Abstract
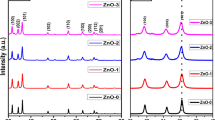
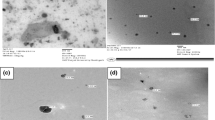
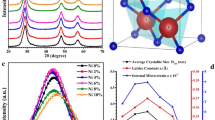
In the present article, the pure and different concentrations as 1, 2, 3, and 5 wt.% Mn-doped ZnO (Mn:ZnO) nanoparticles were synthesized by combustion route. XRD of the prepared samples were fitted using the Lorentz function and the obtained data files were used to calculate the crystallite size. The crystallite sizes were found to be 25.3 nm, 34.6 nm, 31.1 nm, 32.5 nm, and 33.3 nm for pure, 1 wt.%, 2 wt.%, 3 wt.%, and 5 wt.% Mn-doped ZnO NPs, respectively. The agglomerated spherical shape morphology with different particles sizes of pure and 1, 3, and 5 wt.% Mn:ZnO NPs were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The vibrational phonon modes observed at 99–100, 326–331, 435–438, 573–585, 676-681, and 1142–1151 cm−1 were attributed to the presence of intrinsic defects in the samples. The optical band gaps 3.280, 3.218, 3.103, 3.024, and 2.922 eV of pure, 1 wt. %, 2 wt.%, 3 wt.%, and 5 wt.% Mn-doped ZnO NPs were obtained using Kubelka–Munk function, respectively. PL emission spectra exhibit the peaks at 354, 451, 469, 482, 492, and 560 nm under 325 nm excitation wavelength, while emission peaks observed at 389, 451, 468–474, 492, and 557 nm under 350 nm excitation wavelength. The dielectric constant and dielectric losses of the prepared NPs were observed in the range 27.6–23.4 and 29–14, respectively. The greater values of capacitance and impedance of the prepared samples were recorded as 27.3–17.3 (pF) and 2.75 (MΩ)-273 (Ω) over the entire range of the logarithmic frequency. The obtained results of Mn:ZnO nanoparticles were found suitable for the potential applications in optoelectronic devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
K. Omri, J. El Ghoul, O.M. Lemine, M. Bououdina, B. Zhang, L. El Mir, Magnetic and optical properties of manganese doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel technique. Superlattices Microstruct. 60, 139–147 (2013)
J.A. Anta, E. Guillén, R. Tena-Zaera, ZnO-based dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 11413–11425 (2012)
V.D. Mote, J.S. Dargad, Y. Purushotham, B.N. Dole, Effect of doping on structural, physical, morphological and optical properties of Zn1-xMnxO nano-particles. Ceram. Int. 41, 15153–15161 (2015)
Z.W. Jin, Y.-Z. Yoo, T. Sekiguchi, T. Chikyow, Blue and ultraviolet cathodoluminescence from Mn-doped epitaxial ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 39 (2003)
V.A. Karpina, V.I. Lazorenko, C.V. Lashkarev, V.D. Dobrowolski, L.I. Kopylova, V.A. Baturin, S.A. Pustovoytov, AJu. Karpenko, S.A. Eremin, P.M. Lytvyn, Zinc oxide – analogue of GaN with New perspective possibilities. Cryst. Res. Technol. 39, 980–992 (2004)
L. Schmidt-Mende, J.L. MacManus-Driscoll, ZnO – Nanostructures, defects, and devices. Mater. Today. 10, 40–48 (2007)
U. Ozgur, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Dogan, V. Avrutin, S.J. Cho, H. Morkoc, A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005)
Z. Qifeng, Christopher S. Dandeneau, Z. Xiaoyuan, C. Guozhong, ZnO nanostructures for dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Mater. 21, 4087–4108 (2009)
A. Ulyankina, I. Leontyev, M. Avramenko, D. Zhigunov, N. Smirnova, Large-scale synthesis of ZnO nanostructures by pulse electrochemical method and their photocatalytic properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 76, 7–13 (2018)
J. Kaur, S. Bansal, S. Singhal, Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange using ZnO nanopowders synthesized via thermal decomposition of oxalate precursor method. Physica B Condens. Matter. 416, 33–38 (2013)
V.D. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B.N. Dole, Structural, morphological, physical and dielectric properties of Mn doped ZnO nanocrystals synthesized by sol–gel method. Mater. Des. 96, 99–105 (2016)
