Abstract
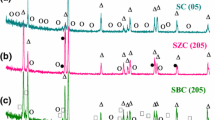
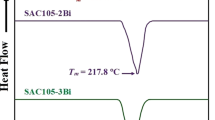
Sn–Zn–Cu is one of the most popular soldering alloys, especially when it has been doped with Bi, which has proved very effective. The Sn–6.5Zn–0.3Cu (SZC–0.0Bi) stress–strain characteristics have been tested and compared to the SZC–1.0 Bi and SZC–3.0 Bi solder alloys. The results of the differential scanning calorimeter confirmed that the melting temperatures, pasty ranges, and undercooling levels would significantly reduce with Bi addition to the SZC solder alloy. Also, it has been found that SZC–3.0 Bi alloy has the highest ultimate tensile stress, yield stress, and Young’s modulus compared to SZC–0.0 Bi and SZC–1.0 Bi alloys. The higher characteristics of stress–strain were caused by the Bi precipitation reinforcing effects as well as solid solution mechanism. The rush of these Bi atoms or particles will greatly improve the microstructure, block dislocation mobility, and raise of percent of Bi to 3.0 wt% enhanced the hardening parameters.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the results of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
E.A. Eid, A.N. Fouda, E.S.M. Duraia, Effect of adding 0.5wt% ZnO nanoparticles, temperature and strain rate on tensile properties of Sn-5.0wt% Sb-0.5wt% Cu (SSC505) lead free solder alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 657, 104–114 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.01.081
E.H. Amalu, N.N. Ekere, High temperature reliability of lead-free solder joints in a flip chip assembly. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212, 471–483 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.10.011
A.A. El-Daly, A.M. El-Taher, S. Gouda, Novel Bi-containing Sn-1.5Ag-0.7Cu lead-free solder alloy with further enhanced thermal property and strength for mobile products. (Elsevier Ltd, Amsterdam, 2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.10.006.
M. Abtew, G. Selvaduray, Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 27, 95–141 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-796X(00)00010-3
A.A. El-Daly, A.E. Hammad, G.S. Al-Ganainy, A.A. Ibrahiem, Design of lead-free candidate alloys for low-temperature soldering applications based on the hypoeutectic Sn-6.5Zn alloy. Mater. Des. 56, 594–603 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.064
C.Y. Liu, M.H. Hon, M.C. Wang, Y.R. Chen, K.M. Chang, W.L. Li, Effects of aging time on the mechanical properties of Sn-9Zn-1.5Ag-xBi lead-free solder alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 229–235 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.022
A.A. El-Daly, A.Z. Mohamad, A. Fawzy, A.M. El-Taher, Creep behavior of near-peritectic Sn-5Sb solders containing small amount of Ag and Cu. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528, 1055–1062 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.11.001
X. Wei, H. Huang, L. Zhou, M. Zhang, X. Liu, On the advantages of using a hypoeutectic Sn-Zn as lead-free solder material. Mater. Lett. 61, 655–658 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.05.029
J. Wu, S.B. Xue, J.W. Wang, S. Liu, Y.L. Han, L.J. Wang, Recent progress of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solders bearing alloy elements and nanoparticles in electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(12), 12729–63 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5407-3
A.A. El-Daly, A.E. Hammad, G.S. Al-Ganainy, M. Ragab, Properties enhancement of low Ag-content Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solders containing small amount of Zn. J. Alloys Compd. 614, 20–28 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.06.009
A.A. El-Daly, A.E. Hammad, G.S. Al-Ganainy, M. Ragab, Influence of Zn addition on the microstructure, melt properties and creep behavior of low Ag-content Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 608, 130–138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.04.070
E. Çadirli, U. Böyük, H. Kaya, N. Maraşli, Determination of mechanical, electrical and thermal properties of the Sn - Bi - Zn ternary alloy. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 357, 2876–2881 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2011.03.025
X.P. Zhang, L.M. Yin, C.B. Yu, Thermal creep and fracture behaviors of the lead-free Sn-Ag-Cu-Bi solder interconnections under different stress levels. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19, 393–398 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9351-0
A.E. Hammad, A.A. Ibrahiem, Enhancing the microstructure and tensile creep resistance of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy by reinforcing nano-sized ZnO particles. Microelectron. Reliab. 75, 187–194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2017.07.034
