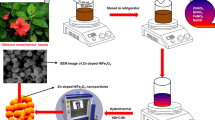
Abstract
Today, due to industrialization and urbanization, the world is facing serious water shortage and environmental alarms. The reusability of polluted water could be a promising approach for the sustainable wastewater management strategy. In the view, the present work compiles the synthesis of zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4) nanoparticles by a simple, economic, and eco-friendly route. The investigation of structural properties, thermal properties, and optical properties was carried out successfully by standard characterization techniques. The X-ray diffraction patterns confirmed the spinel-cubic lattice with Fd-3m space group for all the samples. The presence of vibrational frequency modes of Zn–O and Fe–O was ensured by FTIR spectra. The nano-size, morphology, atomic percentage, and some agglomeration of the nanoparticles were revealed by SEM–EDX and TEM images. The bandgap values were calculated from UV–Visible analysis data, and found to be 2.36 eV. The distribution of pore size by BJH method and BET surface area was evaluated by Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms, and is found to be 19.74 m2/g. The thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis affirmed percentage of weight loss and phase formation. The photocatalytic activity of methylene blue was evaluated under visible light and the removal efficiency of 96% and nano-catalyst shows active reusability. The cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were used for the study of electrochemical properties of nanoparticles. Further, the antimicrobial activity of the nanoparticles was investigated using Gram-positive, Gram-negative bacteria and some selected fungi strains. The obtained results revealed that the newly synthesized ZnFe2O4 can act as potential photocatalyst, electrochemical sensor, and antimicrobial agent.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.M. Dias, C. Petit, Towards the use of metal-organic frameworks for water reuse: a review of the recent advances in the field of organic pollutants removal and degradation and the next steps in the field. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 22484–22506 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta05440k
S.R. Patade, D.D. Andhare, S.B. Somvanshi, S.A. Jadhav, M.V. Khedkar, K.M. Jadhav, Self-heating evaluation of superparamagnetic MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia application towards cancer treatment. Ceram. Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.029
A. Manuscript, Mater. Adv. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MA00251H
S.B. Somvanshi, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, K.M. Jadhav, Influential diamagnetic magnesium (Mg2+) ion substitution in nano-spinel zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4): thermal, structural, spectral, optical and physisorption analysis. Ceram. Int. 46, 8640–8650 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.097
S.A. Jadhav, S.B. Somvanshi, M.V. Khedkar, S.R. Patade, K.M. Jadhav, Magneto-structural and photocatalytic behavior of mixed Ni–Zn nano-spinel ferrites: visible light-enabled active photodegradation of rhodamine B. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 11352–11365 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03684-1
P. Guo, L. Cui, Y. Wang, M. Lv, B. Wang, X.S. Zhao, Facile synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles with tunable magnetic and sensing properties. Langmuir 29, 8997–9003 (2013)
S. Mahvidi, M. Gharagozlou, M. Mahdavian, S. Naghibi, Potency of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles as corrosion inhibitor for stainless steel; the pigment extract study. Mater. Res. 20, 1492–1502 (2017)
S. Mandal, S. Natarajan, A. Tamilselvi, S. Mayadevi, Photocatalytic and antimicrobial activities of zinc ferrite nanoparticles synthesized through soft chemical route: a magnetically recyclable catalyst for water/wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 2706–2712 (2016)
D. Maiti, A. Saha, P.S. Devi, Surface modified multifunctional ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles for hydrophobic and hydrophilic anti-cancer drug molecule loading. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 1439–1450 (2016)
G. Ma, Y. Chen, L. Li, D. Jiang, R. Qiao, Y. Zhu, An attractive photocatalytic inorganic antibacterial agent: preparation and property of graphene/zinc ferrite/polyaniline composites. Mater. Lett. 131, 38–41 (2014)