S. Guo, Q. Hou, C. Zhao, Y. Zhang, Study of the effect of Cu heavy doping on band gap and absorption spectrum of ZnO. Chem. Phys. Lett. 614, 15–20 (2014)
S. Banerjee, M. Mandal, N. Gayathri, M. Sardar, Enhancement of ferromagnetism upon thermal annealing in pure ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 182501 (2007)
P.J. Wellmann, J.M. Garcia, J.-L. Feng, Formation of nanoscale ferromagnetic MnAs crystallites in low-temperature grown GaAs. App. Phys. Left. 71, 2532 (1997)
R. Nasser, W.B.H. Othmen, H. Elhouichet, Effect of Sb doping on the electrical and dielectric properties of ZnO nanocrystals. Ceram. Int. 45, 8000–8007 (2019)
B. Hartiti, M. Siadat, E. Comini, H.M.M.M. Arachchige, S. Fadili, P. Thevenin, Acetone sensor based on Ni doped ZnO nanostructues: growth and sensing capability. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 7681–7690 (2019)
D. Sharma, R. Jha, Transition metal (Co, Mn) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: effect on structural and optical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 698, 532–538 (2017)
N.X. Sang, N.M. Quan, N.H. Tho, N.T. Tuan, T.T. Tung, Mechanism of enhanced photocatalytic activity of Cr-doped ZnO nanoparticles revealed by photoluminescence emission and electron spin resonance. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 34, 25013 (2019)
C. Belkhaoui, R. Lefi, N. Mzabi, H. Smaoui, Synthesis, optical and electrical properties of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 29, 7020–7030 (2018)
L. Zhang, X. Zhu, Z. Wang, S. Yun, T. Guo, J. Zhang, J. Chen, Synthesis of ZnO doped high valence S element and study of photogenerated charges properties. RSC Adv. 9, 4422–4427 (2019)
Y. Zong, Y. Sun, S. Meng, Y. Wang, H. Xing, X. Li, X. Zheng, Doping effect and oxygen defects boost room temperature ferromagnetism of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: experimental and theoretical studies. RSC Adv. 9, 23012–23020 (2019)
H. Liu, X. Zhang, L. Li, Y.X. Wang, K.H. Gao, Z.Q. Li, R.K. Zheng, S.P. Ringer, B. Zhang, X.X. Zhang, Role of point defects in room-temperature ferromagnetism of Cr-doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 072511 (2007)
T. Guo, Y. Zhang, Y. Luo, C.W. Nan, Y.H. Lin, Ferromagnetic and optical properties of Co doped ZnO hexagonal bipods. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 083916 (2012)
O.D. Jayakumar, H.G. Salunke, R.M. Kadam, M. Mohapatra, G. Yaswant, S.K. Kulshreshtha, Magnetism in Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by a co-precipitation method. Nanotechnology 17, 1278 (2006)
S. Kumar, Y. J. Kim, B. H. Koo, S. K. Sharma, J. M. Vargas, M. Knobel, S. Gautam, K. H. Chae, D. K. Kim, Y. K. Kim 2009 Structural and magnetic properties of chemically synthesized Fe doped ZnO J. Appl. Phys. 105: e07C520
R. Boubekri, Z. Beji, K. Elkabous, F. Herbst, G. Viau, S. Ammar, F. Fiévet, H.J. Von Bardeleben, A. Mauger, Annealing effects on Zn(Co)O: from para- to ferromagnetic behavior. J. Chem. Mater. 21, 843–855 (2009)
Y.K. Lakshmi, K. Srinivas, B. Sreedhar, M.M. Raja, M. Vithal, P.V. Reddy, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Zn0.9Co0.1O-based diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 749–755 (2009)
V. Pazhanivelu, A. Paul Blessington Selvadurai, R. Murugaraj 2015 Sintering Effect on Structural, Optical and Unusual Magnetic Behaviour in Zn0.95Co0.05O-Based DMS Materials. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28: e2575
G. Srinet, R. Kumar, V. Sajal, Structural, optical, vibrational, and magnetic properties of sol-gel derived Ni doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 033912 (2013)
K. Samanta, P. Bhattacharya, R.S. Katiyar, Microstructural and ferromagnetic properties of Zn1−xCuxO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 113929 (2009)
T.A. Abdel-Baset, M. Abdel-Hafiez, Effect of metal dopant on structural and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 32, 16153–16165 (2021)
