Abstract
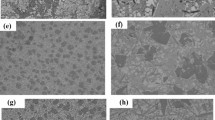
Low silver Sn–0.3Ag–0.7Cu (SAC0307) solders with different amounts of graphene nanosheets (GNSs) prepared by powder metallurgy were used to investigate the impacts of GNSs on the microstructures, melting temperature, wettability, and tensile strength of the SAC0307–xGNSs (x = 0, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, and 0.09 wt%) solders. The experimental results indicate that the wettability of SAC0307 solder can be improved significantly by adding GNSs and the melting temperature of the solder sample ranges from 219.6 to 222.7 °C. It is also revealed that with increasing GNSs content, the morphology of GNSs in the solder matrix changed from the initial dispersion distribution to the agglomeration, while the diameter and depth of the dimples of the solder joint fracture showed a tendency of increasing first and then decreasing. Doped with 0.07 wt% of GNSs, the solders showed the largest tensile strength. When GNS addition exceeds 0.07 wt%, it will induce negative effects on tensile property of the solder.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Borgesen, L. Wentlent, S. Hamasha et al., A mechanistic thermal fatigue model for SnAgCu solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 2526 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6121-0
Y.W. Chang, Y. Cheng, L. Helfen et al., Electromigration mechanism of failure in flip-chip solder joints based on discrete void formation. Sci. Rep. 7, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06250-8
B.T. Ogunsemi, P.P. Ikubanni, A.A. Adediran et al., Effect of stand-off height on the shear strength of ball grid array solder joints under varying pad sizes. SN Appl Sci (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-018-0044-5
T.-T. Chou, R.W. Song, H. Chen et al., Low thermal budget bonding for 3D-package by collapse-free hybrid solder. Mater. Chem. Phys. 238, 121887 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121887
B.L. Silva, A. Garcia, J.E. Spinelli et al., Wetting behavior of Sn-Ag-Cu and Sn-Bi-X alloys: insights into factors affecting cooling rate. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 1581 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.06.016
J.C. Liu, G. Zhang, Z.H. Wang et al., Thermal property, wettability and interfacial characterization of novel Sn-Zn-Bi-In alloys as low-temperature lead-free solders. Mater. Des. 84, 331 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.06.148
Y. Yao, J. Zhou, F. Xue et al., Interfacial structure and growth kinetics of intermetallic compounds between Sn-3.5Ag solder and Al substrate during solder process. J. Alloys Compd. 682, 627 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.263
L. Yin, D. Li, Z. Yao et al., Effects of Sn addition on the microstructure and properties of Bi–11Ag high-temperature solder. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 12028 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9308-5
Y. Lai, X. Hu, Y. Li et al., Interfacial microstructure evolution and shear strength of Sn0.7Cu–xNi/Cu solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 11314 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9219-5
M. Yang, H. Ji, S. Wang et al., Effects of Ag content on the interfacial reactions between liquid Sn-Ag-Cu solders and Cu substrates during soldering. J. Alloys Compd. 679, 18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.177
M. Fayeka, A.S.M.A. Haseeb, M.A. Fazal et al., Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Pb-free SAC 105 and SAC 305 solder alloys: a comparative study. Sains Malaysiana 46, 295 (2017). https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2017-4602-14
H.R. Sharma, J. Sohn, P. Jung et al., Effect of graphene nanoplatelets on wetting, microstructure, and tensile characteristics of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu (SAC) alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47, 494 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3214-8
M. Celikin, M. Maalekian, M. Pekguleryuz et al., Effect of Bi additions on the creep behaviour of SAC solder alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 5842 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6458-4
S. Cheng, C.M. Huang, M. Pecht et al., A review of lead-free solders for electronics applications. Microelectron. Reliab. 75, 77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2017.06.016
H. Sharma, I. Yu, S. Cho et al., ZrO 2 nanoparticle embedded low silver lead free solder alloy for modern electronic devices electron. Mater. Lett. 15, 27 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0089-z
Z. Zhu, Y.C. Chan, Z. Chen et al., Effect of the size of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) on the microstructure and mechanical strength of CNTs-doped composite Sn0.3Ag0.7Cu-CNTs solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 727, 160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.05.002
Y. Ma, X. Li, W. Zhou et al., Reinforcement of graphene nanosheets on the microstructure and properties of Sn58Bi lead-free solder. Mater. Des. 113, 264 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.10.034
Y. Ma, X. Li, L. Yang et al., Effects of graphene nanosheets addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of SnBi solder alloys during solid-state aging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 696, 437 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.105
Y.D. Han, Y. Gao, S.T. Zhang, H.Y. Jing, J. Wei, L. Zhao, L.Y. Xu, Study of mechanical properties of Ag nanoparticle-modified graphene/Sn-Ag-Cu solders by nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138051
M.S. Kang, D.S. Kim, Y.E. Shin, Suppression of the growth of intermetallic compound layers with the addition of graphene nano-sheets to an epoxy Sn-Ag-Cu solder on a Cu substrate. Materials (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060936
M.W.A. Tyson, Surface free energies of solid metals: estimation from liquid surface tension measurements. Surf. Sci. 62, 267 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(77)90442-3
S.M.L. Nai, J. Wei, M. Gupta et al., Influence of ceramic reinforcements on the wettability and mechanical properties of novel lead-free solder composites. Thin Solid Films 504, 401 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2005.09.057
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51674056), the Frontier and Applied Basic Research Projects of Chongqing (No. cstc2018jcyjAX0108 and cstc2019jcyj-msxmX0175), the University outstanding achievement transformation project of Chongqing (No. KJZH17137), and the Opening Project of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Modern Welding Technology (No. 2018002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, L., Zhang, Z., Zuo, C. et al. Microstructures and properties of Sn–0.3Ag–0.7Cu solder doped with graphene nanosheets. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 1861–1867 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02705-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02705-y