Abstract
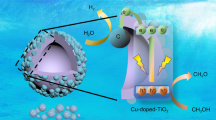
Cu2+-doped CeO2@mSiO2(CDC@mSiO2) samples with hollow structure were prepared by calcining Cu2+-doped cerium-based metal–organic framework (UiO-66 nanocrystals) precursor coated with mesoporous silica (mSiO2). BET analysis shows that Cu2+-doped CeO2@mSiO2 has a mesoporous structure and a large specific surface area (397.7 m2/g), which can provide more active sites for photocatalytic reactions. Ultraviolet absorption spectrum and PL spectrum show that the introduction of Cu2+ makes the absorption edge of the sample red-shift and accelerate the electron–hole separation efficiency. Cu2+ doping makes CeO2 produce more oxygen vacancies, which promotes photocatalysis. The Cu2+-doped CeO2@mSiO2 sample has the best photodegradation efficiency. Under simulated sunlight, the degradation rate of methyl orange within 2 h is 92.6%, and the photocatalytic rate constant is 0.0221/min. After 4 cycles of experiments, it still has excellent photocatalytic activity. Based on the characterization analysis and experimental results, the degradation mechanism of methyl orange is proposed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.S. Chang, Streamlined life cycle CO2 emission assessment of sewage treatment in taiwan. Sains Malays. 44, 1715–1720 (2015)
Y.F. Wang, L. Yan, J. Li et al., A review of technology for small sewage treatment: the Chinese perspective. Oxid. Commun. 39, 275–284 (2016)
X. Xiao, Y.H. Wang, Q. Bo et al., One-step preparation of sulfur-doped porous g-C3N4 for enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance. Dalton Trans. 49, 8041–8050 (2020)
Z.L. Ni, F. Dong, H.W. Huang et al., New insights into how Pd nanoparticles influence the photocatalytic oxidation and reduction ability of g-C3N4 nanosheets. Catal. Sci. Technol. 6, 6448–6458 (2016)
Q.Q. Du, W.P. Wang, Y.Z. Wu et al., Novel carbon dots/BiOBr nanocomposites with enhanced UV and visible light driven photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv. 5, 31057–31063 (2015)
A.Y. Ahmed, T.A. Kandiel, I. Ivanova et al., Photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical oxidation mechanisms of methanol on TiO2 in aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 319, 44–49 (2014)
S. Ahmed, D.K. Macharia, B. Zhu, Blue/red light-triggered reversible color switching based on CeO2-x nanodots for constructing rewritable smart fabrics. Nanoscale 12, 10335–10346 (2020)
Y. Zhao, T. Chen, R. Ma et al., Synthesis of flower-like CeO2/BiOCl heterostructures with enhanced ultraviolet light photocatalytic activity. Micro Nano Lett. 13, 1394–1398 (2018)
E.M. Seftel, M.C. Puscasu, M. Mertens, Assemblies of nanoparticles of CeO2-ZnTi-LDHs and their derived mixed oxides as novel photocatalytic systems for phenol degradation. Appl. Catal. B 150, 157–166 (2014)
C. Lai, F.H. Xu, M.M. Zhang et al., Facile synthesis of CeO2/carbonate doped Bi2O2CO3 Z-scheme heterojunction for improved visible-light photocatalytic performance: photodegradation of tetracycline and photocatalytic mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 588, 283–294 (2021)
Y. Wang, X. Bai, F. Wang, S. Kang, C. Yin, X. Li et al., Nanocasting synthesis of chromium doped mesoporous CeO2 with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 372, 69–76 (2019)
X.L. Zhang, K. Li, W.Y. Shi, Baize-like CeO2 and NiO/CeO2 nanorod catalysts prepared by dealloying for CO oxidation. Nanotechnology 28, 045602 (2017)
S. Mansingh, D. Kandi, K.K. Das et al., A mechanistic approach on oxygen vacancy-engineered CeO2 nanosheets concocts over an oyster shell manifesting robust photocatalytic activity toward water oxidation. ACS Omega 5, 9789–9805 (2020)
