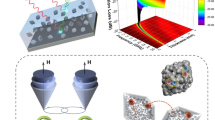
Abstract
It is well known that the electromagnetic (EM) wave absorption performance is determined by nanostructure and material components. Based on this principle, this study reports a facile two-step method for synthesizing porous Fe/α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with a tunable component ratio. The as-prepared hybrids, especially their pore size and phase composition, were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), BET, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Furthermore, the EM wave performance was estimated by the coaxial line method, which revealed that a thin layer of nanoparticles (≤ 1.5 mm) exhibited good performance. The desirable bandwidth (reflection loss, RL ≤ − 10 dB) of 5.2 GHz was obtained when the thickness was 1.2 mm. The bandwidth was greater than 2.0 GHz when the thickness was 1.0 mm. The EM wave loss mechanism, especially the contribution of a porous structure, is discussed in depth. In addition, a suitable weight ratio is essential to balance impedance matching and attenuation ability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Zhao, Y. Li, Q.W. Zeng, L. Wang, J.J. Ding, R. Zhang, R.C. Che, Galvanic replacement reaction involving core-shell magnetic chains and orientation-tunable microwave absorption properties. Small 16, 200352 (2020)
H. Lv, Z. Yang, P.L. Wang, G. Ji, J. Song, L. Zheng, H. Zeng, Z.J. Xu, A voltage-boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv. Mater. 30, 1706343 (2018)
G. Wu, Z. Jia, X. Zhou, G. Nie, H. Lv, Interlayer controllable of hierarchical MWCNTs@ C@ FexOy cross-linked composite with wideband electromagnetic absorption performance. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 128, 105687 (2020)
Q.H. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi, C.Y. Liang, K.P. Yuan, W. She, Y.J. Yang, R.C. Che, CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 28, 486 (2016)
Y. Guo, S. Dong, S. Liu, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang, H. Wang, Fabrication of porous disk-like Ni/NiO microwave absorber and its excellent broad frequency absorption performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 731, 143–149 (2018)
Z. Yang, S.J.H. Ong, C. Wei, H. Liao, S. Xi, Y. Du, G. Ji, Z.J. Xu, A flexible microwave shield with tunable frequency-transmission and electromagnetic compatibility. Adv. Func. Mater. 29(14), 1900163 (2019)
R.C. Che, L.M. Peng, X.F. Duan, Q. Chen, X.L. Liang, Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 16, 401 (2004)
H. Lv, X. Liang, Y. Cheng, G. Ji, D. Tang, B. Zhang, H. Zhang, Y. Du, Facile synthesis of porous coin-like iron and its excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. RSC Adv. 5(33), 25936–25941 (2015)
A. Wang, W. Wang, C. Long, W. Li, J. Guan, H. Gu, G. Xu, Facile preparation, formation mechanism and microwave absorption properties of porous carbonyl iron flakes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2(19), 3769–3776 (2014)
H. Zhang, J. Zhao, G. Ji, Y. Du, Achieving excellent bandwidth absorption by a mirror growth process of magnetic porous polyhedron structures. Nano Res. 9(6), 1813–1822 (2016)
J.W. Liu, R.C. Che, H.J. Chen, F. Zhang, F. Xia, Q.S. Wu, M. Wang, Microwave absorption enhancement of multifunctional composite microspheres with spinel Fe3O4 cores and anatase TiO2 shells. Small 8, 1214 (2012)
Z. Gao, Z. Jia, K. Wang, X.H. Liu, G. Wu, Simultaneous enhancement of recoverable energy density and efficiency of lead-free relator-ferroelectric BNT-based ceramics. Chem. Eng. J. 402, 125951 (2020)
Y. Guo, S. Liu, Z. Zhang, S. Dong, H. Wang, Fabrication of ZnO/Fe rod-like core-shell structure as high-performance microwave absorber. J. Alloy. Compd. 694, 549–555 (2017)
J. Li, J. Ma, S. Chen, Y. Huang, J. He, Adsorption of lysozyme by alginate/graphene oxide composite beads with enhanced stability and mechanical property. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 89, 25–32 (2018)
L. Yang, X. Zhou, Z. Jia, H. Lv, Y. Zhu, J. Liu, Z. Yang, Selective tailoring of covalent bonds on graphitized hollow carbon spheres towards controllable porous structure and wideband electromagnetic absorption. Carbon 167, 843–851 (2020)
T.B. Sharmila, J.V. Antony, M. Jayakrishnan, P.S. Beegum, E.T. Thachil, Mechanical, thermal and dielectric properties of hybrid composites of epoxy and reduced graphene oxide/iron oxide. Mater. Des. 90, 66–75 (2016)