R. Elilarassi, G. Chandrasekaran, Synthesis, structural and optical characterization of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 22, 751–756 (2011)
R. Elilarassi, G. Chandrasekaran, Influence of Co-doping on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized using auto-combustion method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 24, 96–105 (2013)
R. Elilarassi, G. Chandrasekaran, Structural, optical and magnetic characterization of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized using solid state reaction method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 21, 1168–1173 (2010)
V. Pazhanivelu, A.P.B. Selvadurai, R. Murugaraj, I. Panneer Muthuselvam, F.C. Chou, Influence of Co ions doping in structural, vibrational, optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 27, 8580–8589 (2016)
G. Vijayaprasath, R. Murugan, T. Mahalingam, G. Ravi, Comparative study of structural and magnetic properties of transition metal (Co, Ni) doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 26, 7205–7213 (2015)
A. Samanta, M.N. Goswami, P.K. Mahapatra, Structural, optical, dielectric, magnetic and magnetoelectric properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 27, 12271–12278 (2016)
S.B. Rana, R.P.P. Singh, Sandeep arya, structural, optical, magnetic and antibacterial study of pure and cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 2660–2672 (2017)
H. Ji, C. Cai, S. Zhou, W. Liu, Structure, photoluminescence, and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 29, 12917–12926 (2018)
S. Chauhan, M. Kumar, S. Chhoker, S.C. Katyal, V.P.S. Awana, Structural, vibrational, optical and magnetic properties of sol-gel derived Nd doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 5102–5110 (2013)
R. Jeyachitra, V. Senthilnathan, T.S. Senthil, Studies on electrical behavior of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared via co-precipitation approach for photo-catalytic application. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 29, 1189–1197 (2018)
J. El Ghoul, Synthesis of vanadium doped ZnO nanoparticles by sol–gel method and its characterization. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 27, 2159–2165 (2016)
R. Slama, J. El Ghoul, I. Ghiloufi, K. Omri, L. El Mir, A. Houas, Synthesis and physico-chemical studies of vanadium doped zinc oxide nanoparticles and its photocatalysis. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 27, 8146–8153 (2016)
S. Kumar, V. Singh, A. Tanwar, Structural, morphological, optical and photocatalytic properties of Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 27, 2166–2173 (2016)
T. Prakash, G. Neri, A. Bonavita, E. Ranjith Kumar, K. Gnanamoorthi, Structural, morphological and optical properties of Bi-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by a microwave irradiation method. J Mater Sci: Mater. Electron. 26, 4913–4921 (2015)
R.K. Sharma, S. Patel, K.C. Pargaie, Synthesis, characterization and properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystals. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 3, 035005 (2012)
S.V. Vegesna, V.J. Bhat, D. Bu¨rger, J. Dellith, I. Skorupa, O.G. Schmidt, H. Schmidt 2020 Sci. Rep. 10: e6698
X. Yan, D. Hu, H. Li, L. Li, X. Chong, Y. Wang, Nanostructure and optical properties of M doped ZnO (M=Ni, Mn) thin films prepared by sol–gel process. Phys. B. 406, 3956–3962 (2011)
M.A. Dar, D. Varshney, Synthesis, structural, optical and dielectric properties of transition metal doped ZnMnO nanoparticles by sol-gel combustion technique. Superlattices Microstruct. 114, 340–354 (2018)
R. Viswanatha, S. Sapra, S.S. Gupta, B. Satpati, P.V. Satyam, B.N. Dev, D.D. Sarma, Synthesis and characterization of Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 6303–6310 (2004)
J. Han, M. Shen, W. Cao, A.M.R. Senos, P.Q. Mantas, Hopping conduction in Mn-doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 67 (2003)