H.T. Wang, Y. Xue, B.H. Zhu et al., CeO2 nanowires stretch-embedded in reduced graphite oxide nanocornposite support for Pt nanoparticles as potential electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42, 20549–20559 (2017)
B.Y. Ren, P. Sudarsanam, A.E. Kandjani et al., Electrochemical detection of as (III) on a manganese oxide-ceria (Mn2O3/CeO2) nanocube modified Au electrode. Electroanalysis 30, 928–936 (2018)
Z.J. Yang, L. Liu, H. Liang et al., One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of CeO2 hollow microspheres. J. Cryst. Growth 312, 426–430 (2010)
Z. Jiang, H.Y. Sun, Z.H. Qin et al., Synthesis of novel ZnS nanocages utilizing ZIF-8 polyhedral template. Chem. Commun. 48, 3620–3622 (2012)
H.J. Lee, W. Cho, M. Oh, Advanced fabrication of metal-organic frameworks: template-directed formation of polystyrene@ZIF-8 core-shell and hollow ZIF-8 microspheres. Chem. Commun. 48, 221–223 (2012)
Y. Tao, H. Wang, Y.P. Xia et al., Preparation of shape-controlled CeO2 nanocrystals via microwave-assisted method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 124, 541–546 (2010)
D. Lestari, I. Nurhasanah, Z. Arifin, Changes in UV-absorption properties of CeO2 nanoparticles solution caused by X-rays and gamma-rays radiation. Adv. Sci. Lett. 23, 6585–6588 (2017)
Q. Fang, X. Liang, CeO2-Al2O3, CeO2-SiO2, CeO2-TiO2 core-shell spheres: formation mechanisms and UV absorption. RSC Adv. 2, 5370–5375 (2012)
G.P. He, H.Q. Fan, Z.W. Wang, Enhanced optical properties of heterostructured ZnO/CeO2 nanocomposite fabricated by one-pot hydrothermal method: fluorescence and ultraviolet absorption and visible light transparency. Opt. Mater. 38, 145–153 (2014)
D. Garg, I. Matai, A. Garg et al., Tragacanth hydrogel integrated CeO2@rGO nanocomposite as reusable photocatalysts for organic dye degradation. ChemSelect 5, 10663–10672 (2020)
S.W. Ma, S.Y. Chen, H.J. Ge et al., Synergistic effects of the Zr and Sm Co-doped Fe2O3/CeO2 oxygen carrier for chemical looping hydrogen generation. Energy Fuel 34, 10256–10267 (2020)
Y. Qi, J. Ye, S. Zhang et al., Controllable synthesis of transition metal ion-doped CeO2 micro/nanostructures for improving photocatalytic performance. J. Alloys Compd. 782, 780–788 (2019)
A. Santiago, N. Neto, E. Longo et al., Fast and continuous obtaining of Eu3+ doped CeO2 microspheres by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis: characterization and photocatalytic activity. J. Mater Sci. 30, 11508–11519 (2019)
M.K. Kesarla, M.O. Fuentez-Torres, M.A. Alcudia-Ramos et al., Synthesis of g-C3N4/N-doped CeO2 composite for photocatalytic degradation of an herbicide. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 1628–1635 (2019)
D. Channei, K. Chansaenpak, P. Jannoey et al., The staggered heterojunction of CeO2/CdS nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Solid State Sci. 96, 105951 (2019)
G. Liu, H. Wang, D. Chen et al., Photodegradation performances and transformation mechanism of sulfamethoxazole with CeO2/CN heterojunction as photocatalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 237, 116239 (2020)
X. Yang, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang et al., Hollow beta-Bi2O3@CeO2 heterostructure microsphere with controllable crystal phase for efficient photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 387, 124100 (2020)
N. Wang, Y. Pan, T. Lv et al., A new ribbon-ignition method for fabricating p-CuO/n-CeO2 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 403, 699–706 (2017)
K. Wangkawong, S. Phanichphant, D. Tantraviwat et al., Photocatalytic efficiency improvement of Z-scheme CeO2/BiOI heterostructure for RHB degradation and benzylamine oxidation under visible light irradiation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E. 108, 55–63 (2020)
