Abstract
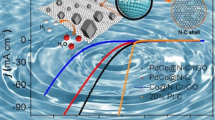
Massive efforts have been made to achieve highly efficient electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen production via water splitting. Here, a three-dimentional (3D) reduced graphene oxide carbon nanotubes (CNTs/rGO) framework for anchoring molybdenum phosphide nanoparticles is reported for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) with high performance. The enhanced electrocatalytic activity is attributed to the plenty of factors: the hierarchical 3D structure of rGO sheets and CNTs with rich active sites, the uniform distribution of RuP2 nanoparticles, chemical bonding character of RuP2 and carbon support, and the interfacial electric effect among different components. The RuP2 anchored on CNTs/rGO with mass ratio of 5:2 exhibit the low onset potential of -14.7 V vs. RHE and the lowest overpotential of 50.1 mV at 10 mA cm−2 in corrosive acidic electrolyte, which are comparable to those of commercial Pt/C (20 wt%). The CNTs in the CNTs/rGO framework can contribute to the well-distribution of RuP2 and rGO sheets and further facilitate the high-rate electron transfer, which will effectively promote the electrocatalytic activity for HER.







Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
N.D. Laws, B.P. Epps, Hydrokinetic energy conversion: Technology, research, and outlook. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 57, 1245–1259 (2016)
J.J. Spivey, Catalysis in the development of clean energy technologies. Catal. Today 100, 171–180 (2005)
R. Sipahutar, S.M. Bernas, M.S. Imanuddin, Renewable energy and hydropower utilization tendency worldwide. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 17, 213–215 (2013)
J.A. Turner, Sustainable hydrogen production. Science 305, 972–974 (2004)
N. Armaroli, V. Balzani, The hydrogen issue. Chem. Sus. Chem. 4, 21–36 (2011)
J.D. Holladay, J. Hu, D.L. King, Y. Wang, An overview of hydrogen production technologies. Catal. Today 139, 244–260 (2009)
Y. Zheng, Y. Jiao, Y.H. Zhu, L.H. Li, H. Yu, Y. Han, Y. Chen, A.J. Du, Hydrogen evolution by a metal-free electrocatalyst. Nat. Commun. 5, 3783 (2014)
X. Zou, Y. Zhang, Noble metal-free hydrogen evolution catalysts for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 5148–5180 (2015)
M.Z. Rahman, M.G. Kibria, C.B. Mullins, Metal-free photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 1887–1931 (2020)
N. Dubouis, A. Grimaud, The hydrogen evolution reaction: from material to interfacial descriptors. Chem. Sci. 10, 9165–9181 (2019)
H. Du, R.M. Kong, X. Guo, F. Qu, J. Li, Recent progress in transition metal phosphides with enhanced electrocatalysis for hydrogen evolution. Nanoscale 10, 21617–21624 (2018)
H. Xu, H.Y. Shang, C. Wang, Y.K. Du, Ultrafine Pt-based nanowires for advanced catalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2000793 (2020)
X.S. Wang, Q. He, L. Song, M. Jaroniec, Breaking the volcano-plot limits for Pt-based electrocatalysts by selective tuning adsorption of multiple intermediates. J. Mater Chem. A 7, 13635–13640 (2019)
F. Guom, Z. Zou, Z. Zhang, T. Zeng, Y. Tan, R. Chen, W. Wu, N.C. Cheng, X.L. Sun, Confined sub-nanometer PtCo clusters as a highly efficient and robust electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. 9, 5468–5474 (2021)
C.J. Li, Y. Xu, D. Yang, D.D. Yang, X.J. Chai, Z.Q. Wang, Boosting electrocatalytic activities of Pt-based mesoporous nanoparticles for overall water splitting by a facile Ni, P Co-incorporation strategy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 9709–9716 (2019)
Y.D. Niu, X. Qian, C. Xu, H.Y. Liu, W.M. Wu, L.X. Hou, Cu-Ni-CoSex quaternary porous nanocubes as enhanced Pt-free electrocatalysts for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells and hydrogen evolution in alkaline medium. Chem. Eng. J. 357, 11–20 (2019)
B. Owens-Baird, Structure-activity relationships for Pt-free metal phosphide hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 24, 7298–7311 (2018)
M.D. Bhatt, J.Y. Lee, Advancement of platinum (Pt)-free (non-Pt precious metals) and/or metal-free (non-precious-metals) electrocatalysts in energy applications: a review and perspectives. Energy Fuel 34, 6634–6695 (2020)
Y. Liu, X. Li, Q.H. Zhang, W.D. Li, Y. Xie, H.Y. Liu, L. Shang, Z.Y. Liu, Z.M. Chen, L. Gu, Z.Y. Tang, T.R. Zhang, S.Y. Lu, A general route to prepare low-ruthenium-content bimetallic electrocatalysts for pH-universal hydrogen evolution reaction by using carbon quantum dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 1718–1726 (2020)
L. Bai, Z.Y. Duan, X.D. Wen, R. Si, Q.Q. Zhang, J.Q. Guan, Highly dispersed ruthenium-based multifunctional electrocatalyst. ACS Catal. 9, 9897–9904 (2019)
S.Y. Bae, J. Mahmood, I.Y. Jeon, J.B. Baek, Recent advances in ruthenium-based electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale Horiz. 5, 43–56 (2020)
W.D. Li, Z.H. Wei, B.Y. Wang, Y. Liu, H.Q. Song, Z.Y. Tang, B. Yang, S.Y. Lu, Carbon quantum dots enhanced the activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction in ruthenium-based electrocatalysts. Mater. Chem. Front. 4, 277–284 (2020)
T.J. Qiu, Z.B. Liang, W.H. Guo, S. Gao, C. Qu, H. Tabassum, H. Zhang, B.J. Zhu, R.Q. Zou, Y. Shao-Horn, Highly exposed ruthenium-based electrocatalysts from bimetallic metal-organic frameworks for overall water splitting. Nano Energy 58, 1–10 (2019)
