Abstract
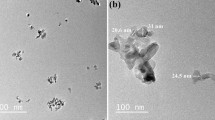
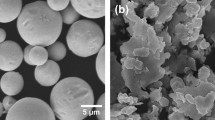
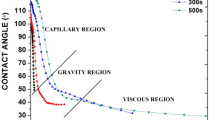
High entropy alloy (HEA) receives noticeable attention in the electronic industry, and one of the best ways to incorporate HEA with the existing assembly setup is to reinforce HEA particles in Pb-free solder. This paper investigates the properties of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu (SAC 305) solder reinforced with HEA particles. FeCoCrNiCu particle was synthesized via ball milling and dispersed in SAC 305 paste by powder mixing technique. DSC analysis confirms a reduction in melting temperature and undercooling with the addition of HEA. The dispersion of HEA in the solder resulted in a significant refinement in β-Sn grain size, Ag3Sn, and Cu6Sn5 IMC particle size. Also, SAC 305 with 0.2 wt% HEA noted a better spreading performance and lowest contact angle. 1608 chip capacitor/HEA reinforced solder joint was assembled, subjected to − 40 to + 125 °C thermal shock, and tested for the shear strength. The reliability analyzed through Weibull analysis showed a 30% increase in the 75% survival probability strength for HEA-added joints. Also, HEA addition till 0.1 wt% suppressed the growth of (Cu, Ni)6Sn5 IMC after thermal shock cycles. After 1000 thermal shock cycles, 0.1 wt% HEA-added solder retained the shear strength of 22.5 MPa, equivalent to the strength exhibited by the SAC 305 in the as-reflow condition.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available upon reasonable request.
Change history
13 April 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08179-9
References
S. Wang, C. Liu, Study of interaction between Cu–Sn and Ni–Sn interfacial reactions by Ni–Sn3.5Ag–Cu sandwich structure. J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1303–1309 (2003)
X. Liu, M. Huang, N. Zhao, L. Wang, Liquid-state and solid-state interfacial reactions between Sn–Ag–Cu–Fe composite solders and Cu substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 328–337 (2014)
D.C. Lin, T.S. Srivatsan, G.-X. Wang, R. Kovacevic, Microstructural development in a rapidly cooled eutectic Sn–3.5% Ag solder reinforced with copper powder. Powder Technol. 166, 38–46 (2006)
Y. Liu, K.N. Tu, Low melting point solders based on Sn, Bi, and In elements. Mater. Today Adv. 8, 100115 (2020)
P.T. Vianco, K.L. Erickson, P.L. Hopkins, Solid state intermetallic compound growth between copper and high temperature, Tin-rich solders part I: experimental analysis. J. Electron. Mater. 23(721), 721–727 (1994)
S. Tikale, K.N. Prabhu, Bond shear strength of Al2O3 nanoparticles reinforced 2220-capacitor/SAC305 solder interconnects reflowed on bare and Ni-coated copper substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 2865–2886 (2021)
A. Lis, C. Kenel, C. Leinenbach, Characteristics of reactive Ni3Sn4 formation and growth in Ni–Sn interlayer systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47, 2596–2608 (2016)
M. Huang, F. Yang, Size effect model on kinetics of interfacial reaction between Sn-xAg-yCu solders and Cu substrate. Sci Rep 4, 7117 (2014)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, M. Paulasto-Kröckel, Impurity and alloying effects on interfacial reaction layers in Pb-free soldering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 68, 1–38 (2010)
L. Zhang, K.N. Tu, Structure and properties of lead-free solders bearing micro and nano particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 82, 1–32 (2014)
P. Yao, J. Ping, Liu, Effects of multiple reflows on intermetallic morphology and shear strength of SnAgCu–xNi composite solder joints on electrolytic Ni/Au metallized substrate. J. Alloy. Compd. 462, 73–79 (2008)
F. Cheng, H. Nishikawa, T. Takemoto, Microstructural and mechanical properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solders with minor addition of Ni and/or Co. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 3643–3648 (2008)
S.L. Tay, A.S.M.A. Haseeb, M.R. Johan, Effect of addition Cobalt nanoparticles on Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder, 2010, in 12th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference, (2010), pp. 433-436
G. Sujan, A. Haseeb, A. Afifi, Effects of metallic nanoparticle doped flux on the interfacial intermetallic compounds between lead-free solder ball and copper substrate. Mater Charact. 97, 199–209 (2014)