H. Kang, S.H. Rajendran, J.P. Jung, Low melting temperature Sn-Bi solder: effect of alloying and nanoparticle addition on the microstructural, thermal, interfacial bonding, and mechanical characteristics. Metals 11(2), 364 (2021)
A.A. El-Daly, H.A. Hashem, N. Radwan, F. El-Tantawy, T.R. Dalloul, N.A. Mansour, H.M. Abd-Elmoniem, E.H. Lotfy, Robust effects of Bi doping on microstructure development and mechanical properties of hypoeutectic Sn–6.5Zn solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 2950–2962 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-4115-8
E.A. Eid, A.M. Deghady, A.N. Fouda, Enhanced microstructural, thermal and tensile characteristics of heat treated Sn-5.0Sb-0.3Cu (SSC-503) Pb-free solder alloy under high pressure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.137
A.B. El Basaty, A.M. Deghady, E.A. Eid, Influence of small addition of antimony (Sb) on thermal behavior, microstructural and tensile properties of Sn-9.0Zn-0.5Al Pb-free solder alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 701, 245–253 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.06.092
M. Kamal, M.S. Mikhail, A.B. Bediwi, E.S. Gouda, Decomposition behavior and properties of Sn-9Zn-1Bi lead-free solder alloy with copper content. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids. 161, 715–721 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1080/10420150600966034
P. Pandey, C.S. Tiwary, K. Chattopadhyay, Effects of Cu and in trace elements on microstructure and thermal and mechanical properties of Sn-Zn eutectic alloy. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 2660–2669 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-06869-x
E.A. Eid, E.H. El-Khawas, A.S. Abd-Elrahman, Impact of Sb additives on solidification performance, microstructure enhancement and tensile characteristics of Sn-6.5Zn-0.3Cu Pb-free solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 6507–6518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00956-3
G. Ren, M.N. Collins, The effects of antimony additions on microstructures, thermal and mechanical properties of Sn-8Zn-3Bi alloys. Mater. Des. 119, 133–140 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.01.061
E.A. Eid, A.B. El-Basaty, A.M. Deghady, S. Kaytbay, A. Nassar, Influence of nano-metric Al2O3 particles addition on thermal behavior, microstructural and tensile characteristics of hypoeutectic Sn-5.0Zn-0.3Cu Pb-free solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 4326–4335 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00726-1
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, H. Khanbareh, N. Jahangiri, Indentation creep of lead-free Sn-9Zn and Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder alloys. Mater. Des. 30, 574–580 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.05.058
F. Yang, L. Zhang, Z. Liu, S. Zhong, J. Ma, L. Bao, Properties and microstructures of Sn-Bi-X lead-free solders. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9265195
A.A. El-Daly, A. Fawzy, S.F. Mansour, M.J. Younis, Thermal analysis and mechanical properties of Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy after modification with SiC nano-sized particles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 2976–2988 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1200-8
A.A. El-Daly, A.M. El-Taher, T.R. Dalloul, Enhanced ductility and mechanical strength of Ni-doped Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu lead-free solders. Mater. Des. 55, 309–318 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.10.009
D. Witkin, Creep behavior of Bi-containing lead-free solder alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 41, 190–203 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-011-1748-0
N. Hidaka, H. Watanabe, M. Yoshiba, Creep behavior of lead-free Sn-Ag-Cu + Ni-ge solder alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 670–677 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0689-3
A.A. El-Daly, A.M. El-Taher, T.R. Dalloul, Improved creep resistance and thermal behavior of Ni-doped Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu lead-free solder. J. Alloys Compd. 587, 32–39 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.10.148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMD: idea, conceptualization, methodology, and writing. MMF: idea, visualization, data curation, and original draft preparation. EAE: investigation, reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict interesting between authors and any person or authorities and the idea of research and its results are owning to the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deghady, A.M., Fadel, M.M. & Eid, E.A. The doping of SZC solders with bismuth to improve their thermal and tensile characteristics for microelectronic applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 4831–4846 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07672-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07672-x