Abstract
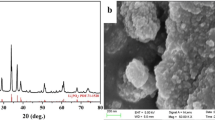
As a high-capacity cathode material with a considerable cycle life, lithium metal orthosilicates have attracted much attention. In this paper, Li2FeSiO4, Li2FeSiO4−xClx and Li2FeSiO4−xFx are successfully synthesized via solid-state method. Li2FeSiO4−xFx is also composited with reduced graphene oxide (rGO). The X-ray diffraction patterns show 0.2% expansion in the lattice volume of Li2FeSiO4−xFx and 0.7% shrinkage for Li2FeSiO4−xClx due to the doping effect. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy also indicates a frequency shift for [SiO4]4− and [LiO4] functional groups due to ion doping. The SEM images confirm that rGO surrounded Li2FeSiO4−xFx microparticles. The electrochemical performance illustrates a reversible ox/red reaction of Fe2+/Fe3+ couple at the potential of 3/2.6 V for Li2FeSiO4, 3.5/2.9 V for Li2FeSiO4−xFx, and 3.3/2.3 V for Li2FeSiO4−xClx. Lithiation curves at 0.05C rate show the first specific capacity of 168 mAh g−1 for Li2FeSiO4 with 84% retention after 25th cycles, 190 mAh g−1 for Li2FeSiO4−xFx with 100% retention, and 120 mAh g−1 for Li2FeSiO4−xClx with 73% retention. Li2FeSiO4−xFx/rGO cathode delivers 265 mAh g−1 with 88% retention after 25th cycles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Ni, Y. Jiang, X. Bi, L. Li, J. Lu, Lithium iron orthosilicate cathode: progress and perspectives. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 1771–1781 (2017)
C. Wang, Y. Xu, X. Sun, B. Zhang, Y. Chen, S. He, Enhanced electrochemical properties of F-doped Li2MnSiO4/C for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 378, 345–352 (2018)
M.M. Kalantarian, S. Asgari, D. Capsoni, P. Mustarelli, An ab initio investigation of Li2M0.5N0.5SiO4 (M, N = Mn, Fe, Co Ni) as Li-ion battery cathode materials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 8035–8041 (2013)
M.M. Kalantarian, S. Asgari, P. Mustarelli, Theoretical investigation of Li2MnSiO4 as a cathode material for Li-ion batteries: a DFT study. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 2847–2855 (2013)
X.L. Wu, L.Y. Jiang, F.F. Cao, Y.G. Guo, L.J. Wan, LiFePO4 nanoparticles embedded in a nanoporous carbon matrix: superior cathode material for electrochemical energy-storage devices. Adv. Mater. 21, 2710–2714 (2009)
A. Kumar, Nanostructured lithium iron silicate/carbon composites as cathode material for next generation of lithium-ion batteries (Wayne State University, Wayne, 2017)
V. Aravindan, K. Karthikeyan, K. Kang, W.S. Yoon, W. Kim, Y.-S. Lee, Influence of carbon towards improved lithium storage properties of Li2MnSiO4 cathodes. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 2470–2475 (2011)
A. Nytén, S. Kamali, L. Häggström, T. Gustafsson, J.O. Thomas, The lithium extraction/insertion mechanism in Li2FeSiO4. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 2266–2272 (2006)
L. Yi, G. Wang, Y. Bai, M. Liu, X. Wang, M. Liu, X. Wang, The effects of morphology and size on performances of Li2FeSiO4/C cathode materials. J. Alloy. Compd. 721, 683–690 (2017)
A. Manthiram, A.V. Murugan, A. Sarkar, T. Muraliganth, Energy Environ. Sci. 1, 621 (2008)
A. Arico, P. Bruce, B. Scrosati, J.-M. Tarascon, W. van Schalkwijk, Nat. Mater 4, 366 (2005)
K. Wang, W. Ren, J. Yang, R. Tan, Y. Liu, F. Pan, Depolarization effects of Li2FeSiO4 nanocrystals wrapped in different conductive carbon networks as cathodes for high performance lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 6, 47723–47729 (2016)
H. Zhou, F. Lou, P.E. Vullum, M.-A. Einarsrud, D. Chen, F. Vullum-Bruer, 3D aligned-carbon-nanotubes@ Li2FeSiO4 arrays as high rate capability cathodes for Li-ion batteries. Nanotechnology 24, 435703 (2013)
Z. Zhang, X. Liu, L. Wang, Y. Wu, H. Zhao, B. Chen, W. Xiong, Fabrication and characterization of carbon-coated Li2FeSiO4 nanoparticles reinforced by carbon nanotubes as high performance cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 168, 8–15 (2015)
Z. Zhang, X. Liu, Y. Wu, H. Zhao, Graphene modified Li2FeSiO4/C composite as a high performance cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 19, 469–475 (2015)
J. Ni, L. Zhang, S. Fu, S. Savilov, S. Aldoshin, L. Lu, A review on integrating nano-carbons into polyanion phosphates and silicates for rechargeable lithium batteries. Carbon 92, 15–25 (2015)
G. Longoni, J.K. Panda, L. Gagliani, R. Brescia, L. Manna, F. Bonaccorso, V. Pellegrini, In situ LiFePO4 nano-particles grown on few-layer graphene flakes as high-power cathode nanohybrids for lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 51, 656–667 (2018)
C. Gao, J. Zhou, G. Liu, L. Wang, Synthesis of F-doped LiFePO4/C cathode materials for high performance lithium-ion batteries using co-precipitation method with hydrofluoric acid source. J. Alloys Compd. 727, 501–513 (2017)