M. Shatnawi, A.M. Alsmadi, I. Bsoul, B. Salameh, M. Mathai, G. Alnawashi, G.M. Alzoubi, F. Al-Dweri, M.S. Bawa’aneh, Influence of Mn doping on the magnetic and optical properties of ZnO nanocrystalline particles. Results Phys. 6, 1064–1071 (2016)
S.K. Neogi, R. Karmakar, A.K. Misra, A. Banerjee, D. Das, S. Bandyopadhyay, Physical properties of antiferromagnetic Mn doped ZnO samples: role of impurity phase. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 346, 130–137 (2013)
S.J.K. Vethanathan, M. Brightson, S.M. Sundar, S. Perumal, Synthesis of Mn doped ZnO nanocrystals by solvothermal route and its characterization. Mater. Chem. Phys. 125, 872–875 (2011)
M.K. Sharma, R.N. Gayen, A.K. Pal, D. Kanjilal, R. Chatterjee, Room temperature ferromagnetism of Mn-doped zinc oxide nanorods prepared by hybrid wet chemical route. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 7259–7266 (2011)
S. Fabbiyola, L.J. Kennedy, A.A. Dakhel, M. Bououdina, J.J. Vijaya, T. Ratnaji, Structural, microstructural, optical and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanostructures. J. Mol. Struct. 1109, 89–96 (2016)
M. Nirmala, P. Smitha, A. Anukaliani, Optical and electrical properties of undoped and (Mn, Co) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by DC thermal plasma method. Superlattices Microstruct. 50, 563–571 (2011)
S. Senthilkumaar, K. Rajendran, S. Banerjee, T.K. Chinic, V. Sengodan, Influence of Mn doping on the microstructure and optical property of ZnO. J. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 11, 6–12 (2008)
M. Nakayama, H. Tanaka, K. Masuko, T. Fukushima, A. Ashida, N. Fujimura, Photoluminescence properties peculiar to the Mn-related transition in a lightly alloyed ZnMnO thin film grown by pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 241908 (2006)
V. Mote, J. Dargad, B. Dole, Effect of Mn doping concentration on structural, morphological and optical studies of ZnO nano-particles. Nanosci. Nanoeng. 1(2), 116–122 (2013)
I. Khan, S. Khan, W. Khan, Temperature-dependent dielectric and magnetic properties of Mn doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 26, 516–526 (2014)
C. Belkhaoui, N. Mzabi, H. Smaoui, Investigations on structural, optical and dielectric properties of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater. Res. Bull. 111, 70–79 (2019)
T. Abdel-Baset, S. Saber, S. El-Sayed, Dielectric relaxations and optical properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 31, 20972–20983 (2020)
Q. Gao, Y. Dai, X. Li, L. Yang, C. Cui, C. Li, Effects of Mn dopant on tuning carrier concentration in Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation technique. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 29, 3568–3575 (2018)
G. Srinet, S. Sharma, B. Prajapati, J.M. Siqueiros, Investigations on the physical properties of Mn-modified ZnO samples prepared by sol-gel route. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 29, 9930–9941 (2018)
N.D. Raskar, D.V. Dake, V.A. Mane, E. Stathatos, U. Deshpande, B. Dole, One step synthesis of vertically grown Mn-doped ZnO nanorods for photocatalytic application. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 30, 10886–10899 (2019)
K. Omri, O.M. Lemine, J. El Ghoul, L. El Mir, Sol–gel synthesis and room temperature ferromagnetism in Mn doped ZnO nanocrystals. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 26, 5930–5936 (2015)
M.K. Satheesan, V. Kumar, Influence of Lithium doping on the correlated ferromagnetic ordering and red shift of band gap in weakly Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 27, 6522–6525 (2016)
P. Norouzzadeh, Kh. Mabhouti, M.M. Golzan, R. Naderali, Comparative study on dielectric and structural properties of undoped, Mn-doped, and Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles by impedance spectroscopy analysis. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 31, 7335–7347 (2020)
