Abstract
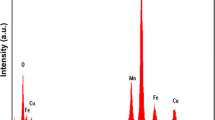
Ferrite-Ferroelectric composites with the generic formula y(Mn0.5Cu0.5Fe2O4)1 − y[Ca0.1Ba0.9Zr0.1Ti0.9] (y = 25%, 50% and 75%) are prepared by solid-state reaction. One of the prepared samples of the composites 25%Mn0.5Cu0.5Fe2O4–75%Ca0.1Ba0.9Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 (MCF-CBZT) is subjected to high-energy mechanical milling for different durations (12 h, 18 h and 30 h). The compositional stoichiometry of all the samples is checked by Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy. All the un-milled and milled samples are characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, FTIR, magnetometry, and dielectric and magnetoelectric coefficient measurements. Magnetoelectric composite possesses biphasic surrounding to exhibit complex behavior of ME effect. The present study reveals influence of mechanical milling on MCF-CBZT magnetoelectric composite. The XRD confirms the presence of ferrite and ferroelectric phases for all the samples and microstructural changes appear in SEM images of milled specimens. FTIR spectra show four characteristic bands in 400–800 cm−1 range. Saturation magnetization and Curie temperature decrease as milling duration increases. Relaxed broad doublet with the distribution of nuclear hyperfine fields is found in Mossbauer spectra indicating good coupling between ferrite-ferroelectric phases caused by mechanical milling for the multiferroic composite. The frequency response of dielectric constant and loss tangent is recorded in the frequency range from 100 Hz to 1 MHz. The static value of magnetoelectric factor has been studied as a function of magnetic field for un-milled and milled MCF-CBZT samples. The maximum value 382 μV/cm·Oe of (ME)H is observed for the 18 h milled MCF-CBZT sample.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Venkata Ramana, F. Figueiras, M.P.F. Graca, M.A. Valente, Observation of magnetoelectric coupling and local piezoresponse in modified (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3–BaTiO3–CoFe2O4 lead-free composites. Dalton Trans. 43, 9934–9943 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4DT00956H
Y. Cheng, B. Peng, Z. Hu, Z. Zhou, M. Liu, Recent development and status of magnetoelectric materials and devices. Phys. Lett. A 382, 3018–3025 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2018.07.014
M.B. Kothale, K.K. Patankar, S.L. Kadam, V.L. Mathe, A.V. Rao, B.K. Chougule, Dielectric behaviour and magnetoelectric effect in copper–cobalt ferrite+barium lead titanate composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 77, 691–696 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(02)00135-9
J.G. Wan, X.W. Wang, Y.J. Wu, M. Zeng, Y. Wang, H. Jiang, W.Q. Zhou, G.H. Wang, J.M. Liu, Magnetoelectric CoFe2O4–Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 composite thin films derived by a sol-gel process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 122501 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1889237
M.I. Bichurin, V.M. Petrov, R.V. Petrov Yu, V. Kiliba, F.I. Bukashev, A.Y. Smirnov, D.N. Eliseev, Magnetoelectric sensor of magnetic field. Ferroelectrics 280, 199–202 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150190214814
S.L. Kadam, K.K. Patankar, V.L. Mathe, M.B. Kothale, R.B. Kale, B.K. Chougule, Electrical properties and magnetoelectric effect in Ni0.75Co0.25Fe2O4+Ba0.8Pb0.2TiO3 composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 78, 684–690 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(02)00352-8
M.I. Bichurin, V.M. Petrov, R.V. Petrov, G.N. Kapralov, Y.V. Kiliba, F.I. Bukashev, AYu Smirnov, A.S. Tatarenko, Magnetoelectric microwave devices. Ferroelectrics 280, 211–218 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150190214807
J. Ryu, S. Priya, K. Uchino, H. Kim, Magnetoelectric effect in composites of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric materials. J. Electroceram. 8, 107–119 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020599728432
S.S. Chougule, B.K. Chougule, Studies on electrical properties and the magnetoelectric effect on ferroelectric-rich (x)Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4+(1−x)PZT ME composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 493–497 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/16/2/030
C.W. Nan, N. Cai, L. Liu, J. Zhai, Y. Ye, Y. Lin, Coupled magnetic–electric properties and critical behavior in multiferroic particulate composites. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5930 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1614866
Y.X. Liu, J.G. Wan, J.M. Liu, C.W. Nan, Effect of magnetic bias field on magnetoelectric coupling in magnetoelectric composites. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5118 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1613811
N. Ortega, A. Kumar, J.F. Scott, R.S. Katiyar, Multifunctional magnetoelectric materials for device applications. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 27, 504002 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/27/50/504002/meta
