Abstract
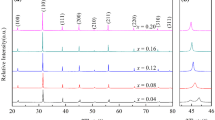
Recently, it is shown that the thin films of BiFeO3–BaTiO3–SrTiO3 have ultrahigh-energy storage density. However, the energy storage properties of BiFeO3–BaTiO3–SrTiO3 ternary bulk ceramics have not been studied. In this work, the BiFeO3–BaTiO3–SrTiO3 ceramics have been prepared by a conventional solid-state reaction method and the dielectric and electrical energy storage properties have been studied in detail. The ceramic with the composition of 0.25BiFeO3–0.30BaTiO3–0.45SrTiO3 is experimental evidenced to be the best with the highest dielectric permittivity in the ternary system. To suppress the dielectric loss and leakage current, 0.25BiFeO3–0.30BaTiO3–0.45SrTiO3 has been doped with Mn. Mn-doped ceramics have the same perovskite structure but the fine grains are formed and the number of pores decreases. Mn-doping reduces dielectric loss, enlarges the thermally stable zone of the dielectric, and improves the electrical energy storage density simultaneously. 2 mol% Mn-doped 0.25BiFeO3–0.30BaTiO3–0.45SrTiO3 has the most optimized electrical energy storage properties. The energy storage density is 1.33 J/cm3 and the efficiency is 88.5% at 185 kV/cm. The discharge energy density is 2.7 times that of undoped 0.25BiFeO3–0.30BaTiO3–0.45SrTiO3 and 90% stored energy can release in 120 ns.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
H. Liu, B. Dkhil, J. Mater. Sci. 52, 6074 (2017)
K. Zou, Y. Dan, H. Xu, Q. Zhang, Y. Lu, H. Huang, Y. He, Mater. Res. Bull. 113, 190 (2019)
L. Yang, X. Kong, F. Li, H. Hao, Z. Cheng, H. Liu, J.-F. Li, S. Zhang, Prog. Mater Sci. 102, 72 (2019)
A. Zeb, S.J. Milne, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 9243 (2015)
X. Wu, H. Liu, J. Chen, J. Mater. Res. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-020-00089-y
Z. Xie, H. Liu, Ceram. Int. 46, 6955 (2020)
H. Liu, B. Dkhil, Z. Krystallog. 226, 163 (2011)
H. Liu, X. Yang, Ferroelectrics 500, 310 (2016)
L. Li, H. Liu, G. Wen, G. Liu, Ceram. Int. 44, S69 (2018)
T.M. Correia, M. McMillen, M.K. Rokosz, P.M. Weaver, J.M. Gregg, G. Viola, M.G. Cain, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 2699 (2013)
H. Liu, Ceram. Int. 46, 8255 (2020)
H. Pan, F. Li, Y. Liu, Q. Zhang, M. Wang, S. Lan, Y. Zheng, J. Ma, L. Gu, Y. Shen, P. Yu, S. Zhang, L.-Q. Chen, Y.-H. Lin, C.-W. Nan, Science 365, 578 (2019)
Y. Shi, F. Yan, X. He, K. Zhu, G. Li, X. Dong, B. Shen, J. Zhai, CrystEngComm 23, 1596 (2021)
F. Kang, L. Zhang, B. Huang, P. Mao, Z. Wang, Q. Sun, J. Wang, D. Hu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 40, 1198 (2020)
S.O. Leontsev, R.E. Eitel, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 2957 (2009)
J. Chen, J. Cheng, J. Guo, Z. Cheng, J. Wang, H. Liu, S. Zhang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 103, 374 (2020)
M. Makarovic, A. Bencan, J. Walker, B. Malic, T. Rojac, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 3693 (2019)
O. Bidault, P. Goux, M. Kchikech, M. Belkaoumi, M. Maglione, Phys. Rev. B 49, 7868 (1994)
Y. Xu, H. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 5221 (2020)
H. Liu, Ceram. Int. 45, 10380 (2019)
Y. Ren, H. Liu, F. Liu, G. Liu, J. Alloy. Compd. 877, 160239 (2021)
C. Neusel, G.A. Schneider, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 63, 201 (2014)
D. Jiang, Y. Zhong, F. Shang, G. Chen, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 12074 (2020)
J. Wei, D. Jiang, W. Yu, F. Shang, G. Chen, Ceram. Int. 47, 11581 (2021)
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11704242; 21703138; 51672226) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, China (Grant No. 17ZR1447200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Liu, H., Liu, F. et al. Dielectric and electrical energy storage properties of BiFeO3–BaTiO3–SrTiO3 ternary bulk ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 21188–21196 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06618-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06618-7