Abstract
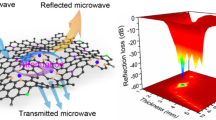
In this work, we successfully synthesize N-doped carbon nanoribbon (NCNR) from polypyrrole precursor and investigate their dielectric and microwaves absorption (MA) properties. NCNR appears as two-dimensional ribbon-like microstructure with tunable N-doping ratio. The dielectric property of NCNR can be tuned by N-doping content controlling. The results demonstrate that NCNR exhibits excellent MA performance at a filler-loading ratio of only 5 wt%. When the sample thickness is 3.3 mm, the maximal absorption reaches − 73.76 dB at 10.48 GHz. The maximum efficient bandwidth gets to 7.4 GHz (10.6–18 GHz), under a sample thickness of 2.7 mm. A model that refers to conductive loss, polarization relaxation, and impedance match is adopted to explain the MA mechanism of NCNR. This research opens up the exploration of NCNR in the field of MA, and provides a new idea for the design of carbon-related broad band MA materials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, T.F. Zhang, H. Chang, P.S. Xiao, H.H. Chen, Z.Y. Huang, Y.S. Chen, Broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam. Adv. Mater. 27, 2049–2053 (2015)
A.M. Xie, F. Wu, M.X. Sun, X.Q. Dai, Z.H. Xu, Y.Y. Qiu, Y. Wang, M.Y. Wang, Self-assembled ultralight three-dimensional polypyrrole aerogel for effective electromagnetic absorption. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 222902 (2015)
A.M. Xie, K. Zhang, M.X. Sun, Y.L. Xia, F. Wu, Facile growth of coaxial Ag@polypyrrole nanowires for highly tunable electromagnetic waves absorption. Mater. Des. 154, 192–202 (2018)
R.C. Che, L.M. Peng, X.F. Duan, Q. Chen, X.L. Liang, Micorwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of feencapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 16, 401–405 (2004)
H. Sun, R.C. Che, X. You, Y.S. Jiang, Z.B. Yang, J. Deng, L.B. Qiu, H.S. Peng, Cross-stacking aligned carbon-nanotube films to tune microwave absorption frequencies and increase absorption intensies. Adv. Mater. 26, 8120–8125 (2014)
L.N. Sha, P. Gao, T.T. Wu, Y.J. Chen, Chemical Ni–C bonding in Ni–carbon nanotube composite by a microwave welding method and its induced high-frequency radar frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 40412–40419 (2017)
A.M. Xie, F. Wu, W.C. Jiang, K. Zhang, M.X. Sun, M.Y. Wang, Chiral induced synthesis of helical polypyrrole (PPy) nano-structures: a lightweight and high-performance material against electromagnetic pollution. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 2175 (2017)
X. Tian, F.B. Meng, F.C. Meng, X.N. Chen, Y.F. Guo, Y. Wang, W.J. Zhu, Z.W. Zhou, Synergistic enhancement of microwave absorption using hybridized polyaniline@helical CNTs with dual chirality. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 15711–15718 (2017)
X.J. Zhang, G.S. Wang, W.Q. Cao, Y.Z. Wei, J.F. Liang, L. Guo, M.S. Cao, Enhanced microwave absorption property of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)-MnFe2O4 nanocomposites and polyvinylidene fluoride. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 7471–7478 (2014)
B. Wen, M.S. Cao, M.M. Lu, W.Q. Cao, H.L. Shi, J. Liu, X.X. Wang, H.B. Jin, X.Y. Fang, W.Z. Wang, J. Yuan, Reduced graphene oxides: light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater. 26, 3484–3489 (2014)
X.H. Liang, B. Quan, G.B. Ji, W. Liu, H.Q. Zhao, S.S. Dai, J. Lv, Y.W. Du, Tunable dielectric performance derived from the metal-organic framework/reduced graphene oxide hybrid with broadband absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 10570–10579 (2017)
B. Quan, W. Gu, J. Sheng, X. Lv, Y. Mao, L. Liu, X. Huang, Z. Tian, G. Ji, From intrinsic dielectric loss to geometry patterns: dual-principles strategy for ultrabroad band microwave absorption. Nano Res. 14, 1495–1501 (2021)