H. Palneedi, V. Annapureddy, S. Priya, J. Ryu, Status and perspectives of multiferroic magnetoelectric composite materials and applications. Actuators 5, 9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010009
H. Zheng, J. Wang, S.E. Lofland, Z. Ma, L.M. Ardabili, T. Zhao, L.S. Riba, S.R. Shinde, S.B. Ogale, F. Bai, D. Viehland, Y. Jia, D.G. Schlom, M. Wuttig, A. Roytburd, R. Ramesh, Science 303, 661–663 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094207
J.F. Scott, Applications of magnetoelectrics. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 4567–4574 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM16137K
R. Ramesh, N.A. Spaldin, Multiferroics: progress and prospects in thin films. Nat. Mater. 6, 21–29 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1805
J.M. Hu, Z. Li, J. Wang, C.W. Nan, Electric-field control of strain-mediated magnetoelectric random access memory. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 093912 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3373593
Y.H. Chu, L.W. Martin, M.B. Holcomb, M. Gajek, S.J. Han, Q. He, N. Balke, C.H. Yang, D. Lee, W. Hu, Q. Zhan, P.L. Yang, A.F. Rodriguez, A. Scholl, S.X. Wang, R. Ramesh, Electric-field control of local ferromagnetism using a magnetoelectric multiferroic. Nat. Mater. 7, 478–482 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2184
A.R. Tanna, U.N. Trivedi, M.C. Chhantbar, H.H. Joshi, Influence of Jahn-Teller Cu2+ (3d9) ion on structural and magnetic properties of Al-Cr co-substituted CuFe2O4. Indian J. Phys. 87, 1087–1092 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-013-0341-1
A.R. Tanna, H.H. Joshi, Influence of mechanical milling on structural and magnetic properties of Cu2+ substituted MnFe2O4. Indian J. Phys. 90, 981–989 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0825-2
M. Sahu, S.K. Pradhan, S. Hajra, B.K. Panigrahi, R.N.P. Choudhary, Studies of structural, electrical, and excitation performance of electronic material: europium substituted 0.9(Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3)-0.1(PbZr0.48Ti0.52O3). Appl. Phys. A 125, 183 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2491-2
K. Auromun, S. Hajra, R.N.P. Choudhary, B. Behera, Structural, dielectric and electrical characteristics of yttrium modified 0.7BiFeO3–0.3PbTiO3. Solid State Sci. 101, 106139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2020.106139
A.R. Tanna, H.H. Joshi, Structural properties of high energy mechanical milled Ca-Zr doped BaTiO3:Ca0.1Ba0.9Zr0.1Ti0.9O3. AIP Conf. Proc. 1536, 827–828 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4810483
A.R. Tanna, H.H. Joshi, Effect of high energy mechanical milling on hysteresis and dielectric properties of CaxBa1-xZrxTi1-xO3 (x = 0 and 0.1) ferroelectric materials. Mater. Res. Express 5, 096302 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aad610
G.F. Goya, H.R. Rechenberg, J.Z. Jiang, Structural and magnetic properties of ball milled copper ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 1101 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.368109
J.F. Scott, Applications of modern ferroelectrics. Science 315, 954–959 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1129564
D.R. Patil, B.K. Chougule, Effect of resistivity on magnetoelectric effect in (x)NiFe2O4-(1−x)Ba0.9Sr0.1TiO3 ME composites. J. Alloys. Compd. 470, 531–535 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.03.006
S.K. Pradhan, S. Bid, M. Gateshki, V. Petkov, Microstructure characterization and cation distribution of nanocrystalline magnesium ferrite prepared by ball milling. Mater. Chem. Phys. 93, 224–230 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.03.017
J. Gass, H. Srikanth, N. Kislov, S.S. Srinivasan, Y. Emirov, Magnetization and magnetocaloric effect in ball-milled zinc ferrite powder. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 07B309 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2829754
N. Kislov, S.S. Srinivasan, Y. Emirov, E.K. Stefanakos, Optical absorption red and blue shifts in ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 153, 70–77 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2008.10.032
R.D. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99, 1727–1734 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.99.1727
N.G. Popravko, A.S. Sidorkin, S.D. Milovidova, O.V. Rogazinskaya, IR spectroscopy of ferroelectric composites. Phys. Solid State 57, 522–526 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783415030233
I. Fedorove, J. Lorenzana, P. Dore, G. De Marzi, P. Maselli, P. Calvani, S.W. Cheong, S. Koval, R. Migoni, Infrared-active phonons of LaMnO3 and CaMnO3. Phys. Rev. B 60, 11875–11878 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.60.11875
N. Sivakumar, A. Narayansamy, N. Ponpandian, Grain size effect on the dielectric behavior of nanostructured Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 084116 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2721379
J.R. Morales, S. Tanju, W.P. Beyermann, J.E. Garay, Exchange bias in large three dimensionals iron oxide nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 013102 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3277147