A. Yakymovych, P. Švec, L. Orovcik, O. Bajana, H. Ipser, Nanocomposite SAC Solders: the effect of adding Ni and Ni–Sn nanoparticles on morphology and mechanical properties of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solders. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 117–123 (2018)
S. Tikale, K.N. Prabhu, Performance and reliability of Al2O3 nanoparticles doped multicomponent Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu–Ni–Ge solder alloy. Microelectron. Reliab. 113(1–14), 113933 (2020)
S.H. Rajendran, S.J. Hwang, J.P. Jung, Shear strength and aging characteristics of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu/Cu solder joint reinforced with ZrO2 nanoparticles. Metals 10, 1295 (2020)
S. Nai, J. Wei, M. Gupta, Effect of carbon nanotubes on the shear strength and electrical resistivity of a lead-free solder. J. Electron. Mater. 37, 515–522 (2008)
M.H. Tsai, J.W. Yeh, High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2, 107–123 (2014)
K.-Y. Tsai, M.-H. Tsai, J.-W. Yeh, Sluggish diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 61(3), 4887–4897 (2013)
J. Peng, L. Fu, Y. Sun, Z. Li, X. Ji, A. Shan, Thermal expansion-adjustable carbon-doped FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloys for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 19366–19380 (2020)
Y. Liu, L. Pu, Y. Yang, Q. He, Z. Zhou, C. Tan, X. Zhao, Q. Zhang, K.N. Tu, A high-entropy alloy as very low melting point solder for advanced electronic packaging. Mater. Today Adv. 7, 100101 (2020)
L. Pu, Y. Liu, Y. Yang, Q. He, Z. Zhou, X. Zhao, C. Tan, K.N. Tu, Effect of adding Ag to the medium entropy SnBiIn alloy on intermetallic compound formation. Mater. Lett. 272, 127891 (2020)
Y.-A. Shen, H.-M. Hsieh, S.-H. Chen, J. Li, S.-W. Chen, H. Nishikawa, Investigation of FeCoNiCu properties: thermal stability, corrosion behavior, wettability with Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu and interlayer formation of multi-element intermetallic compound. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.148931
JIS: Test methods for soldering fluxes, JIS Z 3197:2012, (Japanese Standards Association, 2012)
JEDEC, Test methods for temperature cycling, JESD22-A-104F, Joint Electron Device Engineering Council (Solid State Technology Association, 2020)
S. Praveen, B.S. Murty, R.S. Kottada, Alloying behavior in multi-component AlCoCrCuFe and NiCoCrCuFe high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 534, 83–89 (2012)
R. SreeGanji, P.S. Karthik, K.B.S. Rao, K.V. Rajulapati, Strengthening mechanisms in equiatomic ultrafine grained AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy studied by micro- and nanoindentation methods. Acta Mater. 125, 58–68 (2017)
A. Kumar, P. Dhekne, A.K. Swarnakar, M. Chopkar, Phase evolution of CoCrCuFeNiSix high-entropy alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Res. Express 6, 026532 (2019)
S. Singh, S.M. Shaikh, M.K. PunithKumar, B.S. Murty, C. Srivastava, Microstructural homogenization and substantial improvement in corrosion resistance of mechanically alloyed FeCoCrNiCu high entropy alloys by incorporation of carbon nanotubes. Materialia 14, 100917 (2020)
R.-F. Zhao, B. Ren, G.-P. Zhang, Z.-X. Liu, J.-J. Zhang, Phase transition of as-milled and annealed CrCuFeMnNi high-entropy alloy powder. NANO Brief Rep. Rev. 9, 1850100 (2018)
V. Shivam, J. Basu, V.K. Pandey, Y. Shadangi, N.K. Mukhopadhyay, Alloying behaviour, thermal stability and phase evolution in quinary AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Adv. Powder Technol. 9, 2221–2230 (2018)
Y. Xie, D. Zhou, Y. Luo, T. Xia, W. Zeng, C. Li, J. Wang, D. Zhang, Fabrication of CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy matrix composites by thermomechanical consolidation of a mechanically milled powder. Mater. Charact. 148, 307–316 (2019)
Z. Fu, W. Chen, H. Wen, D. Zhang, Z. Chen, B. Zheng, Y. Zhou, E. J.Lavernia, Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms in an FCC structured single-phase nanocrystalline Co25Ni25Fe25Al7.5Cu17.5 high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater 107, 59–71 (2016)
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater Sci. 46, 1–184 (2001)
S.A. Belyakov, C.M. Gourlay, The influence of Cu on metastable NiSn4 in Sn–3.5Ag–xCu/ENIG joints. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 12–20 (2016)
M.C. Troparevsky, J.R. Morris, P.R.C. Kent, A.R. Lupini, Malcolm stocks, criteria for predicting the formation of single-phase high-entropy alloys. Phys. Rev. X 5, 011041 (2015)