X. Cui, Z. Liu, G. Li et al., Self-generating CeVO4 as conductive channel within CeO2/CeVO4/V2O5 to induce Z-scheme-charge-transfer driven photocatalytic degradation coupled with hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 23921–23935 (2019)
M.Y. Mao, H.Q. Ly, Y.Z. Li et al., Metal support interaction in Pt nanoparticles partially confined in the mesopores of microsized mesoporous CeO2 for highly efficient purification of volatile organic compounds. ACS Catal. 6, 418–427 (2016)
N. Keshvadi, A. Haghighatzadeh, B. Mazinani, Improvement in visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity of Ag-CeO2 Schottky-type contact heterostructures. Appl. Phys. A 126, 1–4 (2020)
S. Kouroush, Self-assembled bio-inspired Au/CeO2 nano-composites for visible white LED light irradiated photocatalysis. Colloid Surf. A 599, 124908 (2020)
S.M. Chaudhari, S. Olviya et al., Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Diclofenac with Agl/CeO2: a comparison with Mn, Cu and Ag-doped CeO2. Mater. Res. Bull. 143, 111463 (2021)
J. Zhang, L.S. Wang, X.Y. Hu et al., Balancing surface acidity, oxygen vacancies and Cu+ of CuOx/CeO2 catalysts by Nb doping for enhancing CO oxidation and moisture resistance and lowering byproducts in plasma catalysis. J. Clean. Prod. 318, 128564 (2021)
G. Li, J. Liu, J. Lan et al., 3D hierarchical anatase TiO2 surperstructures constructed by “nanobricks” built nanosheets with exposed 001 facets: facile synthesis, formation mechanism and superior photocatalytic activity. CrystEngCommun 16, 10547–10552 (2014)
F.P. Pan, X.M. Xiang, Z.C. Du et al., Integrating photocatalysis and thermocatalysis to enable efficient CO2 reforming of methane on Pt supported CeO2 with Zn doping and atomic layer deposited MgO overcoating. Appl. Catal. B 260, 118189 (2020)
I. Rabani, K. Karuppasamy, D. Vikraman et al., Hierarchical structured nano-polyhedrons of CeO2@ZIF-8 composite for high performance supercapacitor applications. J. Alloys Compd. 875, 160074 (2021)
W.Q. Li, L. Jin, F. Gao, Advantageous roles of phosphate decorated octahedral CeO2 {111}/g-C3N4 in boosting photocatalytic CO2 reduction: charge transfer bridge and Lewis basic site. Appl. Catal. B 294, 120257 (2021)
J. Wang, S.W. Lin, Z.Y. Han et al., Glutamine-assisted synthesis of Cu-doped CeO2 nanowires with an improved low-temperature CO oxidation activity. RSC Adv. 5, 28619–28623 (2015)
Z.S. Lu, Z.Z. Yang, B.L. He et al., Cu-doped ceria: oxygen vacancy formation made easy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 510, 60–66 (2011)
Y.M. Wang, X.X. Liu, L. Guo, Metal organic framework-derived C-doped ZnO/TiO2 nanocomposite catalysts for enhanced photodegradation of Rhodamine B. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 599, 566–576 (2021)
Y.H. Shang, T. Wang, Y. Xiao et al., Constructing BiOBr/CoOx/g-C3N4 Z-scheme photocatalyst with CoOx as both redox mediator and cocatalyst for phenol degradation. J. Alloys Compd. 875, 159998 (2021)
M. Alomar, Y.L. Liu, W. Chen et al., Controlling the growth of ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets/CdS nanoparticles by two-step solvothermal synthesis for enhancing photocatalytic activities under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 480, 1078–1088 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (1508085SME219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, M., Liu, X., Wu, H. et al. Construction of Cu2+-doped CeO2 nanocrystals hierarchical hollow structure and its enhanced photocatalytic performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 27576–27586 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07132-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07132-6