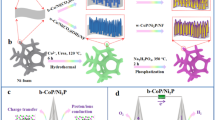
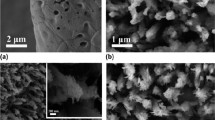
Abstract
Identifying highly efficient, abundant, cheap, Pt-free electrocatalysts for splitting water to produce hydrogen is critical to address the issues related to the fossil fuel consumption and environmental pollution. Nickel–copper phosphides have attracted interest as synergistic components with superior electrocatalytic activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). Herein, we report on branched heterostructures of nickel–copper phosphides (CuNi/P) grown on a 3D nickel foam (NF) substrate that were synthesized using a facile hydrothermal method and subsequent low-temperature phosphidization. These unique, branched heterostructures exhibited a strong synergetic effect between various metallic phosphides, and provided more active sites and improved the material’s electronic conductivity to produce a higher charge transfer rate. Consequently, the synthesized CuNi/P possessed superior electrocatalytic performance with a low overpotential of 99 mV at current density of 10 mA/cm2, and a low Tafel slope of 79 mV/decade for hydrogen evolution in alkaline solution. In addition, this electrocatalyst exhibited electrochemical resilience for at least 10 h, which was a good indication of its possible application for large-term water electrolysis. This reported strategy may provide a path for the development of other bimetallic phosphide materials with superior catalytic performance for the hydrogen evolution reaction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Chow, R.J. Kopp, P.R. Portney, Energy resources and global development. Science 302, 1528–1531 (2003)
M.G. Walter, E.L. Warren, J.R. McKone, S.W. Boettcher, Q. Mi, E.A. Santori, N.S. Lewis, Solar water splitting cells. Chem. Rev. 110, 6446–6473 (2010)
X.Y. Yu, X.W. Lou, Mixed metal sulfides for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1701592 (2018)
K.N. Dinh, P. Zheng, Z. Dai, Y. Zhang, R. Dangol, Y. Zheng, B. Li, Y. Zong, Q. Yan, Ultrathin porous NiFeV ternary layer hydroxide nanosheets as a highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Small 14, 1703257 (2018)
G. Chen, T. Wang, J. Zhang, P. Liu, H. Sun, X. Zhuang, M. Chen, X. Feng, Accelerated hydrogen evolution kinetics on NiFe-layered double hydroxide electrocatalysts by tailoring water dissociation active sites. Adv. Mater. 30, 1706279 (2018)
X. Long, G. Li, Z. Wang, H. Zhu, T. Zhang, S. Xiao, W. Guo, S. Yang, Metallic iron–nickel sulfide ultrathin nanosheets as a highly active electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 11900–11903 (2015)
J.X. Feng, H. Xu, Y.T. Dong, X.F. Lu, Y.X. Tong, G.R. Li, Efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis using cobalt nanotubes decorated with titanium dioxide nanodots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 2960–2964 (2017)
X. Zou, Y. Zhang, Noble metal-free hydrogen evolution catalysts for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 5148–5180 (2015)
A.P. Tiwari, D. Kim, Y. Kim, O. Prakash, H. Lee, Highly active and stable layered ternary transition metal chalcogenide for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 28, 366–372 (2016)
T. Liu, S. Wang, Q. Zhang, L. Chen, W. Hu, C.M. Li, Ultrasmall Ru2P nanoparticles on graphene: a highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst in both acidic and alkaline media. Chem. Commun. 54, 3343–3346 (2018)
Z. Zhu, H. Yin, C.T. He, M. Al-Mamun, P. Liu, L. Jiang, Y. Zhao, Y. Wang, H.G. Yang, Z. Tang, Ultrathin transition metal dichalcogenide/3d metal hydroxide hybridized nanosheets to enhance hydrogen evolution activity. Adv. Mater. 30, 1801171 (2018)
H. Yin, S. Zhao, K. Zhao, A. Muqsit, H. Tang, L. Chang, H. Zhao, Y. Gao, Z. Tang, Ultrathin platinum nanowires grown on single-layered nickel hydroxide with high hydrogen evolution activity. Nat. Commun. 6, 1–8 (2015)
P. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Zhang, S. Wan, S. Guo, G. Lu, J. Yao, X. Huang, Precise tuning in platinum–nickel/nickel sulfide interface nanowires for synergistic hydrogen evolution catalysis. Nat. Commun. 8, 1–9 (2017)
G.-R. Xu, J.-J. Hui, T. Huang, Y. Chen, J.-M. Lee, Platinum nanocuboids supported on reduced graphene oxide as efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Power Sources 285, 393–399 (2015)
