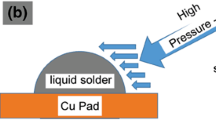
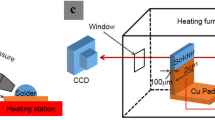
Abstract
The feasibility of the highly reliable and replicable microstructure formation of the transient liquid phase sintering (TLPS) paste during the early soldering and isothermal aging on the Cu substrate had been successfully investigated in this study. By using the Sn–0.7 wt% Cu (SC) solder paste as the base material and the Cu particles in the production of the TLPS Sn–10 wt% Cu (SC10) solder paste, the ensuing Cu6Sn5 phase from the isothermal aging process was found to have reduced the β-Sn area of the bulk SC10 solder microstructure. The growth kinetic for TLPS SC10 resulted in a 26.76 kJ/mol of activation energy level. The real-time synchrotron radiation imaging technique that was employed in studying the growth and formation of the primary intermetallic phases at the solder joints had also discovered the primary intermetallic in TLPS SC10 was not only found to have experienced an early nucleation just after the solder had melted, but its growth was also restricted prior to the solidification of the liquid solder. Therefore, the relevance of the results that were obtained from this research may offer a possible solution for aiding the future development of highly reliable solder joints in high temperature solder applications.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.-H. Jung, K.D. Min, C.-J. Lee, S.-B. Jung, Pressureless die attach by transient liquid phase sintering of Cu nanoparticles and Sn-58Bi particles assisted by polyvinylpyrrolidone dispersant. J. Alloys Compd. 781, 657–663 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.032
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, Transient liquid phase bonding of Sn–Bi solder with added Cu particles. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 4232–4244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4287-x
B.-S. Lee, J.-W. Yoon, Cu-Sn intermetallic compound joints for high-temperature power electronics applications. J. Electron. Mater. 47(1), 430–435 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5792-2
S. Sun, Q. Guo, Z. Zhang, H. Chen, M. Li, Microstructure evolution and mechanical strength evaluation in Ag/Sn/Cu TLP bonding interconnection during aging test. Microelectron. Reliab. 80, 144–148 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2017.12.001
H. Pan, J. Huang, H. Ji, M. Li, Enhancing the solid/liquid interfacial metallurgical reaction of Sn-Cu composite solder by ultrasonic-assisted chip attachment. J. Alloys Compd. 784, 603–610 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.090
H. Feng, J. Huang, X. Peng, Z. Lv, Y. Wang, J. Yang, S. Chen, X. Zhao, A study of Ni3Sn4 growth dynamics in Ni-Sn TLPS bonding process by differential scanning calorimetry. Thermochim. Acta 663, 53–57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2018.03.006
H.Y. Zhao, J.H. Liu, Z.L. Li, Y.X. Zhao, H.W. Niu, X.G. Song, H.J. Dong, Non-interfacial growth of Cu3Sn in Cu/Sn/Cu joints during ultrasonic-assisted transient liquid phase soldering process. Mater. Lett. 186, 283–288 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.10.017
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, The shear strength of transient liquid phase bonded Sn–Bi solder joint with added Cu particles. Adv. Powder Tech. 27(3), 1000–1005 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.04.010
X. Qiao, S.F. Corbin, Development of transient liquid phase sintered (TLPS) Sn–Bi solider pastes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 283, 38–45 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(00)00621-3
K. Chu, Y. Sohn, C. Moon, A comparative study of Cn/Sn/Cu and Ni/Sn/Ni solder joints for low temperature stable transient liquid phase bonding. Scr. Mater. 109, 113–117 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.07.032
A.A. Bajwa, J. Wilde, Reliability modeling of Sn–Ag transient liquid phase die-bonds for high-power SiC devices. Microelectron. Reliab. 60, 116–125 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2016.02.016
H. Shao, A. Wu, Y. Bao, Y. Zhao, G. Zou, L. Liu, Novel transient liquid phase bonding through capillary action for high-temperature power devices packaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.03.097
Z.L. Li, H.J. Dong, X.G. Song, H.Y. Zhao, H. Tian, J.H. Liu, J.C. Feng, J.C. Yan, Homogeneous (Cu, Ni)6Sn5 intermetallic compound joints rapidly formed in asymmetrical Ni/Sn/Cu system using ultrasound-induced transient liquid phase soldering process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 42, 403–410 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.12.005
S.U. Mehreen, K. Nogita, S. McDonald, H. Yasuda, D. StJohn, Suppression of Cu3Sn in the Sn-10Cu peritectic alloy by the addition of Ni. J. Alloys Compd. 766, 1003–1013 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.251
L. Sun, M.-H. Chen, L. Zhang, Microstructure evolution and grain orientation of IMC in Cu-Sn TLP bonding solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 786, 677–687 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.384
X. Liu, S. He, H. Nishikawa, Thermally stable Cu3Sn/Cu composite joint for high-temperature power device. Scr. Mater. 110, 101–104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.08.011
H. Yasuda, K. Morishita, N. Nakatsuka, T. Nishimura, M. Yoshiya, A. Sugiyama, K. Uesugi, A. Takeuchi, Dendrite fragmentation induced by massive-like δ–γ transformation in Fe–C alloys. Nat. Commun. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11079-y
M.A.A. Mohd Salleh, C.M. Gourlay, J.W. Xian, S.A. Belyakov, H. Yasuda, S.D. McDonald, K. Nogita, In situ imaging of microstructure formation in electronic interconnections. Sci. Rep. 7, 40010 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40010
L. Zhang, K.N. Tu, Structure and properties of lead-free solders bearing micro and nano particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 82, 1–32 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2014.06.001
M.A.A. Mohd Salleh, M.M.A. Al-Bakri, M.H. Zan@Hazizi, F. Somidin, N.F.M. Alui, Z.A. Ahmad, Mechanical properties of Sn–0.7Cu/Si3N4 lead-free composite solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 556, 633–637 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.07.039
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, M.Z. Quadir, Thermal aging effects on microstructures and mechanical properties of an environmentally friendly eutectic tin-copper solder alloy. Mater. Des. 110, 275–283 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.08.007
