Abstract
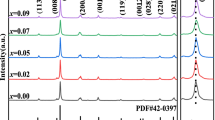
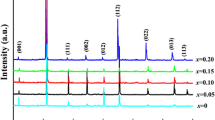
In this work, Sb-doped Ba0.93Ca0.07Ti0.92Sn0.08O3 ceramics were successfully prepared by conventional solid-phase sintering reaction process and their phase structure, microstructure, and electrical properties were investigated systematically. The enhanced piezoelectric and dielectric properties (d33 = 520 pC/N, kp = 0.475, Qm = 149.3, εr = 6113 and tanδ = 1.73%) were obtained due to the co-existence of rhombohedral, orthorhombic and tetragonal phases near the room temperature. Meanwhile, the optimal ferroelectric properties (Pr = 8.17 μC/cm2, Ec = 1.56 kV/cm) were also gained at x = 0.15 mol%. The temperature dependence of dielectric constant reveals relaxation behavior at various frequencies, and relevant diffuse phase transition has been carefully studied. The large d33, εr, low tanδ and the relaxation behavior in (1−x)Ba0.93Ca0.07Ti0.92Sn0.08O3–xSb2O3 (x = 0.15 mol%) ceramic make it as a potential candidate for high power piezoelectric applications and ceramic capacitors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Zhang et al., Advantages and challenges of relaxor-PbTiO3 ferroelectric crystals for electroacoustic transducers—a review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 68, 1–66 (2015)
J.G. Hao et al., Progress in high-strain perovskite piezoelectric ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 135, 1–57 (2019)
S.J. Zhang, F. Li, High performance ferroelectric relaxor-PbTiO3 single crystals: status and perspective. J. Appl. Phys. 111(3), 031301 (2012)
F. Zeng et al., Relaxor phenomenon of (1 − x)(Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.09Ti0.91)O3–xTa + 0.6 wt% Li2CO3 ceramics with high piezoelectric constant and Curie temperature. Ceram. Int. 44(9), 10677–10684 (2018)
M. Kroutvar et al., Optically programmable electron spin memory using semiconductor quantum dots. Nature 432(7013), 81–84 (2004)
W.F. Liu, X.B. Ren, Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(25), 257602 (2009)
L.-F. Zhu et al., Enhanced piezoelectric properties of (Ba1 – xCax)(Ti0.92Sn0.08)O3 lead-free ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96(1), 241–245 (2013)
Y. Yang et al., Phase coexistence and large piezoelectricity in BaTiO3–CaSnO3 lead-free ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101(6), 2594–2605 (2018)
L. Zhao et al., Phase structure and property evaluation of (Ba, Ca)(Ti, Sn)O3 sintered with Li2CO3 addition at low temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97(7), 2164–2169 (2014)
G.-Z. Zang et al., Perovskite (Na0.5K0.5)1 − x(LiSb)xNb1 − xO3 lead-free piezoceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(21), 212908 (2006)
N. Klein et al., A study of the phase diagram of (K, Na, Li)NbO3 determined by dielectric and piezoelectric measurements, and Raman spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 102(1), 014112 (2007)
X. Pang et al., Effects of Sb content on electrical properties of lead-free piezoelectric (K0.4425Na0.52Li0.0375) (Nb0.9625 − xSbxTa0.0375)O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 38(2), 1249–1254 (2012)
J. Ma et al., Dielectric, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of Sb2O3-modified (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 lead-free ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(2), 992–996 (2013)
Y.Y. Wang et al., Phase transition and piezoelectric properties of alkali niobate ceramics through composition tuning. RSC Adv. 5(76), 61989–61997 (2015)
W. Gao, J. Lv, X. Lou, Large electric-field-induced strain and enhanced piezoelectric constant in CuO-modified BiFeO3−BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101(8), 3383–3392 (2018)
K. Tong et al., Enhanced piezoelectric response and high-temperature sensitivity by site-selected doping of BiFeO3−BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(4), 1356–1366 (2018)
L. Zhao et al., High piezoelectricity in CuO-modified Ba(Ti0.90Sn0.10)O3 lead-free ceramics with modulated phase structure. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37(4), 1411–1419 (2017)
C. Zhao et al., Improved temperature stability and high piezoelectricity in lead-free barium titanate-based ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(16), 5411–5419 (2018)
N. Baskaran et al., Phase transformation studies of ceramic BaTiO3 using thermo-Raman and dielectric constant measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 91(12), 10038 (2002)