P. Wang, K. Jiang, G. Wang, J. Yao, X. Huang, Phase and interface engineering of platinum–nickel nanowires for efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 12859–12863 (2016)
M. Zang, N. Xu, G. Cao, Z. Chen, J. Cui, L. Gan, H. Dai, X. Yang, P. Wang, Cobalt molybdenum oxide derived high-performance electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 8, 5062–5069 (2018)
A. Long, W. Li, M. Zhou, W. Gao, B. Liu, J. Wei, X. Zhang, H. Liu, Y. Liu, X. Zeng, MoS2 nanosheets grown on nickel chalcogenides: controllable synthesis and electrocatalytic origins for the hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 21514–21522 (2019)
D. Merki, X. Hu, Recent developments of molybdenum and tungsten sulfides as hydrogen evolution catalysts. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 3878–3888 (2011)
C. Tang, L. Xie, X. Sun, A.M. Asiri, Y. He, Highly efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution based on nickel diselenide nanowall film. Nanotechnology 27, 20LT02 (2016)
B. Liu, Y.F. Zhao, H.Q. Peng, Z.Y. Zhang, C.K. Sit, M.F. Yuen, T.R. Zhang, C.S. Lee, W.J. Zhang, Nickel–cobalt diselenide 3D mesoporous nanosheet networks supported on Ni foam: an all-pH highly efficient integrated electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606521 (2017)
Y. Guo, D. Guo, F. Ye, K. Wang, Z. Shi, X. Chen, C. Zhao, Self-supported NiSe2 nanowire arrays on carbon fiber paper as efficient and stable electrode for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 11884–11891 (2018)
M. Zhou, Q. Weng, Z.I. Popov, Y. Yang, L.Y. Antipina, P.B. Sorokin, X. Wang, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, Construction of polarized carbon–nickel catalytic surfaces for potent, durable, and economic hydrogen evolution reactions. ACS Nano 12, 4148–4155 (2018)
B. Cao, G.M. Veith, J.C. Neuefeind, R.R. Adzic, P.G. Khalifah, Mixed close-packed cobalt molybdenum nitrides as non-noble metal electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 19186–19192 (2013)
Y. Shi, B. Zhang, Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 1529–1541 (2016)
Y.-Y. Ma, C.-X. Wu, X.-J. Feng, H.-Q. Tan, L.-K. Yan, Y. Liu, Z.-H. Kang, E.-B. Wang, Y.-G. Li, Highly efficient hydrogen evolution from seawater by a low-cost and stable CoMoP@C electrocatalyst superior to Pt/C, Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 788–798 (2017)
J. Li, M. Yan, X. Zhou, Z.Q. Huang, Z. Xia, C.R. Chang, Y. Ma, Y. Qu, Mechanistic insights on ternary Ni2–xCoxP for hydrogen evolution and their hybrids with graphene as highly efficient and robust catalysts for overall water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 6785–6796 (2016)
E.J. Popczun, J.R. McKone, C.G. Read, A.J. Biacchi, A.M. Wiltrout, N.S. Lewis, R.E. Schaak, Nanostructured nickel phosphide as an electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 9267–9270 (2013)
Y. Pan, W. Hu, D. Liu, Y. Liu, C. Liu, Carbon nanotubes decorated with nickel phosphide nanoparticles as efficient nanohybrid electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 13087–13094 (2015)
Z. Zhou, L. Wei, Y. Wang, H.E. Karahan, Z. Chen, Y. Lei, X. Chen, S. Zhai, X. Liao, Y. Chen, Hydrogen evolution reaction activity of nickel phosphide is highly sensitive to electrolyte pH. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 20390–20397 (2017)
C. Guan, W. Xiao, H. Wu, X. Liu, W. Zang, H. Zhang, J. Ding, Y.P. Feng, S.J. Pennycook, J. Wang, Hollow Mo-doped CoP nanoarrays for efficient overall water splitting. Nano Energy 48, 73–80 (2018)
J. Chen, J. Liu, J.-Q. Xie, H. Ye, X.-Z. Fu, R. Sun, C.-P. Wong, Co-Fe-P nanotubes electrocatalysts derived from metal-organic frameworks for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction under wide pH range. Nano Energy 56, 225–233 (2019)
Y. Du, Z. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Yang, L. Wang, Nickel–iron phosphides nanorods derived from bimetallic-organic frameworks for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 457, 1081–1086 (2018)
H. Du, X. Zhang, Q. Tan, R. Kong, F. Qu, A Cu3P-CoP hybrid nanowire array: a superior electrocatalyst for acidic hydrogen evolution reactions. Chem. Commun. 53, 12012–12015 (2017)
X.-D. Wang, Y.-F. Xu, H.-S. Rao, W.-J. Xu, H.-Y. Chen, W.-X. Zhang, D.-B. Kuang, C.-Y. Su, Novel porous molybdenum tungsten phosphide hybrid nanosheets on carbon cloth for efficient hydrogen evolution. Energy Environ. Sci. 9, 1468–1475 (2016)