A.A. El-Daly, A. Fawzy, S.F. Mansour, M.J. Younis, Thermal analysis and mechanical properties of Sn–1.0Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy after modification with SiC nano-sized particles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 2976–2988 (2013)
S.K. Kang, W.K. Choi, D.-Y. Shih, D.W. Henderson, T. Gosselin, A. Sarkhel, C. Goldsmith, Puttlitz, Ag3Sn plate formation in the solidification of near-ternary eutectic Sn–Ag–Cu. JOM 55, 61–65 (2003)
P.T. Vianco, A review of interface microstructures in electronic packaging applications: soldering technology. JOM 71, 158–177 (2019)
H. Sun, Y.C. Chan, F. Wu, Reliability performance of tin–bismuth–silver (Sn57.6Bi0.4Ag) solder joints with different content of carbon nano-tubes (CNTs) or nickel (Ni)-modified CNTs. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 8584–8593 (2018)
M. Hosking, F.G. Yost, The Mechanics of Solder Alloy Wetting and Spreading (Springer, Berlin, 1993)
M. Said, A.A. Mohammad, Wettability, microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy prepared by reflow oven and susceptor-assisted microwave. AIP Conf. Proc. 2267, 020004 (2020)
T. Lu, D. Yi, H. Wang, X. Tu, B. Wang, Microstructure, mechanical properties and interface reaction with Cu substrate of Zr-modified SAC 305 solder. J. Alloys Compd. 781, 633–643 (2019)
H.T. Lee, Y.H. Lee, Effects of in-situ nickel particle addition on the microstructure and microhardness of Sn–Ag solder. Sci. Technol. Weld Join. 3, 353–360 (2005)
Y.W. Wang, C.R. Kao, Minor Fe, Co, and Ni additions to SnAgCu solders for retarding Cu3Sn growth, in 2008 International Conference on Electronic Materials and Packaging, (2008), pp. 76-79
J. Banga, D.-Y. Yu, Y.-H. Ko, J.-H. Son, H. Nishikawa, C.-W. Lee, Intermetallic compound growth between Sn–Cu–Cr lead-free solder and Cu Substrate. Microelectron. Reliab. 99, 62–73 (2019)
L. Xu, J.H.L. Pang, F.X. Che, Intermetallic Growth and Failure Study for Sn-Ag-Cu/ENIG PBGA Solder Joints Subject to Thermal Cycling, in Proceedings Electronic Components and Technology, 2005. ECTC ‘05., (2005), pp. 682–686. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC.2005.1441342
S.W. Chen, S.H. Wu, S.W. Lee, Interfacial reactions in the Sn–(Cu)/Ni, Sn–(Ni)/Cu, and Sn/(Cu,Ni) systems. J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1188–1194 (2003)
C.E. Ho, S.C. Yang, C.R. Kao, Interfacial reaction issues for lead-free electronic solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18, 155–174 (2007)
X. Deng, G. Piotrowski, J.J. Williams, N. Chawla, Influence of initial morphology and thickness of Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn intermetallics on growth and evolution during thermal aging of Sn–Ag solder/Cu joints. J. Electron. Mater. 12, 1403–1413 (2003)
K.N. Tu, R.D. Thompson, Kinetics of interfacial reaction in bimetallic Cu3Sn thin films. Acta Metall. 30, 947–952 (1982)
Y. Tian, X. Liu, J. Chow, Y.P. Wu, S.K. Sitaraman, Comparison of Sn–Ag–Cu solder alloy intermetallic compound growth under different thermal excursions for fine-pitch flip-chip assemblies. J. Electron. Mater. 8(42), 2724–2731 (2013)
T.-K. Lee, C.-U. Kim, T.R. Bielerd, Influence of high-G mechanical shock and thermal cycling on localized recrystallization in Sn–Ag–Cu solder interconnects. J. Electron. Mater. 1, 69–79 (2014)
N.M. Poon, C.M.L. Wu, J.K.L. Lai, Y.C. Chan, Residual shear strength of Sn–Ag and Sn–Bi lead-free SMT joints after thermal shock. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 4, 708–714 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/6040.883762
T. An, F. Qin, Intergranular cracking simulation of the intermetallic compound layer in solder joints. Comput. Mater. Sci. 79, 1–14 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. NRF-2020R1A2C1009851).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SHR Methodology, Formal analysis, Conceptualization, writing—original draft, review & editing; DHJ Resources; JPJ Supervision and Funding.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajendran, S.H., Jung, D.H. & Jung, J.P. Investigating the physical, mechanical, and reliability study of high entropy alloy reinforced Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder using 1608 chip capacitor/ENIG joints. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 3687–3710 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07562-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07562-2