J.W. Su, Y. Yang, G.L. Xia, J.T. Chen, P. Jiang, Q.W. Chen, Ruthenium-cobalt nanoalloys encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene as active electrocatalysts for producing hydrogen in alkaline media. Nat. Commun. 8, 16028 (2017)
H. Song, T. Cheng, B. Li, Y. Fan, B. Liu, Z. Tang, S. Lu, Carbon dots and RuP2 nanohybrid as an efficient bifunctional catalyst for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction and hydrolysis of ammonia borane. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 8, 3995–4002 (2020)
J.S. Li, M.J. Huang, Y.W. Zhou, X.N. Chen, S. Yang, J.Y. Zhu, G.D. Liu, L.J. Ma, S.H. Cai, J.Y. Han, RuP2-based hybrids derived from MOFs: highly efficient pH-universal electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 12276–12282 (2021)
J.S. Li, J.Y. Li, M.J. Huang, L.X. Kong, Z.X. Wu, Anchoring RuxP on 3D hollow graphene nanospheres as efficient and pH-universal electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Carbon 161, 44–50 (2020)
Z.H. Pu, I.S. Amiinu, Z.K. Kou, W.Q. Li, S.C. Mu, RuP2-based catalysts with platinum-like activity and higher durability for the hydrogen evolution reaction at all pH values. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 11559–11564 (2017)
A.K. Geim, Graphene: status and prospects. Science 324, 1530–1534 (2009)
X. Huang, X.Y. Qi, F. Boey, H. Zhang, Graphene-based composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 666–686 (2012)
V. Berry, Impermeability of graphene and its applications. Carbon 62, 1–10 (2013)
S. Pei, H.M. Cheng, The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 50, 3210–3228 (2012)
Y. Wang, S.S. Li, H.Y. Yang, J. Luo, Progress in the functional modification of graphene/graphene oxide: A review. RSC. Adv. 10, 15328–15345 (2020)
R. Tarcan, O. Todor-Boer, I. Petrovai, C. Leordean, S. Astilean, L. Botiz, Reduced graphene oxide today. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 1198–1224 (2020)
J. Yan, G. Zhi, D.Z. Kong, H. Wang, T.T. Xu, J.H. Zang, W.X. Shen, J.M. Xu, Y.M. Shi, S.G. Dai, X.J. Li, Y. Wang, 3D printed rGO/CNT microlattice aerogel for a dendrite-free sodium metal anode. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 19843–19854 (2020)
M. Chen, Z. Liu, X. Zhang, A. Zhong, W. Qin, W. Liu, Y. Liu, In-situ phosphatizing of cobalt-molybdenum nanosheet arrays on self-supporting rGO/CNTs film as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 422, 130355 (2021)
C. Tang, K. Zhao, Y.F. Tang, F.P. Li, Q.N. Meng, Forest-like carbon foam templated rGO/CNTs/MnO2 electrode for high-performance supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 375, 137960 (2021)
D.C. Marcano, D.V. Kosynkin, J.M. Berlin, A. Sinitskii, Z.Z. Sun, A. Slesarev, L.B. Alemany, W. Lu, J.M. Tour, Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4, 4806–4814 (2010)
X.L. Li, Y.Q. Liu, L. Fu, L.C. Cao, D.C. Wei, Y. Wang, Efficient synthesis of carbon nanotube–nanoparticle hybrids. Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 2431–2437 (2006)
E. Picheau, A. Impellizzeri, D. Rybkovskiy, M. Bayle, J.Y. Mevellec, F. Hof, H. Saadaoui, L. Noe, A.C.T. Dias, J.L. Duvail, Intense Raman D band without disorder in flattened carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 15, 596–603 (2021)
H.Q. Song, Y.J. Cheng, B.J. Li, Y.P. Fan, B.Z. Liu, Z.Y. Tang, S.Y. Lu, Carbon dots and RuP2 nanohybrid as an efficient bifunctional catalyst for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction and hydrolysis of ammonia borane. ACS Sust. Chem. Eng. 8, 3995–4002 (2020)
T. Liu, S. Wang, Q. Zhang, L. Chen, W. Hu, C.M. Li, Ultrasmall Ru2P nanoparticles on graphene: a highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst in both acidic and alkaline media. Chem. Commun. 54, 3343–3346 (2018)
C.H. Liu, L. Sun, L.L. Luo, W.C. Wang, H.L. Dong, Z.D. Chen, Integration of Mo2C/MoC heterojunction for multi-process strategy toward highly-active hydrogen evolution in acidic and alkaline conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 13, 22646–22654 (2021)
Y. Wang, Z. Ge, X. Li, J.P. Zhao, B. Ma, Y.T. Chen, Cu2S nanorod arrays with coarse surfaces to enhance the electrochemically active surface area for water oxidation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 567, 308–315 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (22178031) , Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges of Changzhou (CZ20210036), Scientific Research Foundation of Jiangsu Provincial Education Department (21KJA480001), the Top-notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (TAPP), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and Qinglan Project Foundation of Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL, ZL, and LZ contribute to the preparation and data collections. WX and TZ contribute to the materials characterizations. CL and ZC contribute to the critical revision, Project administration, and Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, L., Liu, C., Li, Z. et al. Anchoring ultrafine molybdenum phosphide on hierarchical three-dimensional CNTs/rGO framework as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 3175–3185 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07519-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07519-5