W. Gu, X. Cui, J. Zheng, J. Yu, Y. Zhao, G. Ji, Heterostructure design of Fe3N alloy/porous carbon nanosheet composites for efficient microwave attenuation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 67, 265–272 (2021)
B. Zhao, C. Ma, L.Y. Liang, W.H. Guo, B.B. Fan, X.Q. Guo, R. Zhang, An impedance match method used to tune the electromagnetic wave absorption properties of hierarchical ZnO assembled by porous nanosheets. CrystEngComm 19, 3640–3648 (2017)
B. Quan, X. Liang, G. Ji, J. Ma, P. Ouyang, H. Gong, G. Xu, Y. Du, Strong electromagnetic wave response derived from the construction of dielectric/magnetic media heterostructure and multiple interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 9964–9974 (2017)
B. Quan, X. Liang, G. Ji, J. Lv, S. Dai, G. Xu, Y. Du, Laminated graphene oxide-supported high-efficiency microwave absorber fabricated by an in situ growth approach. Carbon 129, 310–320 (2018)
H.L. Lv, Y.H. Guo, G.L. Wu, G.B. Ji, Y. Zhao, Z.C.J. Xu, Interface polarization strategy to solve electromagnetic wave interference issue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 5660–5668 (2017)
E. Pomerantseva, F. Bonaccorso, X.L. Feng, Y. Cui, Y. Gogotsi, Energy storage: the future enabled by nanomaterials. Science 366, 969 (2019)
H.L. Fei, J.C. Dong, D.L. Chen, T.D. Hu, X.D. Duan, I. Shakir, Y. Huang, X.F. Duan, Single atom electrocatalysts supported on graphene or graphene-like carbons. Soc. Rev. 48, 5207–5241 (2019)
Z. Meng, R.M. Stolz, L. Mendecki, K.A. Mirica, Electrically-transduced chemical sensors based on two-dimensional nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 119, 478–598 (2019)
Z.P. Chen, C. Xu, C.Q. Ma, W.C. Ren, H.M. Cheng, Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 25, 1296–1300 (2013)
N. Yousefi, X.Y. Sun, X.Y. Lin, X. Shen, J.J. Jia, B. Zhang, B.Z. Tang, M. Chan, J.K. Kim, Highly aligned graphene/polymer nanocomposites with excellent dielectric properties for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 26, 5480–5487 (2014)
C.H. Choi, S.H. Park, S.I. Woo, Binary and ternary doping of nitrogen, boron, and phosphorus into carbon for enhancing electrochemical oxygen reduction activity. ACS Nano 6, 7084–7091 (2012)
P.B. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, W.J. He, W.H. Huang, J.H. Luo, Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122653 (2019)
D.L. Isac, ŞG. Şoriga, I.C. Man, How do the coadsorbates affect the oxygen reduction reaction activity of undoped and N-doped graphene nanoribbon edges? A density functional theory study. J. Phys. Chem. C 124, 23177–23189 (2020)
R.C. Wei, Y. Gu, L.L. Zou, B.J. Xi, Y.X. Zhao, Y.N. Ma, Y.T. Qian, S.L. Xiong, Q. Xu, Nanoribbon superstructures of graphene nanocages for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Lett. 20, 7342–7349 (2020)
M. Zare, R. Asgari, Probing divacancy defects in a zigzag graphene nanoribbon through an RKKY exchange interaction. J. Phys. D 54, 095302 (2021)
F.P. Pan, B.Y. Li, E. Sarnello, Y.H. Fei, Y. Gang, X.M. Xiang, Z.C. Du, P. Zhang, G.F. Wang, H.T. Nguyen, T. Li, Y.H. Hu, H.C. Zhou, Y. Li, Atomically dispersed iron–nitrogen sites on hierarchically mesoporous carbon nanotube and graphene nanoribbon networks for CO2 reduction. ACS Nano 14, 5506–5516 (2020)
M.R. Rezapour, G. Leeand, K.S. Kim, A high performance N-doped graphene nanoribbon based spintronic device applicable with a wide range of adatoms. Nanoscale Adv. 2, 5905–5911 (2020)
R. Zuzak, P. Brandimarte, P. Olszowski, I. Izydorczyk, M. Markoulides, B. Such, M. Kolmer, M. Szymonski, A.G. Lekue, D.S. Portal, A. Gourdon, S. Godlewski, On-surface synthesis of chlorinated narrow graphene nanoribbon organometallic hybrids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 10290–10297 (2020)