A.R. Tanna, H.H. Joshi, Computer aided X-ray diffraction intensity analysis for spinels: hands-on computing experience. Int. J. Phys. Math. Sci. 7, 334–341 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1333917
A. Kale, S. Gubbala, R.D.K. Misra, Magnetic behavior of nanocrystalline nickel ferrite synthesized by the reverse micelle technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 277, 350–358 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.11.015
J.Z. Jiang, G.F. Goya, H.R. Rechenberg, Magnetic properties of nanostructured CuFe2O4. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 11, 4063 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/11/20/313
S.J. Stewart, M.J. Tueros, G. Cernicchiaro, R.B. Scorzelli, Magnetic size growth in nanocrystalline copper ferrite. Solid State Commun. 129, 347–351 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2003.11.010
A.G. Flores, V. Raposo, L. Torres, J. Iniguez, Ferrimagnetic resonance of manganese ferrites with iron excess. Appl. Phys. A 73, 327–330 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100
A.R. Tanna, K.M. Sosa, H.H. Joshi, Study of superparamagnetic nano particles of MnxCo1−xFe2O4 ferrite system prepared by co-precipitation technique. Mater. Res. Express 4, 115010 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa9393
K.K. Patankar, V.L. Mathe, R.N. Patil, B.K. Chougule, Structural analysis, magnetic properties, and magnetoelectric effect in piezomagnetic–piezoelectric composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 96, 197–200 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.07.009
M.A. Gilleo, Superexchange interaction in ferrimagnetic garnets and spinels which contain randomly incomplete linkages. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 13, 33–39 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(60)90124-4
S.L. Kadam, K.K. Patanakar, C.M. Kanamadi, B.K. Chougule, Electrical conduction and magnetoelectric effect in Ni0.50Co0.50Fe2O4+Ba0.8Pb0.2TiO3 composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 39, 2265–2272 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2004.07.021
N. Ponpandian, P. Balaya, A. Narayanasamy, Electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of nanocrystalline NiFe2O4 spinel. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 14, 3221 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/14/12/311
S.A. Mazen, H.A. Dawoud, Temperature and composition dependence of dielectric properties in Li–Cu ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 557–566 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(03)00200-1
Y. Zhi, A. Chen, Maxwell-Wagner polarization in ceramic composites BaTiO3-(Ni0.3Zn0.7)Fe2.1O4. J. Appl. Phys. 91, 794 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1421033
W.A. Yager, The distribution of relaxation times in typical dielectrics. J. Appl. Phys. 7, 434–450 (1936). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1745355
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121–124 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.83.121
I.V. Lisnevskaya, N.A. Levshina, Influence of the preparation conditions and percolation threshold on the properties of lead zirconate titanate/cobalt nickel ferrite magnetoelectric composites. Inorg. Mater. 54, 851–858 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168518080113
R.S. Devan, B.K. Chougule, Magnetic properties and dielectric behavior in ferrite/ferroelectric particulate composites. Phys. B 393, 161–166 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2007.01.001
M. Ram, S. Chakrabarti, Dielectric and modulus studies on LiFe1/2Co1/2VO4. J. Alloys Compd. 462, 214–219 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.08.001
K.P. Padmasree, D.K. Kanchan, A.R. Kulkarni, Impedance and Modulus studies of the solid electrolyte system 20CdI2–80[xAg2O–y(0.7V2O5–0.3B2O3)], where 1 ≤x/y ≤ 3. Solid State Ion. 177, 475–482 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2005.12.019
A. Dutta, T.P. Sinha, S. Shannigrahi, Dielectric relaxation and electronic structure of double perovskite Sr2FeSbO6. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 064114 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2978218
V. Prakash, S.N. Choudhary, T.P. Sinha, Dielectric relaxation in complex perovskite oxide BaCo1/2W1/2O3. Phys. B 403, 103–108 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2007.08.015
V. Prakash, A. Dutta, S.N. Choudhary, T.P. Sinha, Dielectric relaxation in perovskite Ba(Zn1/2W1/2)O3. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 142, 98–105 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2007.07.007
A. Selmi, S. Hcini, H. Rahmouni, A. Omri, M.L. Bouazizi, A. Dhahri, Synthesis, structural and complex impedance spectroscopy studies of Ni0.4Co0.4Mg0.2Fe2O4 spinel ferrite. Phase Trans. 90(10), 942–954 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2017.1309403
S.K. Mandal, S. Singh, P. Dey, J.N. Roy, P.R. Mandal, T.K. Nath, Frequency and temperature dependence of dielectric and electrical properties of TFe2O4 (T= Ni, Zn, Zn0.5Ni0.5) ferrite nanocrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 887–896 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.045