R. Khan, C.I. Zulfiqar, L.de Araujo, T. Khan, Muneeb-Ur-Rahman, Zia-Ur-Rehman, A. Khan, B. Ullah, S. Fashu, Influence of oxygen vacancies on the structural, dielectric, and magnetic properties of (Mn, Co) co-doped ZnO nanostructures. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 29, 9785–9795 (2018)
M. Zulfiqar, A. Zubair, T. Khan, N. Hua, S. Ilyas, A.M. Fashu, M.A. Afzal, R. Khan. Safeen, Oxygen vacancies induced room temperature ferromagnetism and enhanced dielectric properties in Co and Mn co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 32, 9463–9474 (2021)
A. Ali Fatima, S. Devadason, T. Mahalingam, Structural, luminescence and magnetic properties of Mn doped ZnO thin films using spin coating technique. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 25, 3466–3472 (2014)
S. Muthukumaran, R. Gopalakrishnan, Structural, optical and photoluminescence studies of heavily Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles annealed under Ar atmosphere. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23, 1393–1401 (2012)
S.M. Mousavi, A.R. Mahjoub, R. Abazari, Facile green fabrication of nanostructural Ni-doped ZnO hollow sphere as an advanced photocatalytic material for dye degradation. J. Mol. Liq. 242, 512–519 (2017)
S. Aksoy, Y. Caglar, Synthesis of Mn doped ZnO nanopowders by MW-HTS and its structural, morphological and optical characteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 781, 929–935 (2019)
P. Norouzzadeh, Kh. Mabhouti, M.M. Golzan, R. Naderali, Comparative study on dielectric and structural properties of undoped Mn-doped, and Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles by impedance spectroscopy analysis. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 31, 7335–7347 (2020)
K.V. Chandekar, M. Shkir, A. Khan, B.M. Al-Shehri, M.S. Hamdy, S. AlFaify, M.A. El-Toni, A. Aldalbahi, A.A. Ansari, H. Ghaithan, A facile one-pot flash combustion synthesis of La@ZnO nanoparticles and their characterizations for optoelectronic and photocatalysis applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 395, 112465 (2020)
K.V. Mohd Shkir, Badria M. Chandekar, A. Alshehri, S. AlFaify. Khan, Mohamed S. Hamdy, A remarkable enhancement in photocatalytic activity of facilely synthesized Terbium@Zinc oxide nanoparticles by flash combustion route for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 1811–1823 (2020)
M.S. Hamdy, K.V. Chandekar, Mohd. Shkir, S. AlFaify, Essam H. Ibrahim, Zubair Ahmad, Mona Kilany, Badria M. Al-Shehri, Khadijah S. Al-Namshah, Novel Mg@ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by facile one-step combustion route for anti-microbial, cytotoxicity and photocatalysis applications. J Nanostruct Chem. 11, 147–163 (2021)
K.V. Chandekar, M. Shkir, B.M. Al-Shehri, S. AlFaify, R.G. Halor, A. Khan, K.S. Al-Namshah, M.S. Hamdy, Visible light sensitive Cu doped ZnO: facile synthesis, characterization and high photocatalytic response. Mater. Charact. 165, 110387 (2020)
K.V. Chandekar, Mohd. Shkir, S. AlFaify, Badria M. Al-Shehri, Khadijah S. Al-Namshah, Mohamed S. Hamdy, A noticeable consistent improvement in photocatalytic efficiency of hazardous textile dye through facile flash combustion synthesized Li-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 32, 3437–3450 (2021)
T.C. Damen, S.P.S. Porto, B. Tell, Raman effect in zinc oxide. Phys Rev 142, 570 (1966)
F. Decremps, J. Pellicer-Porres, A.M. Saitta, J.C. Chervin, A. Polian, High-pressure Raman spectroscopy study of wurtzite ZnO. Phys. Rev. B. 65, 092101 (2002)
R. Jothilakshmi, V. Ramakrishnan, R. Thangavel, J. Kumar, A. Saruac, M. Kuball, Micro-Raman scattering spectroscopy study of Li-doped and undoped ZnO needle crystals. J. Raman Spectrosc. 40, 556–561 (2009)
S. Guo, Z. Du, S. Dai, Analysis of Raman modes in Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystals. Phys. Status Solidi B 246, 2329–2332 (2009)
L. Yang, Y. Tang, A. Hu, X. Chen, K. Liang, L. Zhang, Raman scattering and luminescence study on arrays of ZnO doped with Tb3+. Phys B. 403, 2230–2234 (2008)
