Abstract
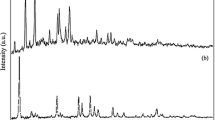
CuInS2 (CIS) thin films with petal-like nanostructures were synthesized in situ on copper substrates through a facile, one-step solvothermal method using InCl3 and thioacetamide ethylene glycol solution. In order to reveal the growth mechanism of CIS petal-like nanostructures, we synthesized CIS thin films with different morphologies at various reaction times. CIS thin films had a petal-like nanostructure. The petal possesses the preferentially exposed (222) facet, which becomes bigger and thicker as the increase of the reaction time. CIS petal-like nanostructures exhibited excellent light absorption properties. The average light absorption value of CIS synthesized at a reaction time of 4 h reached to 96.5%, and the minimum light absorption value even reached to 92% for that synthesized at a reaction time of 10 h. The CIS petal-like nanostructures synthesized at a reaction time of 4 h exhibit a band gap of 1.58 eV, which is much larger than that of the corresponding bulk material (1.04 eV). Furthermore, the band gap of CIS petal-like nanostructure decreases with increasing reaction time due to the increased “petal” thickness. All these results showed that the light absorption properties and band gap of CIS petal-like nanostructures can be adjusted by controlling the reaction time, which also indicated the application advantages of CIS petal-like nanostructures in photovoltaic and photocatalysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
Y. Kwon, J. Seo, Y. Kang, D. Kim, J. Kim, Opt. Express 26, A30–A38 (2018)
A.H. Hu, J. Zhou, P.J. Zhong, X.Y. Qin, M.F. Zhang, Y.X. Jiang, X.Z. Wu, D.R. Yang, Sol. Energy 214, 319–325 (2021)
Y. Cao, W.W. Li, Z. Liu, Z.Q. Zhao, Z.Y. Xiao, W. Zi, N.A. Cheng, CrystEngComm. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CE01566K
M. Li, R.J. Zhao, Y.J. Su, Z. Yang, Y.F. Zhang, Nanoscale. 8, 8559-8567 (2016)
L.Q. Li, W.X. Zhang, P. Li, Cryst. Res. Technol. 1–5, 1900178 (2020)
L.Q. Li, M. Li, P. Li, Mater. Charact. 172, 110900 (2021)
R. Inguanta, P. Livreri, S. Piazza, C. Sunseri, Solid-State Lett 13, k22–k25 (2010)
J.S. Luo, L. Steier, M.K. Son, M. Schreier, M.T. Mayer, M. Grätzel, Nano Lett. 16, 1848–1857 (2016)
F. Fu, G. Cha, N. Denisov, Y.Y. Chen, Y. Zhang, P. Schmuki, CrystEngComm. 7, 2792–2796 (2020)
Y. Yang, M.R. Hoffmann, Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 11888–11894 (2016)
Y. Lei, H.M. Jia, Z. Zheng, Y.H. Gao, X.W. Chen, H.W. Hou, CrystEngComm. 13, 6212–6217 (2011)
J. Li, H.X. Zhao, X.H. Chen, H.M. Jia, Z. Zheng, Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 2940–2943 (2013)
S.C. Li, K. Yu, Y. Wang, Z.L. Zhang, C.Q. Song, H.H. Yin, Q. Ren, Z.Q. Zhu, CrystEngComm. 15, 1753–1761 (2013)
P.T. Sheng, W.L. Li, X. Tong, X. Wang, Q.Y. Cai, J. Mater. Chem. A. 2, 18974–18987 (2014)
M. Moriya, T. Minegishi, H. Kumagai, M. Katayama, J. Kubota, K. Domen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 3733–3735 (2013)
Y. Choi, M. Beak, K. Yong, Nanoscale. 6, 8914–8918 (2014)
H. Kaga, Y. Tsutsui, A. Nagane, A. Iwase, A. Kudo, J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 21815–21823 (2015)
T.J. Jacobsson, C.P. Björkman, M. Edoff, T. Edvinsson, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38, 15027–15035 (2013)
J.J. Ning, Z.H. Duan, S.V. Kershaw, A.L. Rogach, ACS Nano 14, 11799–11808 (2020)
P. Dube, A.O. Juma, C.M. Muiva, Ceram. Int. 46, 7396–7402 (2020)
M. Dehghani, E. Parvazian, N.A. Tehrani, N. Taghavinia, M. Samadpour, Mater. Today. 26, 102050 (2021)
S.O.M. Hinterding, M.J.J. Mangnus, P.T. Prins, H.J. Jöbsis, S. Busatto, D. Vanmaekelbergh, C.M. Donega, F.T. Rabouw, Nano Lett. 21, 658–665 (2021)
M. Li, R.J. Zhao, Y.J. Su, J. Hu, Z. Yang, Y.F. Zhang, Adv. Mater. Interfaces. 3, 1600410–1600494 (2016)
X.L. Tu, M. Li, Y.J. Su, G.L. Yin, J. Lu, D.N. He, J. Alloy. Compd. 809, 151794 (2019)
M.B. Rabeh, M. Kanzari, B. Rezig, J. Optoelectron. Adv. M. 1, 70–78 (2009)
D.Y. Lee, J.H. Kim, Thin Solid Films 518, 6537–6541 (2010)
T. Gotoh, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 20301 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11704237, 11875183, 61804156, U1404115 and 11647019), Key teacher program of Henan Province (Grant No. 2018GGJS135), Henan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 212102210221), Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province (Grant No. 16IRTSTHN028), and Shanghai Sailing Program (Grant No. 18YF1427800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Chen, Y., Lv, Z. et al. In situ one-step synthesis of CuInS2 thin films with different morphologies and their optical properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 2995–3001 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07499-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07499-6