Abstract
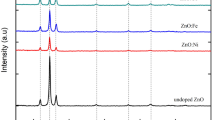
Nickel-doped mesoporous tin dioxide Sn1−xNixO2 (where x = 0, 0.01, 0.03, and 0.05) nanoparticles using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as surfactant were prepared by hydrothermal technique. The morphology, structure, optical, magnetic, and electrochemical properties of the mesoporous tin oxide nanopowders were investigated extensively as a function of nickel doping concentration. XRD patterns confirm that the obtained nanoparticles are SnO2 with tetragonal rutile structure fully compatible with JCPDS card no. 41-1445. The crystallite size was measured by Scherrer formula and was found to be 39–30 nm. FTIR findings showed that the change in the shapes and positions of absorption peaks shows the existence of stretching modes that give an implication of successful doping Ni to tin dioxide nanopowders. To analyze the optical properties, the wavelength range 350–1100 nm was used. The result demonstrates that the existence of specifically permitted optical transitions with energy gap varies in the range of 3.6–2.3 eV with Ni concentration. The electrochemical analysis using cyclic voltammetry showed a pair of redox peaks in Ni-doped tin dioxide electrode. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) denoted a significant decrease in charge transfer resistance (RCT), indicating an improved electrochemical performance of the electrode. Ni doping was found to be interesting due to the co-existence of room-temperature ferromagnetism and an enhanced electrochemical behavior, hence making it a probable material for magnetically controlled electrochemical cells.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Xu, D. Li, J. Guo, Y. Hu, P. Yang, Aluminum and silver doped effects on the electrical structure and optical properties of SnO2. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 148, 109763 (2021)
X.-L. Zhang, L.-F. Liu, W.-M. Liu, Quantum anomalous Hall effect and tunable topological states in 3d transition metals doped silicene. Sci. Rep. 3, 2908 (2013)
D. Liu, J. Pan, J. Tang, W. Liu, S. Bai, R. Luo, Ag decorated SnO2 nanoparticles to enhance formaldehyde sensing properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 124, 36–43 (2019)
Y.-H. Chen, H.-S. Tao, D.-X. Yao, W.-M. Liu, Kondo metal and ferrimagnetic insulator on the triangular Kagome lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 246402 (2012)
A.-C. Ji, X.C. Xie, W.M. Liu, Quantum magnetic dynamics of polarized light in arrays of microcavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 183602 (2007)
S. Liu, Q. Sun, J. Wang, H. Hou, Charge imbalance induced oxygen-adsorption enhances the gas-sensing properties of Al-doped SnO2 powders. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 124, 163–168 (2019)
Z.F. Jiang, R.D. Li, S.-C. Zhang, W.M. Liu, Semiclassical time evolution of the holes from Luttinger Hamiltonian. Phys. Rev. 72, 04520 (2005)
G.M. Lekha, S. George, Colloidal magnetic metal oxide nanocrystals and their applications. In Colloidal Metal Oxide Nanoparticles (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2020), pp 289–335
P. Robkhob, I.-M. Tang, S. Thongmee, Increased bound magnetic polaron formation in the dilute magnetic semiconductor Zn1−xNixO. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 260, 114644 (2020)
D.P. Rai, A. Laref, A. Shankar, A. Sandeep, A.P. Sakhya, R. Khenata, R.K. Thapa, Spin-induced transition metal (TM) doped SnO2 a dilute magnetic semiconductor (DMS): a first principles study. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 120, 104–108 (2018)
T. Deitl, H. Onho, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 1019 (2000)
R.V. Ingle, S.F. Shaikh, P.K. Bhujbal, H.M. Pathan, V.A. Tabhane, Polyaniline doped with protonic acids: optical and morphological studies. ES Mater. Manuf. 8, 54–59 (2020)
M. Idrees, L. Liu, S. Batool, H. Luo, J. Liang, B. Xu, S. Wang, J. Kong, Cobalt-doping enhancing electrochemical performance of silicon/carbon nanocomposite as highly efficient anode materials in lithium-ion batteries. Eng. Sci. 6, 64–76 (2019)
T. Ouyang, Q. Liu, M. Chen, C. Tang, J. Li, C. Zhang, C. He, H. Bao, J. Zhong, M. Hu, Doping induced abnormal contraction and significant reduction of lattice thermal conductivity of open framework Si24. ES Energy Environ. 3, 88–95 (2019)