G.L. Kabongo, G.H. Mhlongo, T. Malwela, B.M. Mothudi, K.T. Hillie, M.S. Dhlamini, Microstructural and photoluminescence properties of sol–gel derived Tb3+ doped ZnO nanocrystals. J Alloy Compd. 591, 156–163 (2014)
D. Montenegro, V. Hortelano, O. Martínez, M. Martínez-Tomas, V. Sallet, V. Muñoz Sanjosé, J. Jiménez, Non-radiative recombination centres in catalyst-free ZnO nanorods grown by atmospheric-metal organic chemical vapour deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46, 235302 (2013)
K. Samanta, P. Bhattacharya, R.S. Katiyar, W. Iwamoto, P.G. Pagliuso, C. Rettori, Raman scattering studies in dilute magnetic semiconductor Zn1−xCoxO. Phys. Rev. B. 73, 245213 (2006)
J. Li, F. Luo, Q. Zhao, Z. Li, H. Yuanb, D. Xiao, Coprecipitation fabrication and electrochemical performances of coral-like mesoporous NiO nanobars. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 4690–4697 (2014)
M. Robles-Águila, J. Luna-López, Á. Hernández de la Luz, J. Martínez-Juárez, M. Rabanal, Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 8, 406 (2018)
F. Kubelka, Munk, A contribution to the optics of pigments. Z. Tech. Phys. 12, 593–599 (1931)
G. Kortum, W. Braun, G. Herzog, Principles and techniques of diffuse-reflectance spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2, 333–341 (1963)
A.E. Morales, E.S. Mora, U. Pal, Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Revista Mexicana de Fisica S. 53, 18–22 (2007)
X. Zhao, J.Y. Lee, C.R. Kim, J.H. Heo, C.M. Shin, J.Y. Leem, H. Ryu, J.H. Chang, H.C. Lee, W.G. Jung, C.S. Son, B.C. Shin, W.J. Lee, S.T. Tan, J. Zhao, X. Sun, Dependence of the properties of hydrothermally grown ZnO on precursor concentration. Physica E 41, 1423 (2009)
A.A. Manoharan, R. Chandramohan, K.D.A. Kumar, S. Valanarasu, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, H. Algarni, S. AlFaify, Transition metal (Mn) and rare earth (Nd) di-doped novel ZnO nanoparticles: a facile sol–gel synthesis and characterization. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 13077–13086 (2018)
K. Sakai, T. Kakeno, T. Ikari, S. Shirakata, T. Sakemi, K. Awai, T. Yamamoto, Defect centers and optical absorption edge of degenerated semiconductor ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 043508–043514 (2006)
Y. Sun, N.G. Ndifor-Angwafor, D.J. Riley, M.N.R. Ashfold, Synthesis and photoluminescence of ultra-thin ZnO nanowire/ nanotube arrays formed by hydrothermal growth. Chem. Phys. Lett. 431, 352–357 (2006)
I. Hamberg, C.G. Granqvist, Evaporated Sn-doped In2O3 films: basic optical properties and applications to energy-efficient windows. J. Appl. Phys. 60, R123–R160 (1986)
D. Zhao, S. Xu, M. Xie, S. Tong, H. Yang, Stress and its effect on optical properties of GaN epilayers grown on Si (111), 6H-SiC (0001), and c-plane sapphire. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 677–679 (2003)
R.B. Bylsma, W.M. Becker, J. Kossut, U. Debska, D. Yoder-Short, Dependence of energy gap on x and T in Zn1-xMnxSe: The role of exchange interaction. Phys. Rev. B. 33, 8207–8215 (1986)
P. Koidl, Optical absorption of Co2+ in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B. 15, 2493–2499 (1977)
B. Halperin, M. Lax, Impurity-band tails in the high-density limit. I. Minimum counting methods. Phys. Rev 148(2), 722–740 (1966)
H. Zeng, G. Duan, Y. Li, S. Yang, X. Xu, W. Cai, Blue luminescence of ZnO nanoparticles based on non-equilibrium processes: defect origins and emission controls. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20(4), 561–572 (2010)
R. Kripal, A.K. Gupta, R.K. Srivastava, S.K. Mishra, Photoconductivity and photoluminescence of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via co-precipitation method, Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 79(5), 1605–1612 (2011)
P. Li, S. Wang, J. Li, Y. Wei, Structural and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanocrystallites prepared by a one-step solution route. J. Lumin. 132, 220–225 (2012)