F. Lu, Y. Zhou, J. Liu, Y. Pan, Enhancement of F-doping on the electrochemical behavior of carbon-coated LiFePO4 nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal route. Electrochim. Acta 56, 8833–8838 (2011)
M. Armand, M.A.Y. de Dompablo, Benefits of N for O substitution in polyoxoanionic electrode materials: a first principles investigation of the electrochemical properties of Li2FeSiO4−y Ny (y= 0, 0.5, 1). J. Mater. Chem. 21, 10026–10034 (2011)
C.S. Sun, Y. Zhang, X.J. Zhang, Z. Zhou, Structural and electrochemical properties of Cl-doped LiFePO4/C. J. Power Sources 195, 3680–3683 (2010)
G. Du, Y. NuLi, J. Yang, J. Wang, Fluorine-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for 5V cathode materials of lithium-ion battery. Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 3607–3613 (2008)
N. Wiriya, P. Chantrasuwan, S. Kaewmala, J. Nash, S. Srilomsak, N. Meethong, W. Limphirat, Doping effect of manganese on the structural and electrochemical properties of Li2FeSiO4 cathode materials for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 171, 108753 (2020)
L. Qu, D. Luo, S. Fang, Y. Liu, L. Yang, S.-I. Hirano, C.-C. Yang, Mg-doped Li2FeSiO4/C as high-performance cathode material for lithium-ion battery. J. Power Sources 307, 69–76 (2016)
H. Qiu, H. Yue, T. Zhang, Y. Ju, Y. Zhang, Z. Guo, C. Wang, G. Chen, Y. Wei, D. Zhang, Enhanced electrochemical performance of Li2FeSiO4/C positive electrodes for lithium-ion batteries via yttrium doping. Electrochim. Acta 188, 636–644 (2016)
C. Deng, S. Zhang, S. Yang, B. Fu, L. Ma, Synthesis and characterization of Li2Fe0.97M0.03SiO4 (M= Zn2+, Cu2+, Ni2+) cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 196, 386–392 (2011)
X. Wang, Z. Feng, X. Hou, L. Liu, M. He, X. He, J. Huang, Z. Wen, Fluorine doped carbon coating of LiFePO4 as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 379, 122371 (2020)
E.M. Mokoena, A.K. Datye, N.J. Coville, A systematic study of the use of DL-tartaric acid in the synthesis of silica materials obtained by the sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 28, 307–317 (2003)
J. Bai, Z. Gong, D. Lv, Y. Li, H. Zou, Y. Yang, Nanostructured 0.8Li2FeSiO4/0.4Li2SiO3/C composite cathode material with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 12128–12132 (2012)
K. Gao, C.-S. Dai, J. Lv, S.-D. Li, Thermal dynamics and optimization on solid-state reaction for synthesis of Li2MnSiO4 materials. J. Power Sources 211, 97–102 (2012)
K. Zaghib, A.A. Salah, N. Ravet, A. Mauger, F. Gendron, C. Julien, Structural, magnetic and electrochemical properties of lithium iron orthosilicate. J. Power Sources 160, 1381–1386 (2006)
S. Singh, A.K. Raj, R. Sen, P. Johari, S. Mitra, Impact of Cl doping on electrochemical performance in orthosilicate (Li2FeSiO4): a density functional theory supported experimental approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 26885–26896 (2017)
S. Singh, M.R. Panda, R. Sen, P. Johari, A. Sinha, S.S. Meena, S. Mitra, Study of higher discharge capacity, phase transition, and relative structural stability in Li2FeSiO4 cathode upon lithium extraction using an experimental and theoretical approach and full cell prototype study. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 6584–6598 (2019)
P. Sivaraj, K.P. Abhilash, B. Nalini, P.C. Selvin, S. Goel, S.K. Yadav, Insight into cations substitution on structural and electrochemical properties of nanostructured Li2FeSiO4/C cathodes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 103, 1685–1697 (2020)
H. Qiu, D. Jin, C. Wang, G. Chen, L. Wang, H. Yue, D. Zhang, Design of Li2FeSiO4 cathode material for enhanced lithium-ion storage performance. Chem. Eng. J. 379, 122329 (2020)
P. Kumta, D. Gallet, A. Waghray, G. Blomgren, M. Setter, Synthesis of LiCoO2 powders for lithium-ion batteries from precursors derived by rotary evaporation. J. Power Sources 72, 91–98 (1998)
W. Tang, X.J. Wang, Y.Y. Hou, L.L. Li, H. Sun, Y.S. Zhu, Y. Bai, Y.P. Wu, K. Zhu, T. van Ree, Nano LiMn2O4 as cathode material of high rate capability for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 198, 308–311 (2012)
X.-L. Wu, Y.G. Guo, J. Su, J.-W. Xiong, Y.-L. Zhang, L.-J. Wan, Carbon-nanotube-decorated nano-LiFePO4@C cathode material with superior high-rate and low-temperature performances for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 3, 1155–1160 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Materials and Energy Research Center (MERC) in Tehran, Iran (Grant Number 471396060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahertalari, M., Massoudi, A., Ji, X. et al. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of F- and Cl-doped Li2FeSiO4 cathode material for lithium-ion battery. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 2310–2321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07431-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07431-y