E. Shi, T. Feng, J.-H. Bahk, Y. Pan, W. Zheng, Z. Li, G. Jeffery Snyder, S.T. Pantelides, Y. Wu, Experimental and theoretical study on well-tunable metal oxide doping towards high-performance thermoelectrics. ES Energy Environ. 2, 43–49 (2018)
Z. Liu, X. Yi, J. Wang, I. Ferguson, N. Lu, J. Li, Theoretical analysis and experimental realization of highly effective acceptor ionization in GaN via Mg co-doped with 4d-element (In). ES Mater. Manuf. 4, 25–30 (2019)
C.B.S. Valentin, R.L. de Sousa e Silva, P. Banerjee, A. Franco, Investigation of Fe-doped room temperature dilute magnetic ZnO semiconductors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 96, 122–126 (2019)
P. Vairale, V. Sharma, A. Waghmare, P. Shinde, S. Pandharkar, A. Punde, V. Doiphode, Y. Hase, R. Aher, S. Nair, V. Jadkar, N. Patil, S. Rondiya, P. Shelke, M. Prasad, S. Jadkar, Study of structural, optical, morphology and photoelectrochemical properties of melanin sensitized TiO2 Thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition method. ES Mater. Manuf. 10, 5–15 (2020)
M.A. Kashfipour, N. Mehra, R.S. Dent, J. Zhu, Regulating intermolecular chain interaction of biopolymer with natural polyol for flexible, optically transparent and thermally conductive hybrids. Eng. Sci. 8, 11–18 (2019)
M. Waghmare, P. Sonone, P. Patil, V. Kadam, H. Pathan, A. Ubale, Spray pyrolytic deposition of zirconium oxide thin films: influence of concentration on structural and optical properties. Eng. Sci. 5, 79–87 (2019)
H.D. Shelke, A.C. Lokhande, J.H. Kim, C.D. Lokhande, Effect of copper content on structural, morphological, optical and photoelectrochemical properties of SILAR deposited Cu3SnS4 thin films. ES Mater. Manuf. 10, 22–28 (2020)
R. Li, W. Li, M. Liu, Q. He, Y. Wang, Q. Zhan, T. Wang, Structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties of Cu-doped PbS nanofilms. ES Mater. Manuf. 4, 38–44 (2019)
S. Suthakaran, S. Dhanapandian, N. Krishnakumar, N. Ponpandian, Hydrothermal synthesis of surfactant assisted Zn doped SnO2 nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic performance and energy storage performance. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 141, 109407 (2020)
S. Asaithambi, P. Sakthivel, M. Karuppaiah, G. Udhaya Sankar, K. Balamurugan, R. Yuvakkumar, M. Thambidurai, G. Ravi, Investigation of electrochemical properties of various transition metals doped SnO2 spherical nanostructures for supercapacitor applications. J. Energy Storage 31, 101530 (2020)
L.C.J. Pereira, M.R. Nunes, O.C. Monteiro, Magnetic properties of Co-doped TiO2 anatase nanopowders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 222502 (2008)
T.A. Abdel-Baset, Y.-W. Fang, B. Anis, C.-G. Duan, M. Abdel-Hafiez, Structural and magnetic properties of transition-metal-doped Zn1−xFexO. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 115 (2016)
M. Hassan Farooq, R. Hussain, L. Zhang, Fabrication, characterization and magnetic properties of Mn-doped SnO2 nanostructures via hydrothermal method. Mater. Lett. 131, 350–353 (2014)
J. Khajonrit, N. Prasoetsopha, T. Sinprachim, P. Kidkhunthod, S. Pinitsoontorn, S. Maensiri, Structure, characterization, and magnetic/electrochemical properties of Ni-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 015010 (2017)
K. Shiva, M.S.R.N. Kiran, U. Ramamurthy, A broad pore size distribution mesoporous SnO2 as anode for lithium-ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 16, 3643–3649 (2012)
A.D. Adhikari, R. Oraon, S.K. Tiwari, P. Saren, C.K. Maity, J.H. Lee, N.H. Kim, G.C. Nayak, Zn-doped SnO2 nano-urchin enriched 3D carbonaceous m framework for supercapacitor application. N. J. Chem. 42, 955–963 (2018)
M. Kuppan, S. Kaleemulla, N. Madhusudhana Rao, N. SaiKrishna, M. Rigana Begam, D. Sreekantha Reddy, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped SnO2 thin films prepared by flash evaporation technique. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 6(3), 1933–1935 (2014)
J. Fan, M. Guerrero, A. Carretero-Genevrier, M.D. Baro, S. Surinach, E. Pellicer. J. Sort, Evaporation-induced self-assembly synthesis of Ni-doped mesoporous SnO2 thin films with tunable room temperature magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 5517 (2017)