C. Rauta, D.A. Dasgupta, D.C. Hillman, Solder Phase Coarsening, Fundamentals, Preparation, Measurement and Prediction.
Y.C. Chan, A.C.K. So, J.K.L. Lai, Growth kinetic studies of Cu–Sn intermetallic compound and its effect on shear strength of LCCC SMT solder joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 55, 5–13 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5107(98)00202-5
M.S. Park, M.K. Stephenson, C. Shannon, L.A. Cáceres Díaz, K.A. Hudspeth, S.L. Gibbons, J. Muñoz-Saldaña, R. Arróyave, Experimental and computational study of the morphological evolution of intermetallic compound (Cu6Sn5) layers at the Cu/Sn interface under isothermal soldering conditions. Act. Mater. 60(13–14), 5125–5134 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.06.008
Z.L. Li, L.X. Cheng, G.Y. Li, J.H. Huang, Y. Tang, Effects of joint size and isothermal aging on interfacial IMC growth in Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-0.1TiO2 solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 697, 104–113 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.131
B.S.S.C. Rao, J. Wen, L. Shen, T.K. Lee, K.Y. Zeng, Morphology and mechanical properties of intermetallic compounds in SnAgCu solder joints. Microelectron. Eng. 87, 2416–2422 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2010.04.017
Y. Tang, S.M. Luo, K.Q. Wang, G.Y. Li, Effect of Nano-TiO2 particles on growth of interfacial Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn layers in Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-xTiO2 solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 648, 299–309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.148
A.K. Gain, Y.C. Chan, Growth mechanism of intermetallic compounds and damping properties of Sn–Ag–Cu-1 wt% nano-ZrO2 composite solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 945–955 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.01.026
C.-C. Wang, C.-Y. Wen, Lin, Solid-state interfacial reactions of Sn and Sn–Ag–Cu solders with an electroless Co(P) layer deposited on a Cu substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 662, 475–483 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.060
M.A.A. Mohd Salleh, S.D. McDonald, C.M. Gourlay, H. Yasuda, K. Nogita, Suppression of Cu6Sn5 in TiO2 reinforced solder joints after multiple reflow cycles. Mater. Des. 108, 418–428 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.06.121
M.A. Rabiatul Adawiyah, O. Saliza Azlina, Comparative study on the isothermal aging of bare Cu and ENImAg surface finish for Sn-Ag-Cu solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 740, 958–966 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.054
M.A.A. Mohd Salleh, S.D. McDonald, K. Nogita, Effects of Ni and TiO2 additions in as-reflowed and annealed Sn0.7Cu solders on Cu substrates. J. Mater. Process Technol. 242, 235–245 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.11.031
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Azmah Hanim, O.J. Ojo-Kupoluyi, R. Calin, Impact of different isothermal aging conditions on the IMC layer growth and shear strength of MWCNT-reinforced Sn–5Sb solder composites on Cu substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 808, 151714 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151714
M.A.A. Mohd Salleh, S.D. McDonald, C.M. Gourlay, S.A. Belyakov, H. Yasuda, K. Nogita, Effect of Ni on the formation and growth of primary Cu6Sn5 intermetallics in Sn-0.7 wt%Cu solder pastes on Cu substrates during the soldering process. J. Electron. Mater. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-015-4121-x
P. Lü, H.P. Wang, Direct formation of peritectic phase but no primary phase appearance within Ni83.25Zr16.75 peritectic alloy during free fall. Sci. Rep 6, 22641 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22641
Z. Xuan, F. Mao, Z. Cao, T. Wang, L. Zou, In situ observation on the solidification of Sn-10Cu hyperperitectic alloy under direct current field by synchrotron microradiography. J. Alloys Compd. 721, 126–133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.302
W. Zhai, B. Wei, Direct nucleation and growth of peritectic phase induced by substantial undercooling condition. Mater. Lett. 108, 145–148 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.06.084
X. Hu, Y. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, Z. Min, Microstructure and shear strength of Sn37Pb/Cu solder joints subjected to isothermal aging. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(8), 1575–1582 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.04.003
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their sincere gratitude to the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia, University Malaysia Perlis and Nihon Superior Co. Ltd. for their financial support throughout the research project. The in situ synchrotron radiation experiments were performed at the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) at the BL20XU beamline of the SPring-8 Synchrotron, under proposal No: 2017B1519 and supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (S) (No. 17H06155), JSPS, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohd Said, R., Mohd Salleh, M.A.A., Saud, N. et al. Microstructure and growth kinetic study in Sn–Cu transient liquid phase sintering solder paste. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 11077–11094 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03657-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03657-4