B. Zhao, X. Guo, W. Zhao, J. Deng, B. Fan, G. Shao, Z. Bai, R. Zhang, Facile synthesis of yolk-shell Ni@ void@ SnO2 (Ni3Sn2) ternary composites via galvanic replacement/Kirkendall effect and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. Nano Res. 10(1), 331–343 (2017)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Z. Yang, Z. Jia, H. Wu, L. Yang, H. Li, P. Guo, H. Lv, Design of carbon sphere/magnetic quantum dots with tunable phase compositions an high frequency d boost dielectric loss behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 333, 519–528 (2018)
H. Lv, H. Zhang, G. Ji, Z.J. Xu, Interface strategy to achieve tunable attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(10), 6529–6538 (2016)
B. Zhao, Y. Li, J. Liu, L. Fan, K. Gao, Z. Bai, L. Liang, X. Guo, R. Zhang, Symmetrical polyhedron-bowl Co/CoO with hexagonal plate to forward electromagnetic wave absorption ability. CrystEngComm 21(5), 816–826 (2019)
F. Wang, Y. Sun, D. Li, B. Zhong, Z. Wu, S. Zuo, D. Yan, R. Zhuo, J. Feng, P. Yan, Microwave absorption properties of 3D cross-linked Fe/C porous nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Carbon 134, 264–273 (2018)
Z. Li, X. Han, Y. Ma, D. Liu, Y. Wang, P. Xu, C. Li, Y. Du, MOFs-derived hollow Co/C microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(7), 8904–8913 (2018)
Q. Qi, L. Ma, B. Zhao, S. Wang, X. Liu, Y. Lei, C.B. Park, An effective design strategy for the sandwich structure of PVDF/GNP-Ni-CNT composites with remarkable electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(32), 36568 (2020)
X. Liang, G. Ji, H. Zhang, Y. Du, Porous three-dimensional flower-like Co/CoO and its excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7(18), 9776–9783 (2015)
Y. Guo, Z. Yang, T. Guo, H. Wu, G. Liu, L.Y. Wang, R. Wu, Doping strategy to boost the electromagnetic wave attenuation ability of hollow carbon spheres at elevated temperatures. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 1539–1544 (2018)
J. Yu, F. Chi, Y. Sun, J. Guo, X. Liu, Assembled porous Fe3O4@ g-C3N4 hybrid nanocomposites with multiple interface polarization for stable microwave absorption. Ceram. Int. 44(16), 19207–19216 (2018)
B. Zhao, L. Liang, J. Deng, Z. Bai, J. Liu, X. Guo, K. Gao, W. Guo, R. Zhang, 1D Cu@ Ni nanorods anchored on 2D reduced graphene oxide with interfacial engineering to enhance microwave absorption properties. CrystEngComm 19(44), 6579–6587 (2017)
T.Q. Hou, Z.R. Jia, S.Q. He, Y. Su, X.D. Zhang, B.H. Xu, X.H. Liu, G.L. Wu, Design and synthesis of NiCo/Co4S3@C hybrid material with tunable and efficient electromagnetic absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 583, 321–330 (2020)
G. Ji, X. Liang, H. Zhang, Y. Du, A novel rod-like MnO2@ Fe loading on graphene giving excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 3(19), 5056–5064 (2015)
S. Jana, A. Mondal, A. Ghosh, Fabrication of stable NiO/Fe2O3 heterostructure: a versatile hybrid material for electrochemical sensing of glucose, methanol, and enhanced photodecomposition and/photoreduction of water contaminants. Appl. Catal. B 232, 26–36 (2018)
S. Liu, Y. Guo, S. Dong, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang, H. Wang, Y. Li, Facile synthesis of a Sn/SnO2@ C ternary composite with superior broader frequency performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 711, 184–189 (2017)
H. Lv, Y. Guo, G. Wu, G. Ji, Y. Zhao, Z.J. Xu, Interface polarization strategy to solve electromagnetic wave interference issue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9(6), 5660–5668 (2017)
C. Song, X. Yin, M. Han, X. Li, Z. Hou, L. Zhang, L. Cheng, Three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide foam modified with ZnO nanowires for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 116, 50–58 (2017)
K. Ali, J. Iqbal, T. Jan, I. Ahmad, D. Wan, A. Bahadur, S. Iqbal, Synthesis of CuFe2O4-ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 705, 559–565 (2017)
B. Zhao, X. Zhang, J. Deng, Z. Bai, L. Liang, Y. Li, R. Zhang, A novel sponge-like 2D Ni/derivative heterostructure to strengthen microwave absorption performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20(45), 28623–28633 (2018)
H. Lv, Y. Guo, Z. Yang, Y. Cheng, L.P. Wang, B. Zhang, Y. Zhao, Z.J. Xu, G. Ji, A brief introduction to the fabrication and synthesis of graphene based composites for the realization of electromagnetic absorbing materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 5(3), 491–512 (2017)
L. Yang, H. Lv, M. Li, J. Liu, Z. Yang, Multiple polarization effect of shell evolution on hierarchical hollow C@ MnO2 composites and their wideband electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 392, 123666 (2020)
K. Ali, J. Iqbal, T. Jana, N. Ahmad, I. Ahmad, D. Wan, Enhancement of microwaves absorption properties of CuFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles embedded in MgO matrix. J. Alloy. Compd. 696, 711–717 (2017)