A.A. Letailleur, S.Y. Grachev, E. Barthel, E. Søndergard, K. Nomenyo, C. Couteau, S.M. Murtry, G. Le´rondel, E. Charlet, E. Peter, High efficiency white luminescence of alumina doped ZnO. J. Lumin. 131, 2646–2651 (2011)
S. Anandan, A. Vinu, K.L.P. Sheeja Lovely, N. Gokulakrishnan, P. Srinivasu, T. Mori, V. Murugesan, V. Sivamurugan, K. Ariga, Photocatalytic activity of La-doped ZnO for the degradation of monocrotophos in aqueous suspension. J Mol Catal A Chem 266, 149–157 (2007)
P.K. Sharma, A.C. Pandey, G. Zolnierkiewicz, N. Guskos, C. Rudowicz, Relationship between oxygen defects and the photoluminescence property of ZnO nanoparticles: a spectroscopic view. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 094314 (2009)
J. Liu, X. Huang, Y. Li, Q. Zhong, L. Ren, Preparation and photoluminescence of ZnO complex structures with controlled morphology. Mater. Lett. 60, 1354–1359 (2006)
S. Bayan, D. Mohanta, Defect mediated optical emission of randomly oriented ZnO nanorods and unusual rectifying behavior of schottky nanojunctions. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 054316 (2011)
S. Mahamuni, K. Borgohain, B.S. Bendre, Spectroscopic and structural characterization of electrochemically grown ZnO quantum dots. J. Appl. Phys. 85, 2861 (1999)
K. Ravichandrana, R. Rathia, M. Baneto, K. Karthika, P.V. Rajkumar, B. Sakthivel, R. Damodaran, Effect of Fe+F doping on the antibacterial activity of ZnO powder. Ceram. Int. 41, 3390–3395 (2015)
K. Vanheusden, W.L. Warren, C.H. Seager, D.R. Tallant, J.A. Voigt, B.E. Gnade, Mechanisms behind green photoluminescence in ZnO phosphor powders. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 7983–7990 (1996)
A. Azam, A.S. Ahmed, M.S. Ansari, A.H. Naqvi, Study of electrical properties of nickel doped SnO2 ceramic nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 506, 237–242 (2010)
K.W. Wagner, Zur theorie der unvollkommenen dielektrika. Ann Phys. 345, 817–855 (1913)
R. Zamiri, A. Kaushal, A. Rebelo, J.M.F. Ferreira, Er doped ZnO nanoplates: synthesis, optical and dielectric properties. Ceram. Int. 40, 1635–1639 (2014)
K.V. Chandekar, M. Shkir, A. Khan, S. AlFaify, An in-depth study on physical properties of facilely synthesized Dy@CdS NPs through microwave route for optoelectronic technology. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 118, 105184 (2020)
S.M. Sze, K.K. Ng, Physics of semiconductor devices (Wiley, Hoboken, 2006)
D. Varshney, S. Dwivedi 2015 3d transition metal doped Zn0.95Tm0.05O (Tm = Mn, Co, Ni, Cu): structure, microstructure, Raman, dielectric constant and magnetism. Mater. Res. Express 2, e106102
M. Ashokkumar, S. Muthukumaran, Effect of Ni doping on electrical, photoluminescence and magnetic behavior of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 162, 97–103 (2015)
X. Li, X. Cao, L. Xu, L. Liu, Y. Wang, C. Meng, Z. Wang, High dielectric constant in Al-doped ZnO ceramics using high-pressure treated powders. J. Alloys Compd. 657, 90–94 (2016)
A.K. Jonscher’s, The universal’ dielectric response. Nature. 267, 673–679 (1977)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia for funding this work through Research Groups Program under Grant No. R.G.P.2/160/42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kamlesh V. Chandekar, Mohd. Shkir, S.P. Yadav, and Pravata Kumar Behera contributed to conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, and writing and preparation of the original draft; Mohd. Shkir and S. AlFaify contributed to funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandekar, K.V., Shkir, M., Yadav, S.P. et al. Facile synthesis of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles by flash combustion route and their characterizations for optoelectronic applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 3849–3869 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07576-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07576-w