Abstract
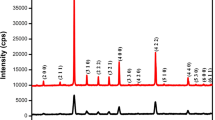
The Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 (referred to as BCZT) ceramic powders were synthesized by the sol–gel method followed by calcining, and then the ceramics were obtained by sintering at different temperatures varied from 1200 to 1350 °C. The effects of sintering temperature on the microstructure, impedance spectroscopy, dielectric, and ferroelectric properties for BCZT ceramics have been thoroughly investigated. The pure perovskite structure and homogenous microstructure with high relative density (> 90%) for all BCZT ceramics are identified by XRD analysis and SEM measurement, and the stability is identified by the variable-temperature dielectric characterization. The impedance spectroscopy and well-defined polarization–electric field hysteresis loops for BCZT samples were detected at room temperature. In particular, the BCZT ceramic sintered at 1300 °C resulted the highest dielectric constant (εr ~ 2170), the lowest dielectric loss (tan δ ~ 0.027), and the highest grain boundary resistance (Rgb ~ 8.9 × 107 Ω cm).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Wei, Y. Huang et al., Optical characteristics of Er3+-doped PMN–PT transparent ceramics. Ceram. Int. 4(38), 3397–3402 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.12.051
A. Ecija, K. Vidal, A. Larrañaga et al., Structure and properties of perovskites for SOFC cathodes as a function of the A-site cation size disorder. Solid State Ion. 11(235), 14–21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2013.01.010
T.R. Shrout, S.J. Zhang, Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics: alternatives for PZT? J. Electroceram. 1(19), 113–126 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9047-0
T. Takenaka, H. Nagata, Current status and prospects of lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 12(25), 2693–2700 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2005.03.125
M.R. Panigrahi, S. Panigrahi, Diffuse phase transition and dielectric study in Ba0.95Ca0.05TiO3 ceramic. Physica B 11(405), 2556–2559 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.03.031
X. Wang, H. Yamada, C.N. Xu, Large electrostriction near the solubility limit in BaTiO3–CaTiO3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2(86), 022905 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1850598
T. Maiti, R. Guo, A.S. Bhalla, The evolution of relaxor behavior in Ti4+ doped BaZrO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 11(100), 114106–114109 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2392996
Z. Yu, A. Chen, R. Guo et al., Ferroelectric-relaxor behavior of Ba(Ti0.7Zr0.3)O3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 5(92), 2655–2657 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150190902889325
Z. Sun, L. Li, J. Li et al., Influence of Nb2O5 addition on dielectric properties and diffuse phase transition behavior of BaZr0.2Ti0.8O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 9(42), 10833–10837 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.03.212
S. Ye, J. Fuh, L. Lu, Effects of Ca substitution on structure, piezoelectric properties, and relaxor behavior of lead-free Ba(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 piezoelectric ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 22(541), 396–402 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.06.084
H. Yu, Z.G. Ye, Dielectric properties and relaxor behavior of a new (1–x)BaTiO3–xBiAlO3 solid solution. J. Appl. Phys. 3(103), 034114–034115 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2838479
L. Zhang, X. Wang, W. Yang et al., Structure and relaxor behavior of BaTiO3–CaTiO3–SrTiO3 ternary system ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 1(104), 1354 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2949253
A. Shukla, R.N.P. Choudhary, A.K. Thakur, Thermal, structural and complex impedance analysis of Mn modified BaTiO3 electroceramic. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 11(70), 1401–1407 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2009.08.015
X. Wang, P. Jia, X. Wang et al., Calcining temperature dependence on structure and dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater Electron. 27, 12134–12140 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5366-8
X. Wang, P. Jia, L. Sun et al., Improved dielectric properties in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics modified by TiO2. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater Electron. 29, 2244–2250 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8139-0
W. Bai, D. Chen, J. Zhang et al., Phase transition behavior and enhanced electromechanical properties in (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(ZrxTi1-x)O3 lead-free piezoceramics. Ceram. Int. 2(42), 3598–3608 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.11.023
W. Liu, X. Ren, Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 25(103), 257602 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.257602
P. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Lu, Enhanced piezoelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 lead-free ceramics by optimizing calcination and sintering temperature. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 11(31), 2005–2012 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.04.023
D. Xue, Y. Zhou, H. Bao et al., Elastic, piezoelectric, and dielectric properties of Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3–50(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 Pb-free ceramic at the morphotropic phase boundary. J. Appl. Phys. 5(109), 809 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3549173
D. Segal, Chemical synthesis of advanced ceramic materials. J. Mater. Chem. 8(7), 1297–1305 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1039/a700881c