L. Sha, J. Yin, K. Ye, G. Wang, K. Zhu, K. Cheng, J. Yan, G. Wang, D. Cao, The construction of self-supported thorny leaf-like nickel–cobalt bimetal phosphides as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for urea electrolysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 9078–9085 (2019)
L. Wen, Y. Sun, C. Zhang, J. Yu, X. Li, X. Lyu, W. Cai, Y. Li, Cu-doped CoP nanorod arrays: efficient and durable hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalysts at all pH values. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1, 3835–3842 (2018)
L. Yan, B. Zhang, J. Zhu, S. Zhao, Y. Li, B. Zhang, J. Jiang, X. Ji, H. Zhang, P.K. Shen, Chestnut-like copper cobalt phosphide catalyst for all-pH hydrogen evolution reaction and alkaline water electrolysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 14271–14279 (2019)
X. Zhang, X. Zhang, H. Xu, Z. Wu, H. Wang, Y. Liang, Iron-doped cobalt monophosphide nanosheet/carbon nanotube hybrids as active and stable electrocatalysts for water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1606635 (2017)
C. Du, M. Shang, J. Mao, W. Song, Hierarchical MoP/Ni2P heterostructures on nickel foam for efficient water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 15940–15949 (2017)
Y. Liu, X. Hua, C. Xiao, T. Zhou, P. Huang, Z. Guo, B. Pan, Y. Xie, Heterogeneous spin states in ultrathin nanosheets induce subtle lattice distortion to trigger efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 5087–5092 (2016)
Y. Li, J. Xu, Z. Liu, H. Yu, Synthesis of Ni12P5 on Co3S4 material for effectively improved photocatalytic hydrogen production from water splitting under visible light. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 11694–11705 (2019)
S. Chu, W. Chen, G. Chen, J. Huang, R. Zhang, C. Song, X. Wang, C. Li, K.K. Ostrikov, Holey Ni–Cu phosphide nanosheets as a highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B 243, 537–545 (2019)
M. Asnavandi, B.H. Suryanto, W. Yang, X. Bo, C. Zhao, Dynamic hydrogen bubble templated NiCu phosphide electrodes for pH-insensitive hydrogen evolution reactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 2866–2871 (2018)
C.-C. Hou, Q.-Q. Chen, C.-J. Wang, F. Liang, Z. Lin, W.-F. Fu, Y. Chen, Self-supported cedarlike semimetallic Cu3P nanoarrays as a 3D high-performance Janus electrode for both oxygen and hydrogen evolution under basic conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 23037–23048 (2016)
A. Han, H. Zhang, R. Yuan, H. Ji, P. Du, Crystalline copper phosphide nanosheets as an efficient janus catalyst for overall water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 2240–2248 (2017)
X. Zhang, W. Gu, E. Wang, Self-supported ternary Co0.5Mn0.5P/carbon cloth (CC) as a high-performance hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. Nano Res. 10, 1001–1009 (2017)
J. Wei, M. Zhou, A. Long, Y. Xue, H. Liao, C. Wei, Z.J. Xu, Heterostructured electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction under alkaline conditions. Nano-micro Lett. 10, 75 (2018)
R. Daiyan, W.H. Saputera, Q. Zhang, E. Lovell, S. Lim, Y.H. Ng, X. Lu, R. Amal, 3D heterostructured copper electrode for conversion of carbon dioxide to alcohols at low overpotentials. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 3, 1800064 (2019)
R.K. Shervedani, A. Lasia, Study of the hydrogen evolution reaction on Ni–Mo–P electrodes in alkaline solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145, 2219 (1998)
M. Popczyk, The influence of molybdenum and silicon on activity of Ni+W composite coatings in the hydrogen evolution reaction. Surf. Interface Anal. 40, 246–249 (2008)
R. Daiyan, X. Lu, Y.H. Ng, R. Amal, Surface engineered tin foil for electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to formate. Catal. Sci. Technol. 7, 2542–2550 (2017)
R. Daiyan, X. Lu, X. Tan, X. Zhu, R. Chen, S.C. Smith, R. Amal, Antipoisoning nickel–carbon electrocatalyst for practical electrochemical CO2 reduction to CO. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 8002–8009 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Xiang, J. & Li, H. Branched heterostructures of nickel–copper phosphides as an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 11425–11433 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03691-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03691-2