S.B. Somvanshi, P.B. Kharat, M.V. Khedkar, K.M. Jadhav, Hydrophobic to hydrophilic surface transformation of nano-scale zinc ferrite via oleic acid coating: magnetic hyperthermia study towards biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 46, 7642–7653 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.11.265
S.B. Somvanshi, P.B. Kharat, T.S. Saraf, S.B. Somwanshi, S.B. Shejul, K.M. Jadhav, Multifunctional nano-magnetic particles assisted viral RNA-extraction protocol for potential detection of COVID-19. Mater. Res. Innov. 00, 1–6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/14328917.2020.1769350
H. Liu, Y. Guo, Y. Zhang, F. Wu, Y. Liu, D. Zhang, Synthesis and properties of ZnFe2O4 replica with biological hierarchical structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178, 1057–1061 (2013)
X. Hangxun, B.W. Zeiger, K.S. Suslick, Sonochemical synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 2555–2567 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35282f
C.G. Anchieta, D. Sallet, E.L. Foletto, S. Syllos, O. Chiavone-filho, A.O. Claudio, Synthesis of ternary zinc spinel oxides and their application in the photodegradation of organic pollutant. Ceram. Int. 40, 4173–4178 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.08.074
Z. Zhong-wei, O. Kingsam, W. Ming, Structural macrokinetics of synthesizing ZnFe2O4 by mechanical ball milling. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 20, 1131–1135 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60267-3
V.L. Ranganatha, K.S. Nithin, S.A. Khanum, G. Nagaraju, C. Mallikarjunaswamy, Zinc oxide nanoparticles: a significant review on synthetic strategies, characterization and applications, in: AIP Conf. Proc., AIP Publishing, (2019), p. 20089.
C. Mallikarjunaswamy, V. Lakshmi Ranganatha, R. Ramu, Udayabhanu, G. Nagaraju, Facile microwave-assisted green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: application to photodegradation, antibacterial and antioxidant. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02612-2
A. Bardhan, C.K. Ghosh, M.K. Mitra, G.C. Das, S. Mukherjee, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Low temperature synthesis of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. Solid State Sci. 12, 839–844 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2010.02.007
L. Han, X. Zhou, L. Wan, Y. Deng, S. Zhan, Synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanoplates by succinic acid-assisted hydrothermal route and their photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B under visible light. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 123–130 (2014)
X. Huang, J. Zhang, S. Xiao, T. Sang, G. Chen, Unique electromagnetic properties of the zinc ferrite nanofiber. Mater. Lett. 124, 126–128 (2014)
O.V. Yelenich, S.O. Solopan, T.V. Kolodiazhnyi, V.V. Dzyublyuk, A.I. Tovstolytkin, A.G. Belous, Magnetic properties and high heating ef fi ciency of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 146, 129–135 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.03.010
G. Sangeetha, S. Rajeshwari, R. Venckatesh, Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aloe Barbadensis miller leaf extract: structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 2560–2566 (2011)
R. Rathnasamy, P. Thangasamy, R. Thangamuthu, S. Sampath, V. Alagan, Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Carica papaya leaf extracts for photocatalytic and photovoltaic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 10374–10381 (2017)
B. Siripireddy, B.K. Mandal, Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Eucalyptus globulus and their photocatalytic and antioxidant activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 785–797 (2017)
Y. Zheng, L. Fu, F. Han, A. Wang, W. Cai, J. Yu, J. Yang, F. Peng, Green biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Corymbia citriodora leaf extract and their photocatalytic activity. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 8, 59–63 (2015)
T. Karnan, S.A.S. Selvakumar, Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum L.) peel extract and their photocatalytic activity on methyl orange dye. J. Mol. Struct. 1125, 358–365 (2016)
C.A. Soto-Robles, O.J. Nava, A.R. Vilchis-Nestor, A. Castro-Beltrán, C.M. Gómez-Gutiérrez, E. Lugo-Medina, A. Olivas, P.A. Luque, Biosynthesized zinc oxide using Lycopersicon esculentum peel extract for methylene blue degradation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 3722–3729 (2018)