J. Divya, A. Pramothkumar, S. Joshua Gnanamuthu, D.C. Bernice Victoria, P.C. Jobe Prabakar, Structural, optical, electrical and magnetic properties of Cu and Ni doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared via Co-precipitation approach. Physica B 588, 412169 (2020)
M. Aliahmad, M.D. Iranica, Ni-doped SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method. J. Energy Environ. 4(1), 49–52 (2013)
A. Azam, A.S. Ahmed, M. Chaman, A.H. Naqvi, Investigation of electrical properties of Mn doped tin oxide nanoparticles using impedance spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 094329 (2010)
W.-T. Li, X.-D. Zhang, X. Guo, Electrospun Ni-doped SnO2 nanofiber array for selective sensing of NO2. Sens. Actuators B 244, 509–521 (2017)
A. Sharma, M. Varshney, S. Kumar, K.D. Verma, R. Kumar, Magnetic properties of Fe and Ni doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 1(1), 29–33 (2011)
S. Kumar, Exploration of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of transition metal doped SnO2 films grown using pulsed laser deposition. Vacuum 182, 109725 (2020)
C. Cajas, F.H. Aragón, C.M. Campo, J.A.H. Coaquira, J.E. Rodrıguez-Paez, Synthesis and characterization of Fe-doped SnO2. Rev. Mex. Fıs. S 58(2), 12–15 (2012)
L. Soussi, T. Garmim, O. Karzazi, A. Rmili, A. El Bachiri, A. Louardi, H. Erguig, Effect of (Co, Fe, Ni) doping on structural, optical and electrical properties of sprayed SnO2 thin film. Surf. Interfaces 19, 100467 (2020)
A. Ammari, M. Trari, B. Bellal, N. Zebbar, Effect of Sb doping on the transport and electrochemical properties of partially amorphous SnO2 thin films. J. Electroanal. Chem. 823, 638–646 (2018)
B. Liang, J. Wang, S. Zhang, X. Liang, H. Huang, D. Huang, W. Zhou, J. Guo, Hybrid of Co-doped SnO2 and graphene sheets as anode material with enhanced lithium storage properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 533, 147447 (2020)
S. Hao, Y. Shen, H. Wu, J. Meng, L. Xie, T. Wen, N. Gu, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, H. Xu, Modulatory effects of the composition and structure on the osteogenic enhancement for superparamagnetic scaffolds. Eng. Sci. 4, 100–110 (2018)
L. Doan, Y. Lu, M. Karatela, V. Phan, C. Jeffryes, T. Benson, E.K. Wujcik, Surface modifications of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with polylactic acid–polyethylene glycol diblock copolymer and graphene oxide for a protein delivery vehicle. Eng. Sci. 7, 10–16 (2019)
Z. Wang, K. Sun, P. Xie, Y. Liu, Q. Gu, R. Fan, Permittivity transition from positive to negative in acrylic polyurethane–aluminum composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 188, 107969 (2020)
Z. Wang, K. Sun, H. Wu, P. Xie, Z. Wang, X. Li, R. Fan, Compressible sliver nanowires/polyurethane sponge metacomposites with weakly negative permittivity controlled by elastic deformation. J. Mater. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05126-z
D.K. Das, Electrochemical determination of Zn2+ ion using diphenylamine/single walled carbon nanotube/cetyltrimethylammonium bromide modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Surf. Sci. Technol. 24, 149–162 (2008)
J. Huang, Diffusion impedance of electroactive materials, electrolytic solutions and porous electrodes: Warburg impedance and beyond. Electrochim. Acta 281(10), 170–188 (2018)
M. Bakierska, M. Swietosławski, M. Gajewska, A. Kowalczyk, Z. Piwowarska, L. Chmielarz, R. Dziembaj, M. Molenda, Enhancement of electrochemical performance of LiMn2O4 spinel cathode material by synergetic substitution with Ni and S. Materials 9, 366 (2016)
P. Baraneedharam, C. Siva, K. Nehru, M. Sivakumar, Investigations on structural, optical and electrochemical properties of blue luminescence SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2, 255–261 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blessi, S., Anand, S., Manikandan, A. et al. Influence of Ni substitution on opto-magnetic and electrochemical properties of CTAB-capped mesoporous SnO2 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 7630–7646 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05479-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05479-4