S. Sahoo, P.K. Mahapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, M.L. Nandagoswamy, Dielectric and impedance spectroscopy of (Ba, Sm)(Ti, Fe)O3 system in the low-medium frequency range. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 6572–6584 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3255-1
M. Atif, M. Idrees, M. Nadeem, M. Siddique, M.W. Ashraf, Investigation on the structural, dielectric and impedance analysis of manganese substituted cobalt ferrite i.e., Co1−xMnxFe2O4 (0.0≤ x ≤ 0.4). RSC Adv. 6, 20876–20885 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA20621A
J.T.S. Irvine, D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, Electroceramics: characterization by impedance spectroscopy. Adv. Mater. 2, 132–138 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.19900020304
P. Sateesh, J. Omprakash, G.S. Kumar, G. Prasad, Studies of phase transition and impedance behavior of Ba(Zr, Ti)O3 ceramics. J. Adv. Dielectr. 5, 1550002 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1142/S2010135X15500022
M.A. Dar, K.M. Batoo, V. Verma, W.A. Siddiqui, R.K. Kotnala, Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized pure and Al-doped lithium ferrite having high value of dielectric constant. J. Alloys Compd. 493, 553–560 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.12.154
R.P. Mahajan, K.K. Patankar, M.B. Kothale, S.A. Patil, Conductivity, dielectric behaviour and magnetoelectric effect in copper ferrite-barium titanate composites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 23, 273–279 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02720082
G. Srinivasan, E.T. Rasmussen, J. Gallegos, R. Srinivasan, Y.I. Bokhan, V.M. Laletin, Magnetoelectric bilayer and multilayer structures of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric oxides. Phys. Rev. B 64, 214408 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.64.214408
J.H. Kim, F.F. Fang, H.J. Choi, Y. Seo, Magnetic composites of conducting polyaniline/nano-sized magnetite and their magnetorheology. Mater. Lett. 62, 2897–2899 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2008.01.067
J.A. Bas, J.A. Calero, M.J. Dougan, Sintered soft magnetic materials. Properties and applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 254, 391–398 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00934-4
S. Srinivas, J.Y. Li, Y.C. Zhou, A.K. Soh, The effective magnetoelectroelastic moduli of matrix-based multiferroic composites. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 043905 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2173035
A. Broese, P.F. Van Groenon, A.L. Bongers, Stuyts, Magnetism, microstructure and crystal chemistry of spinel ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. 3, 317–392 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5416(69)90042-1
A. Kyono, S.A. Gramsch, Y. Nakamoto, M. Sakata, M. Kato, T. Tamura, T. Yamanaka, High-pressure behavior of cuprospinel CuFe2O4: Influence of the Jahn-Teller effect on the spinel structure. Am. Mineral. 100, 1752–1761 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2015-5224
G. Srinivasan, E.T. Rasmussen, A.A. Bush, K.E. Kamentsev, V.F. Meshcheryakov, Y.K. Fetisov, Structural and magnetoelectric properties of MFe2O4-PZT (M = Ni, Co) and Lax(Ca, Sr)1−xMnO3-PZT multilayer composites. Appl. Phys. A 78, 721–728 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-002-1987-2
S. Choudhury, Y.L. Li, C. Krill, L.Q. Chen, Effect of grain orientation and grain size on ferroelectric domain switching and evolution: phase field simulations. Acta Mater. 55, 1415–1426 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.09.048
R.A. Islam, S. Priya, Effect of piezoelectric grain size on magnetoelectric coefficient of Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3-Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 particulate composites. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 3560–3568 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2562-9
B.K. Bammannavar, G.N. Chavan, L.R. Naik, B.K. Chougule, Magnetic properties and magnetoelectric (ME) effect in ferroelectric rich Ni0.2Co0.8Fe2O4+PbZr0.8Ti0.2O3 ME composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 117, 46–50 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.03.040
C.W. Nan, Magnetoelectric effect in composites of piezoelectric and piezomagnetic phases. Phys. Rev. B 50, 6082 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.50.6082
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge Professor Caltun Ovidiu Florin, Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iasi, Romania for providing support for magnetic and ME coefficient measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanna, A.R., Srinivasan, S.S. & Joshi, H.H. Enhancement in magnetoelectric properties of lead-free multiferroic composite through high-energy mechanical milling. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 9306–9320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03470-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03470-z