W. Liu, H. Zhang, Y. Du, Achieving hierarchical hollow carbon@ Fe@ Fe3O4 nanospheres with superior microwave absorption properties and lightweight features. Journal of Materials Chemistry C 3(39), 10232–10241 (2015)
P. Kaur, A. Duong, S. Chawla, S.B. Narang, S.S. Meena, Effect of precursors on the structural, magnetic, dielectric, microwave and electromagnetic properties of Co–Zr doped nanocrystalline strontium hexaferrites synthesized via sol–gel method. SN Appl. Sci. 1(10), 1239 (2019)
Z. Lou, C. Yuan, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Cai, L. Yang, W. Wang, H. Han, J. Zou, Synthesis of porous carbon matrix with inlaid Fe3C/Fe3O4 micro-particles as an effective electromagnetic wave absorber from natural wood shavings. J. Alloy. Compd. 775, 800–809 (2019)
Y. Cheng, Y. Guo, Z. Zhang, S. Dong, H. Wang, Facile synthesis of NixCo3-xS4 hollow nanoprism with broader electromagnetic absorption properties: Effect of Ni/Co atomic ratios. J. Alloy. Compd. 767, 323–329 (2018)
H. Lv, Z. Yang, H. Xu, L. Wang, R. Wu, An electrical switch-driven flexible electromagnetic absorber. Adv. Func. Mater. 30(4), 1907251 (2020)
W. Xu, G.-S. Wang, P.-G. Yin, Designed fabrication of reduced graphene oxides/Ni hybrids for effective electromagnetic absorption and shielding. Carbon 139, 759–767 (2018)
Z. Jia, B. Wang, A. Feng, J. Liu, M. Zhang, Z. Huang, G. Wu, Development of spindle-cone shaped of Fe/α-Fe2O3 hybrids and their superior wideband electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 799, 216–223 (2019)
H. Lv, Y. Li, Z. Jia, L. Wang, X. Guo, B. Zhao, R. Zhang, Exceptionally porous three-dimensional architectural nanostructure derived from CNTs/graphene aerogel towards the ultra-wideband EM absorption. Compos. B Eng. 196, 108122 (2020)
M. Qiao, X. Lei, Y. Ma, L. Tian, K. Su, Q. Zhang, Dependency of tunable microwave absorption performance on morphology-controlled hierarchical shells for core-shell Fe3O4@ MnO2 composite microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 304, 552–562 (2016)
W. You, W. She, Z. Liu, H. Bi, R. Che, High-temperature annealing of an iron microplate with excellent microwave absorption performance and its direct micromagnetic analysis by electron holography and Lorentz microscopy. J. Mater. Chem. C 5(24), 6047–6053 (2017)
G. Sun, B. Dong, M. Cao, B. Wei, C. Hu, Hierarchical dendrite-like magnetic materials of Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption. Chem. Mater. 23(6), 1587–1593 (2011)
X. Liang, Y. Cheng, H. Zhang, D. Tang, B. Zhang, G. Ji, Y. Du, Coin-like α-Fe2O3@ CoFe2O4 core-shell composites with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7(8), 4744–4750 (2015)
G. Wu, H. Zhang, X. Luo, L. Yang, H. Lv, Investigation and optimization of Fe/ZnFe2O4 as a Wide-band electromagnetic absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 536, 548–555 (2019)
Z. Lou, R. Li, P. Wang, Y. Zhang, B. Chen, C. Huang, C. Wang, H. Han, Y. Li, Phenolic foam-derived magnetic carbon foams (MCFs) with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 391, 123571 (2020)
A. Feng, Z. Jia, Y. Zhao, H. Lv, Development of Fe/Fe3O4@ C composite with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 745, 547–554 (2018)
T.Q. Hou, Z.R. Jia, A. Feng, Z.H. Zhou, X.H. Liu, H. Lv, G.L. Wu, Hierarchical composite of biomass derived magnetic carbon framework and phytic acid doped polyanilne with absorption capacity. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 68, 61–69 (2021)
Z.C. Lou, R. Li, J. Liu, Q.Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y.J. Li, Used dye adsorbent derived N-doped magnetic carbon foam with enhanced electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 854, 157286 (2021)
F. Zhang, W. Cui, B.B. Wang, B.H. Xu, X.H. Liu, X.H. Liu, Z. Jia, G. Wu, Morphology-control synthesis of polyaniline decorated porous carbon with remarkable electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities. Compos. B Eng. 204, 108491 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51702132) and the partial support from the National Demonstration Center for Experimental Materials Science and Engineering Education (Jiangsu University of Science and Technology) is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Chen, P., Dong, S. et al. Development of a porous iron-based magnetic absorber with enhanced electromagnetic absorption performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 6799–6809 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05385-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05385-9