M. Sriramulu, D. Shukla, S. Sumathi, Aegle marmelos leaves extract mediated synthesis of zinc ferrite: antibacterial activity and drug delivery. Mater. Res. Express. 5, 115404 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aadd88
S.G. Shingade, S.B. Bari, U.B. Waghmare, Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of 5-chloroindoline-2, 3-dione derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 21, 1302–1312 (2012)
S.B. Somvanshi, S.A. Jadhav, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, S.D. More, K.M. Jadhav, Structural, thermal, spectral, optical and surface analysis of rare earth metal ion (Gd3+) doped mixed Zn–Mg nano-spinel ferrites. Ceram. Int. 46, 13170–13179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.091
S. Sun, X. Yang, Y. Zhang, F. Zhang, J. Ding, J. Bao, C. Gao, Enhanced photocatalytic activity of sponge-like ZnFe2O4 synthesized by solution combustion method. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 22, 639–643 (2012)
C. Liu, Y. Ni, L. Zhang, F. Guo, T. Wu, Simple solution-combusting synthesis of octahedral ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals and additive-promoted photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv. 4, 47402–47408 (2014)
M.N.Z. Ahmed, K.B. Chandrasekhar, A.A. Jahagirdar, H. Nagabhushana, B.M. Nagabhushana, Photocatalytic activity of nanocrystalline ZnO, α-Fe2O3 and ZnFe2O4/ZnO. Appl. Nanosci. 5, 961–968 (2015)
C. Singh, S. Jauhar, V. Kumar, J. Singh, S. Singhal, Synthesis of zinc substituted cobalt ferrites via reverse micelle technique involving in situ template formation: a study on their structural, magnetic, optical and catalytic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 156, 188–197 (2015)
X. Cao, L. Gu, X. Lan, C. Zhao, D. Yao, W. Sheng, Spinel ZnFe2O4 nanoplates embedded with Ag clusters: preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic application. Mater. Chem. Phys. 106, 175–180 (2007)
S.B. Patil, H.S.B. Naik, G. Nagaraju, R. Viswanath, S.K. Rashmi, Sugarcane juice mediated eco-friendly synthesis of visible light active zinc ferrite nanoparticles: application to degradation of mixed dyes and antibacterial activities. Mater. Chem. Phys. 212, 351–362 (2018)
B.S. Surendra, Green engineered synthesis of Ag-doped CuFe2O4: characterization, cyclic voltammetry and photocatalytic studies. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Dev. 3, 44–50 (2018)
B.S. Surendra, H.P. Nagaswarupa, M.U. Hemashree, J. Khanum, Jatropha extract mediated synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanopowder: excellent performance as an electrochemical sensor, UV photocatalyst and an antibacterial activity. Chem. Phys. Lett. 739, 136980 (2020)
N. Matinise, K. Kaviyarasu, N. Mongwaketsi, S. Khamlich, L. Kotsedi, N. Mayedwa, M. Maaza, Green synthesis of novel zinc iron oxide (ZnFe2O4) nanocomposite via Moringa oleifera natural extract for electrochemical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 446, 66–73 (2018)
B.S. Surendra, M. Veerabhdraswamy, K.S. Anantharaju, H.P. Nagaswarupa, S.C. Prashantha, Green and chemical-engineered CuFe2O4: characterization, cyclic voltammetry, photocatalytic and photoluminescent investigation for multifunctional applications. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 8, 45–59 (2018)
Acknowledgements
Dr. Lakshmi Ranganatha V gratefully acknowledges the financial support provided by the NIE Management through NIE-CRD project to carry out this research work. Dr. G. Nagaraju thanks DST Nanomission, Government of India, New Delhi, for financial support (No. SR/NM/NS-1262/2013 (G) dated 18-03-2015). Dr. Mallikarjunaswamy C and Ms. Pramila S acknowledge the JSS College of Arts, Commerce and Science for providing the laboratory facility. Further, also acknowledge ‘DSC-SAIF Cochin’ Cochin University of Science and Technology for instrumentation facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmi Ranganatha, V., Pramila, S., Nagaraju, G. et al. Cost-effective and green approach for the synthesis of zinc ferrite nanoparticles using Aegle Marmelos extract as a fuel: catalytic, electrochemical, and microbial applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 17386–17403 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04295-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04295-6