Y.Z. Jiao, F. Wu, K. Zhang, M.X. Sun, A.M. Xie, W. Dong, Ultra-broad polypyrrole (PPy) nano-ribbons seeded by racemic surfactants aggregates and their high-performance electromagnetic radiation elimination. Nanotechnology 28, 315701 (2017)
H. Peng, Z.L. Hou, K.L. Zhang, J. Li, K. Yin, S. Feng, S. Bi, Lightweight ferroferric oxide nanotubes with natural resonance property and design for broadband microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 8258–8267 (2017)
Y.Z. Jiao, S.Y. Cheng, F. Wu, X.H. Panet, A.M. Xie, X.F. Zhu, W. Dong, MOF-Guest complex derived Cu/C nanocomposites with multiple heterogeneous interfaces for excellent electromagnetic waves absorption. Compos. B 211, 108643 (2021)
M. Zhang, M. Cao, J. Shu, W. Cao, L. Li, J. Yuan, Electromagnetic absorber converting radiation for multifunction. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 145, 100627 (2021)
M.X. Sun, C. Xu, J.L. Li, L.Q. Xing, T. Zhou, F. Wu, Y.F. Shang, A.M. Xie, Protonic doping brings tuneable dielectric and electromagnetic attenuated properties for polypyrrole nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122615 (2020)
L.P. Wu, F. Wu, Q.Y. Sun, J.Y. Shi, A.M. Xie, X.F. Zhu, W. Dong, A TTF-TCNQ complex: an organic charge-transfer system with extraordinary electromagnetic response behaviors. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 3316–3323 (2021)
Y.H. Cheng, P. Hu, S.B. Zhou, L.W. Yan, B.Q. Sun, X.H. Zhang, W.B. Han, Achieving tunability of effective electromagnetic wave absorption between the whole X-band and Ku-band via adjusting PPy loading in SiC nanowires/graphene hybrid foam. Carbon 132, 430–443 (2018)
S. Dong, W.Z. Zhang, X.H. Zhang, P. Hu, J.C. Han, Designable synthesis of core-shell SiCw@C heterostructures with thickness-dependent electromagnetic wave absorption between the whole X-band and Ku-band. Chem. Eng. J. 354, 767–776 (2018)
S. Dong, J.T. Song, X.H. Zhang, P. Hu, B.Q. Sun, S.T. Zhou, X.G. Luo, Strong contribution of in situ grown nanowires to enhance the thermostabilities and microwave absorption properties of porous graphene foams under different atmospheres. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 11837–11846 (2017)
Y. Hou, L.F. Cheng, Y.N. Zhang, Y. Yang, C.R. Deng, Z.H. Yang, Q. Chen, P. Wang, L.X. Zheng, Electrospinning of Fe/SiC hybrid fibers for highly efficient microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 7265–7271 (2017)
Y.H. Cheng, M.Y. Tan, P. Hu, X.H. Zhang, B.Q. Sun, L.W. Yan, S.B. Zhou, W.B. Han, Strong and thermostable SiC nanowires/graphene aerogel with enhanced hydrophobicity and electromagnetic wave absorption property. Appl. Surf. Sci. 448, 138–144 (2018)
M. Cao, W. Song, Z. Hou, B. Wen, J. Yuan, The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 48, 788–796 (2010)
Q. Sun, X. Zhang, R. Liu, S. Shen, F. Wu, A. Xie, Nickel-assisted synthesis of magnetic bamboo-shaped N-doped carbon nanostructure for excellent microwaves absorption. Synth. Met. 272, 116644 (2021)
N. Zhou, Q.D. An, Z.Y. Xiao, S.R. Zhai, Z. Shi, Solvothermal synthesis of three-dimensional, Fe2O3 NPs-embedded CNT/N-doped graphene composites with excellent microwave absorption performance. RSC Adv. 7, 45156–45169 (2017)
M. Cao, X. Wang, M. Zhang, J. Shu, W. Cao, H. Yang, X. Fang, J. Yuan, Electromagnetic response and energy conversion for functions and devices in low-dimensional materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1807398 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51908288, No. 41627801) is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, L., Yang, Z., Sun, Q. et al. Polypyrrole-derived N-doped carbon nanoribbon for broadband microwaves absorption. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 26151–26160 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06548-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06548-4