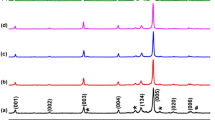
Abstract
Thermoelectric properties of BiCuSeO oxyselenide ceramics were improved combining Y doping and grain refinement. Bi1−xYxCuSeO (x = 0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.10) (called as BYCSO below) samples were prepared by mechanical alloying and resistance pressing sintering (RPS). The testing results indicate that Y doping can increase the carrier concentration and electrical conductivity, increase the thermal conductivity. On the basis of Y doping, grain refinement by increasing ball milling strength was indicated to increase the concentration of Cu vacancies, which enhanced the electrical conductivity and power factor, and reduce the thermal conductivity. Finally, the ZT value is increased to 0.93, which is 98% higher than that of the pure sample.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.B. Riffat, X. Ma, Thermoelectrics: a review of present and potential applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 23(8), 913–935 (2003)
T. Kajikawa, Thermoelectric application for power generation in Japan. Adv. Sci. Technol. 74(4), 83–92 (2010)
I. Petsagkourakis, K. Tybrandt, X. Crispin et al., Thermoelectric materials and applications for energy harvesting power generation. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 19(1), 836–862 (2018)
J. He, T.M. Tritt, Advances in thermoelectric materials research: looking back and moving forward. Science 357(6358), eaak9997 (2017)
T. Mori, S. Priya, Materials for energy harvesting: at the forefront of a new wave. MRS Bull. 43(3), 176–180 (2018)
B. Poudel, Q. Hao, Y. Ma et al., High thermoelectric performance of nanostructured bismuth antimony telluride bulk alloys. Science 320(5876), 634–638 (2008)
J.P. Heremans, V. Jovovic, E.S. Toberer et al., Enhancement of thermoelectric efficiency in PbTe by distortion of the electronic density of states. Science 321(5888), 554–557 (2008)
R. Funahashi, Waste heat recovery using thermoelectric oxide materials. Sci. Adv. Mater. 3(4), 682–686 (2011)
S. Walia, S. Balendhran, H. Nili et al., Transition metal oxides-thermoelectric properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 58(8), 1443–1489 (2013)
L.D. Zhao, J. He, D. Berardan et al., BiCuSeO oxyselenides: new promising thermoelectric materials. Energy Environ. Sci. 7(9), 2900–2924 (2014)
X. Zhang, C. Chang, Y. Zhou et al., BiCuSeO thermoelectrics: an update on recent progress and perspective. Materials 10(2), 198 (2017)
Y.L. Pei, H. Wu, D. Wu et al., High thermoelectric performance realized in a BiCuSeO system by improving carrier mobility through 3D modulation doping. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(39), 13902–13908 (2014)
C. Barreteau, D. Berardan, L. Zhao et al., Influence of Te substitution on the structural and electronic properties of thermoelectric BiCuSeO. J. Mater. Chem. A 1(8), 2921–2926 (2013)
J.L. Lan, Y.C. Liu, B. Zhan et al., Enhanced thermoelectric properties of Pb-doped BiCuSeO ceramics. Adv. Mater. 96(9), 2710–2713 (2013)
J. Li, J. Sui, Y. Pei et al., The roles of Na doping in BiCuSeO oxyselenides as a thermoelectric material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(14), 4903–4906 (2014)
B. Feng, G. Li, Z. Pan et al., Enhanced thermoelectric performances in BiCuSeO oxyselenides via Er and 3D modulation doping. Ceram. Int. 45(4), 4493–4498 (2019)
Y. Liu, L. Zhao, Y. Zhu et al., Synergistically optimizing electrical and thermal transport properties of BiCuSeO via a dual-doping approach. Adv. Energy Mater. 6(9), 1502423 (2016)
A.P. Novitskii et al., Effect of praseodymium and lanthanum substitution for bismuth on the thermoelectric properties of BiCuSeO oxyselenides. Semiconductors 53, 215–219 (2019)
A. Novitskii, G. Guélou, D. Moskovskikh et al., Reactive spark plasma sintering and thermoelectric properties of Nd-substituted BiCuSeO oxyselenides. J. Alloys Compd. 785, 96–104 (2019)
