015)
N.R. Alluri, B. Saravanakumar, S.J. Kim, Flexible, hybrid piezoelectric film (BaTi(1–x)ZrxO3)/PVDF nanogenerator as a self-powered fluid velocity sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 9831–9840 (2015)
A.F. Devonshire, “XCVI. Theory of barium titanate—part I”, London Edinburgh Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 40(309), 1040–1063 (1949)
B. Jaffe, W.R. Cook, H. Jaffe, Piezoelectric ceramics (Academic Press, London, 1971)
X. Zhu, J. Yang, D. Dastan, H. Garmestani, R. Fan, Z. Shi, Fabrication of core-shell structured Ni@BaTiO3 scaffolds for polymer, composites with ultrahigh dielectric constant and low loss. Compos. A 125, 105521 (2019)
M. Saleem, M.S. Butt, A. Maqbool, M.A. Umer, M. Shahid, F. Javaid, R.A. Malik, H. Jabbar, H.M.W. Khalil, L.D. Hwan, M. Kim, B.K. Koo, S.J. Jeong, Percolation phenomena of dielectric permittivity of a microwave-sintered BaTiO3-Ag nanocomposite for high energy capacitor. J. Alloy. Compd. 822, 153525 (2020)
S.S. Vadla, T. Costanzo, S. John, G. Caruntu, S.C. Roy, Local probing of magnetoelectric coupling in BaTiO3-Ni 1–3 composites. Scr. Mater. 159, 33–36 (2019)
S.K. Ray, J. Cho, J. Hur, A critical review on strategies for improving efficiency of BaTiO3-based photocatalysts for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 290, 119 (2021)
M. Arshad, W. Khan, M. Abushad, M. Nadeem, S. Husain, A. Ansari, V.K. Chakradhary, Correlation between structure, dielectric and multiferroic properties of lead free Ni modified BaTiO3 solid solution. Ceram. Int. 46, 27336–27351 (2020)
H. Zhao, X. Yang, D. Pang, X. Long, Enhanced energy storage efficiency by modulating field-induced strain in BaTiO3-Bi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3 lead-free ceramics. Ceram. Int. 47, 22734–22740 (2021)
C.P. Kempter, Vegard’s Law. Phys. Status Solidi 18, K117–K118 (1966)
Y.C. Huang, S.S. Cgen, W.H. Tuan, Process window of BaTiO3–Ni ferroelectric-ferromagnetic composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 1438–1443 (2007)
R.N.P. Rutuparna Das, Choudhary, structural, electrical, and leakage-current characteristics of double perovskite: Sm2CoMnO6. Appl. Phys. A 125, 864 (2019)
S. Chikada, K. Hirose, T. Yamamoto, Analysis of local environment of Fe ions in hexagonal BaTiO3 Japan. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 091502 (2010)
B. Park. An interactive powder diffraction data interpretations and indexing program version 2.1, E. WU School of Physical Sciences, Flinders University of South Australia, SA 5042
H. Gong, X. Wang, S. Zhang, Z. Tian, L. Li, Electrical and reliability characteristics of Mn-doped nano BaTiO3-based ceramics for ultrathin multilayer ceramic capacitor application. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 114119 (2012)
H. Schmid, Multi-ferroic magnetoelectric. Ferroelectrics 162, 317–338 (1994)
A. Kumar, I. Rivera, R.S. Katiyar, J.F. Scott, Multiferroic Pb(Fe0.66W0.33)0.80Ti0.20O3 thin films: a room-temperature relaxor ferroelectric and weak ferromagnetic. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 132913 (2008)
P. Mandal, A. Iyo, Y. Tanaka, A. Sundaresan, C.N.R. Rao, Structure, magnetism and giant dielectric constant of BiCr0.5Mn0.5O3 synthesized at high pressures. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 1646–1650 (2010)
Y. Guo, P. Xiao, R. Wen, Y. Wan, Q. Zheng, D. Shi, K. Ho Lam, M. Liu, D. Lin, Critical roles of Mn-ions in enhancing the insulation, piezoelectricity and multiferroicity of BiFeO3-based lead-free high temperature ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 5811–5824 (2015)
V.I. Gibalov, G.J. Pietsch, Dynamics of dielectric barrier discharges in different arrangements. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 21, 024010 (2012)
J.E. Garcia, V. Gomis, R. Perez, A. Albareda, J.A. Eiran, Unexpected dielectric response in lead zirconate titanate ceramics: the role of ferroelectric domain wall pinning effects. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 0429021 (2007)
K.R.S. Preethi Meher, K.B.R. Varma, Colossal dielectric behavior of semiconducting Sr2TiMnO6 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 034113 (2009)
C. Behera, P.R. Das, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural and electrical properties of La-modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 composites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 2086–2095 (2014)
C. Behera, P.R. Das, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural and electrical properties of mechanothermally synthesized NiFe2O4 nanoceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 3539–3549 (2014)
R.N.P. Choudhary, C. Behera, P.R. Das, R.R. Das, Development of bismuth-based electronic materials from Indian red mud. Ceram. Int. 40, 12253–12264 (2014)
E. Pervaiz, I.H. Gul, A. Habib, Hydrothermal synthesis, structural and electrical properties of antimony (Sb3+) substituted nickel ferrites. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 27, 881–890 (2014)
J.S. Kim, Electric modulus spectroscopy of lithium tetraborate (Li2B4O7) single crystal. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 70, 3129–3133 (2001)
H. Nara, T. Yokoshima, T. Osaka, Technology of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for an energy-sustainable society. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 20, 66–77 (2020)
C. Behera, A.K. Pattanaik, Structural, dielectric and ferroelectric properties of lead free Gd modified BiFeO3–BaTiO3 solid solution. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 5470–5477 (2019)
W. Chen, X. Zhao, J. Sun, L. Zhang, L. Zhong, Effect of the Mn doping concentration on the dielectric and ferroelectric properties of different-routes-fabricated BaTiO3-based ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 670, 48–54 (2016)
J. Liu, X. Wei, Y. Lian, Q. Liu, X. Xu, D. Lu, Influence of Sr ions on the structure and dielectric properties of Cu/Nb Co-doped BaTiO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 47, 18669–18676 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behera, C., Patel, P., Pradhan, N. et al. Studies of structural, dielectric and electrical characteristics of nickel-modified barium titanate for device applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 1657–1669 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07709-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07709-9