Abstract
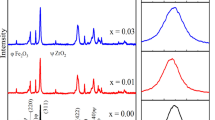
Polycrystalline ceramic powders of copper doped manganese ferrite (Mn1−xCuxFe2O4, x = 0.25, 0.50 and 0.75) synthesized by ceramic technique have been subjected to high-energy ball-milling to study the influence of mechanical milling on structural and magnetic properties through X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and magnetization measurements. The compositional stoichiometry has been ascertained by energy dispersive analysis of X-rays mapping before commencement of high-energy ball milling of the powders. The X-ray diffraction patterns of all as prepared specimens show cubic (fcc) spinel structure with no traces of any impurity of ingredients or unexpected structural phase. The Jahn–Teller (JT) structural distortion evolves after 30 h of prolonged ball milling in all the samples, in fact the tetragonal distortion of the unit cell appears in the sample with x = 0.75 just after 18 h of milling duration. The saturation magnetization at 77 K temperature in the peak field of 5 kOe has been measured for each specimen and the Curie temperatures have been determined through thermal variation of low field (0.5 Oe) AC susceptibility. Infrared spectra also reflect the JT distortion of the unit cell due to ball milling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y Pu, X Tao, J Zhai and J F Chen Mater. Res. Bull. 45 616 (2010)
Y M Z Ahmed, M M Hessien, M M Rashad and I A Ibrahim J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321 181 (2009)
T Zhang, G Li, T Qian, J F Qu, X Q Xiang and X G Li J. Appl. Phys. 100 094324 (2006)
L Fei, X Dan, G M Xing, H S Park and T Fujita Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 17 1444 (2007)
B J Evans and S S Hafner J. Appl. Phys. 39 694 (1968)
M Feng, A Yang, X Zuo, C Vittoria and V G Harris J. Appl. Phys. 107 09A521 (2010)
M M Rashad, R M Mohamed, M A Ibrahim, L F M Ismail and E A Abdel-Aal Adv. Powder Technol. 23 315 (2012)
Y Zhu and Q Wu J. Nanoparticle Res. 1(3) 393 (1999)
G F Goya, H R Rechenberg and J Z Jiang J. Appl. Phys. 84(2) 1101 (1998)
J F Scott Science 315 954 (2007)
A R Tanna, U N Trivedi, M C Chhantbar and H H Joshi Indian J. Phys 87(11) 1087 (2013)
A M Kapitonov and E M Smokotin Phys. Status Solidi (a) 34 K47 (1976)
S S D Shenoy, P A Joy and M R Anantharaman J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 269 217(2004)
T Sato IEEE Trans. Magn. Magn. 6 795 (1970)
T F Marinca, I Chicinas and O Isnard Ceram. Inter. 38 1951 (2012)
A R Tanna and H H Joshi World Acad. of Sci. Engg. and Techno. 75 74 (2013)
A Globus, H Pascard and V Cagan J. Phys. Suppl. 438(c-1) 439 (1977)
S A Mazen, M H Abdalla, R I Nakhla, H M Zaki and F Metawe Mater. Chem. Phys. 34 35 (1993)
[19] J Z Jiang, G F Goya and H R Rechenberg J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 11 4063 (1999)
T F Marinca, I Chicinas, O Isnard, V Pop and F Popa J. Alloys Compd. 509 7931 (2011)
L Néel Ann. Phys. 3 137 (1948)
S J Stewart, M J Tueros, G Cernicchiaro and R B Scorzelli Solid State Commun. 129 347 (2004)
B D Cullity and C D Graham Introduction to Magnetic Materials 2nd ed. (New Jersey; IEEE Press & Wiley) (2009)
A Rosencwaig Can. J. Phys. 48 2857 (1970)
R H Kodama, A E Berkowitz, E J McNiff and S Foner Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 394 (1996)
R H Kodama and A E Berkowitz Phys. Rev. B 59 6321 (1999)
J P Chen, C M Sorensen, K J Klabunde, G C Hadjipanayis, E Devlin and A Kostikas Phys. Rev. B. 54(13) 9288 (1996)
R D Waldron Phys. Rev. 99 1727 (1955)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanna, A.R., Joshi, H.H. Influence of mechanical milling on structural and magnetic properties of Cu2+ substituted MnFe2O4 . Indian J Phys 90, 981–989 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0825-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0825-2