Y. Wang, Y. Sui, J. Cheng et al., Influence of Y3+ doping on the high-temperature transport mechanism and thermoelectric response of misfit-layered Ca3Co4O9. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 99(2), 451–458 (2010)
Y. Wang, Y. Sui, X. Wang et al., Effects of substituting La3+, Y3+ and Ce4+ for Ca2+ on the high temperature transport and thermoelectric properties of CaMnO3. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42(5), 055010 (2009)
T. Jun, K. Song, Y. Jung et al., Bias stress stable aqueous solution derived Y-doped ZnO thin film transistors. J. Mater. Chem. 21(35), 13524–13529 (2011)
Q.S. Meng, L.Q. Wang, B.S. Li et al., Thermoelectric properties of Y-doped Mg2Si prepared by field-activated and pressure-assisted reactive sintering. Adv. Mater. Res. 79–82, 1639–1642 (2009)
A.J. Minnich, M.S. Dresselhaus, Z.F. Ren et al., Bulk nanostructured thermoelectric materials: current research and future prospects. Energy Environ. Sci. 2(5), 466 (2009)
J.F. Li, W.S. Liu, L.D. Zhao et al., High-performance nanostructured thermoelectric materials. NPG Asia Mater. 2(4), 152–158 (2010)
J.R. Szczech, J.M. Higgins, J. Song, Enhancement of the thermoelectric properties in nanoscale and nanostructured materials. J. Mater. Chem. 21(12), 4037–4055 (2011)
X. Fan, X. Cai, Z. Rong et al., Resistance pressing sintering: a simple, economical and practical technique and its application to p-type (Bi, Sb)2Te3, thermoelectric materials. J. Alloys Compd. 607(24), 91–98 (2014)
M. Ishizawa, Y. Yasuzato, H. Fujishiro, T. Naito, H. Katsui, T. Goto, Oxidation states and thermoelectric properties of BiCuSeO bulks fabricated under Bi or Se deficiencies in the nominal composition. J. Appl. Phys. 123, 245104 (2018)
M.A. Rodriguez, R.M. Ferrizz, C.S. Snow et al., X-ray powder diffraction data for ErH2−xDx. Powder Diffr. 23(3), 259–264 (2008)
G.K. Ren, S.Y. Wang, Y.C. Zhu et al., Enhancing thermoelectric performance in hierarchically structured BiCuSeO by increasing bond covalency and weakening carrier–phonon coupling. Energy Environ. Sci. 10(7), 1590–1599 (2017)
H. Ohta, S.W. Kim, Y. Mune et al., Giant thermoelectric Seebeck coefficient of a two-dimensional electron gas in SrTiO3. Nat. Mater. 6(2), 129–134 (2007)
G.A. Slack, The thermal conductivity of nonmetallic crystals. Solid State Phys. Adv. Res. Appl. 34, 1–71 (1979)
D.T. Morelli, G.A. Slack, High lattice thermal conductivity solids, in High Thermal Conductivity Materials (Springer, New York, 2006), pp. 37–68
J. Yang, G.P. Meisner, L. Chen, Strain field fluctuation effects on lattice thermal conductivity of ZrNiSn-based thermoelectric compounds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(7), 1140–1142 (2004)
F. Li, J.F. Li, L.D. Zhao et al., Polycrystalline BiCuSeO oxide as a potential thermoelectric material. Energy Environ. Sci. 5(5), 7188–7195 (2012)
M. Vashista, S. Paul, Correlation between full width at half maximum (FWHM) of XRD peak with residual stress on ground surfaces. Philos. Mag. 92(33), 4194–4204 (2012)
A.P. Zhilyaev, I. Shakhova, A. Morozova et al., Grain refinement kinetics and strengthening mechanisms in Cu–0.3Cr–0.5Zr alloy subjected to intense plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 654, 131–142 (2016)
J. Mao, H. Zhu, Z. Ding et al., High thermoelectric cooling performance of n-type Mg3Bi2-based materials. Science 365(6452), 495–498 (2019)
S.I. Kim, K.H. Lee, H.A. Mun et al., Dense dislocation arrays embedded in grain boundaries for high-performance bulk thermoelectrics. Science 348(6230), 109–114 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51674181).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, B., Li, G., Hu, X. et al. Enhancement of thermoelectric performances of BiCuSeO through Y doping and grain refining. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 4915–4923 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03056-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03056-9