V. Sreenivas-Puli, A. Kumar, D.B. Chrisey et al., Barium zirconate-titanate/barium calcium-titanate ceramics via sol-gel process: novel high-energy-density capacitors. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39(44), 395403 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/44/39/395403
Z.W. Tan, W.G. Fu, X.Y. Deng et al., Ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of (1–x)BaTi0.8Zr0.2O3-xBa0.7Ca0.3TiO3 ceramics prepared by sol-gel technique. Adv. Mater. Res. 148, 1480–1485 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.148-149.1480
M. Wang, R. Zuo, S. Qi et al., Synthesis and characterization of sol–gel derived (Ba, Ca)(Ti, Zr)O3 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 3(23), 753–757 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0484-9
J.P. Praveen, K. Kumar, A.R. James et al., Large piezoelectric strain observed in sol–gel derived BZT–BCT ceramics. Curr. Appl. Phys. 3(14), 396–402 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2013.12.026
X. Wang, B. Zhang, G. Shen et al., Colossal permittivity and impedance analysis of tantalum and samarium co-doped TiO2 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 43, 13349–13355 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA07746C
X. Wang, B. Zhang, L. Xu et al., Dielectric properties of Y and Nb co-doped TiO2 ceramics. Sci. Rep. 7, 8517 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09141-0
X. Wang, B. Zhang, L. Sun et al., Colossal dielectric properties in (Ta0.5Al0.5)xTi1-xO2 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 745, 856–862 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.159
J. Khemprasit, B. Khumpaitool, Influence of Cr doping on structure and dielectric properties of LixCryNi1−x−yO ceramics. Ceram. Int. 1(41), 663–669 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.08.119
L.N. Gao, S.N. Song, J.W. Zhai et al., Effects of buffer layers on the orientation and dielectric properties of Ba(Zr0.20Ti0.80)O3 thin films prepared by sol–gel method. J. Cryst. Growth 6(310), 1245–1249 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2007.12.015
S.B. Li, C.B. Wang, L. Li et al., Effect of annealing temperature on structural and electrical properties of BCZT ceramics prepared by plasma activated sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 730, 182–190 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.09.310
M. Sindhu, N. Ahlawat, S. Sanghi et al., Effect of Zr substitution on phase transformation and dielectric properties of Ba0.9Ca0.1TiO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 16(114), 3850 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4825123
M.A. Rafiq, M.N. Rafiq, K.V. Saravanan, Dielectric and impedance spectroscopic studies of lead-free barium-calcium-zirconium-titanium oxide ceramics. Ceram. Int. 9(41), 11436–11444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.05.107
J. Rani, K.L. Yadav, S. Prakash, Structural, dielectric and optical properties of sol–gel synthesized 0.55Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3–0.45(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 ceramic. Appl. Phys. A 3(117), 1131–1137 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8482-4
V.S. Puli, D.K. Pradhan, D.B. Chrisey et al., Structure, dielectric, ferroelectric, and energy density properties of (1–x)BZT–xBCT ceramic capacitors for energy storage applications. J. Mater. Sci. 5(48), 2151–2157 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6990-1
X. Wang, B. Zhang, L. Shi et al., Dielectric relaxation behavior and energy storage properties in Ba1-x(Bi0.5K0.5)xTi0.85Zr0.15O3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 789, 983–990 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.02.004
Q. Jin, Pu Yong-Ping, C. Wang et al., Enhanced energy storage performance of Ba0.4Sr0.6TiO3 ceramics: influence of sintering atmosphere. Ceram. Int. 43, S232–S238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.05.229
W. Xia, N. Zhang, H. Yang et al., Energy storage BaZr0.2Ti0.8O3 bilayer relaxor ferroelectric ceramic thick films with high discharging efficiency and fatigue resistance. J. Alloys Compd. 19, 30804–30807 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.332
T. Qi, D. Viehland, Grain size dependence of relaxor characteristics in La-modified lead zirconate titanate. Ferroelectrics 1(193), 157–165 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150199708228329
C.J. Huang, K. Li, S.Y. Wu et al., Variation of ferroelectric hysteresis loop with temperature in (SrxBa1-x)Nb2O6 unfilled tungsten bronze ceramics. J. Materiomics 2(1), 146–152 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2015.02.004
H.X. Yan, F. Inam, G. Viola et al., The contribution of electrical conductivity, dielectric permittivity and domain switching in ferroelectric hysteresis loops. J. Adv. Dielectr. 1(01), 107–118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1142/S2010135X11000148
Acknowledgements
This work has been financially supported by the Key Scientific Research Foundation in Henan Province (No. 19B430005), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51402091, 51601059, 11847136), the Special Scientific Research Foundation in Henan Normal University (No. 20180543), and the National University Student Innovation Program (No. 20160098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.W., Zhang, B.H., Li, Y.Y. et al. Structure, dielectric, and ferroelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 ceramics sintered at various temperatures. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 4732–4742 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03030-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03030-5