A. Jalalian, A.M. Grishin, Biocompatible ferroelectric (Na, K)NbO3 nanofibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(1), 012904 (2012)
R. Hayati et al., Effects of Bi2O3 additive on sintering process and dielectric, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 lead-free piezoceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36(14), 3391–3400 (2016)
Y. Yang et al., Coexistence of three ferroelectric phases and enhanced piezoelectric properties in BaTiO3–CaHfO3 lead-free ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(2), 557–566 (2018)
J. Pokorný et al., Use of Raman spectroscopy to determine the site occupancy of dopants in BaTiO3. J. Appl. Phys. 109(11), 114110 (2011)
R. Jing et al., Comparative study on structure, dielectric, and piezoelectric properties of (Na0.47Bi0.47Ba0.06)0.95A0.05TiO3 (A = Ca2+/Sr2+) ceramics: effect of radii of A-site cations. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(9), 3111–3117 (2018)
T. Wang et al., Microstructure and electrical properties of (1 − x)[0.8Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-0.2Bi0.5K0.5TiO3]–xBiCoO3 lead-free ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 186, 407–414 (2017)
L. Zhao et al., Effect of Li2O addition on sintering and piezoelectric properties of (Ba, Ca) (Ti, Sn)O3 lead-free piezoceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35(2), 533–540 (2015)
N. Ma, B.-P. Zhang, W.-G. Yang, Low-temperature sintering of Li2O-doped BaTiO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. J. Electroceram. 28(4), 275–280 (2012)
L. Zhao et al., Piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of (Ba, Ca) (Ti, Sn)O3 lead-free ceramics sintered with Li2O additives: analysis of point defects and phase structures. Ceram. Int. 42(1), 1086–1093 (2016)
Q. Zhang et al., Enhanced piezoelectric response of (Ba, Ca) (Ti, Zr)O3 ceramics by super large grain size and construction of phase boundary. J. Alloy Compd. 794, 542–552 (2019)
N. Lei et al., Effect of lattice occupation behavior of Li+ cations on microstructure and electrical properties of (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3-based lead-free piezoceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 109(5), 054102 (2011)
J. Du et al., Sintering and electrical properties of La-modified (Na0.52K0.45Li0.03)1 − 3xLax(Nb0.88Sb0.09Ta0.03)O3 lead-free ceramics. Ceram. Int. 40(3), 4319–4322 (2014)
J. Xing et al., Properties and structures of nonstoichiometric (K, Na)NbO3-based lead-free ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101(4), 1632–1645 (2018)
Z. Cen et al., Improving piezoelectric properties and temperature stability for KNN-based ceramics sintered in a reducing atmosphere. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101(9), 4108–4117 (2018)
F. Du et al., Synthesis, characterization, and dielectric properties of Ba(Ti1 – xSnx)O3 nanopowders and ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 44(9), 1930–1934 (2009)
B.D. Begg, E.R. Vance, J. Nowotny, Effect of particle size on the room-temperature crystal structure of barium titanate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 77(12), 6 (1994)
M.H. Frey, D.A. Payne, Grain-size effect on structure and phase transformations for barium titanate. Phys. Rev. B 54(5), 3158–3168 (1996)
M. Kuwabara, H. Matsuda, Shift of the Curie point of barium titanate ceramics with sintering temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 7 (1997)
M.-J. Pan, C.A. Randall, A brief introduction to ceramic capacitors. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 26(3), 44–50 (2010)
Z.G. Ye, Relaxor ferroelectric complex perovskites: structure, properties and phase transitions. Key Eng. Mater. 155–156, 81–122 (1998)
P.-F. Zhou et al., High piezoelectricity due to multiphase coexistence in low-temperature sintered (Ba, Ca)(Ti, Sn)O3-CuOx ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(17), 172904 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by High-Level Innovative Talents Plan of Guizhou Province No.(2015)4009 and Specialized Funds from Industry and Information Technology Department of Guizhou Province No. 2016056. And the authors also acknowledged the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Project No. 51602066.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, S., Zeng, F., Wang, Y. et al. Structure and electrical properties in Sb-doped Ba0.93Ca0.07Ti0.92Sn0.08O3 ceramics near the phase coexistence point. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 16235–16246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04166-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04166-0