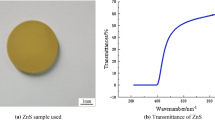
Abstract
ZnS has been widely used as infrared windows in defense applications and the ZnS glass with high purity has shown high transmittance in mid-infrared and near-infrared lights. The fabrication temperature of the ZnS ceramic was suggested to be reduced to avoid phase transformation of ZnS and sacrifice its good transparency. Similarly, the joining process of ZnS should be at a lower temperature. Traditionally, mechanical assembly and spicing techniques were used to assembly ZnS transparent windows with metal frames at the aircraft. Nevertheless, the assembly strength was still too low and might increase the risk for the safety of aircraft. Recently, low temperature bonding or soldering process has gradually become an opinion to reduce the safety risk. In this study, we utilized a pre-metallization method coating Ni–P on ZnS transparent ceramics and soldered with Sn–3Ag–0.5Cu at a low temperature. In this paper, we evaluated the solder wettability, bonding temperature, holding time and coating thickness of Ni–P layer in terms of the interfacial morphology and joining mechanism. Finally, the most failures of mechanical tests happened at Ni–P/ZnS interface due to long time reaction and weak interface coating forces between Ni–P/ZnS.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.C. Greene, D.C. Reynolds, S.J. Czyzak et al., Method for growing large CdS and ZnS single crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 29(6), 1375–1380 (1958)
M. Sakaguchi, T. Hirabayashi, Role of firing atmosphere on the rate of transformation of ZnS crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 44(6), 2530–2532 (1973)
A.F. Shchurov, E.M. Gavrishchuk, V.B. Ikonnikov et al., Effect of hot isostatic pressing on the elastic and optical properties of polycrystalline CVD ZnS. Inorg. Mater. 40(4), 336–339 (2004)
D.C. Harris, Development of Hot-Pressed and Chemical-Vapor-Deposited Zinc Sulfide and Zinc Selenide in the United States for Optical Windows; 654502, p. 27 in Proc. SPIE 6545—Window and Dome Technologies and Materials X, Edited by R.W. Tustison (SPIE, Orlando, 2007)
Y. Li, Y. Wu, Transparent and luminescent ZnS ceramics consolidated by vacuum hot pressing method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98(10), 2972–2975 (2015)
K.T. Lee, B.H. Choi, J.U. Woo et al., Microstructural and optical properties of the ZnS ceramics sintered by vacuum hot-pressing using hydrothermally synthesized ZnS powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(12), 4237–4244 (2018)
C. Chlique, O. Merdrignac-Conanec, N. Hakmeh et al., Transparent ZnS ceramics by sintering of high purity monodisperse nanopowders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96(10), 3070–3074 (2013)
C. Chlique, G. Delaizir, O. Merdrignac-Conanec et al., A comparative study of ZnS powders sintering by hot uniaxial pressing (HUP) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). Opt. Mater. 33(5), 706–712 (2011)
Y. Chen, L. Zhang, J. Zhang et al., Fabrication of transparent ZnS ceramic by optimizing the heating rate in spark plasma sintering process. Opt. Mater. 50, 36–39 (2015)
Z.A. Munir, U. Anselmi-Tamburini, M. Ohyanagi, The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: a review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 41(3), 763–777 (2006)
Z. Shen, M. Johnsson, Z. Zhao et al., Spark plasma sintering of alumina. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85(8), 1921–1927 (2002)
Y.H. Han, T. Nishimura, Spark plasma sintering (2014)
S. Xu, X. Qi, X. Xu et al., Effects of electroless nickel plating method for low temperature joining ZnS ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 30(16), 15236–15249 (2019)
Z. Zhang, X. Hu, X. Jiang et al., Influences of mono-Ni (P) and dual-Cu/Ni (P) plating on the interfacial microstructure evolution of solder joints. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 50(1), 480–492 (2019)
Y. Wan, X. Hu, T. Xu et al., Interfacial IMC growth of SAC305/Cu joint with a novel dual-layer of Ni (P)/Cu plating during solid-state aging. Microelectron. Eng. 199, 69–79 (2018)
M. Abtew, G. Selvaduray, Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. 27(5–6), 95–141 (2000)
S. Zhang, S.H. Kim, T.W. Kim et al., A study on the solder ball size and content effects of solder ACFs for flex-on-board assembly applications using ultrasonic bonding. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 5(1), 9–14 (2014)
M. Yang, Y.H. Ko, J. Bang et al., Growth inhibition of interfacial intermetallic compounds by pre-coating oriented Cu6Sn5 grains on Cu substrates. J. Alloys Compds. 701, 533–541 (2017)
S. Zhang, M. Yang, Y. Wu et al., A study on the optimization of anisotropic conductive films for Sn-3Ag-0.5 Cu-Based flex-on-board application at a 250 C bonding temperature. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 8(3), 383–391 (2018)
M. Takeuchi, K. Kamiyama, K. Suganuma, Suppression of tin whisker formation on fine pitch connectors by surface roughening. J. Electron. Mater. 35(11), 1918–1925 (2006)
X. Niu, K.L. Lin, Investigations of the wetting behaviors of Zn–25Sn, Zn–25Sn–XPr and Zn–25Sn–YAl high temperature lead free solders in air and Ar ambient. J. Alloys Compds. 646, 852–858 (2015)
J. Shen, Y.C. Liu, H.X. Gao et al., Formation of bulk Ag 3 Sn intermetallic compounds in Sn-Ag lead-free solders in solidification. J. Electron. Mater. 34(12), 1591–1597 (2005)
C.Y. Li, G.J. Chiou, J.G. Duh, Phase distribution and phase analysis in Cu 6 Sn 5, Ni 3 Sn 4, and the Sn-rich corner in the ternary Sn-Cu-Ni isotherm at 240°C. J. Electron. Mater. 35(2), 343–352 (2006)
H. Okamoto, Ni-P (nickel-phosphorus). J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 31(2), 200–201 (2010)
G. Chen, H. Peng, V.V. Silberschmidt et al., Performance of Sn–3.0 Ag–0.5 Cu composite solder with TiC reinforcement: physical properties, solderability and microstructural evolution under isothermal ageing. J. Alloys Compds. 685, 680–689 (2016)
X. Yan, K. Xu, J. Wang et al., Effect of P and Ge doping on microstructure of Sn-0.3 Ag-0.7 Cu/Ni-P solder joints. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 28(4), 215–221 (2016)
Y. Liu, W. Zhao, T. Zhou et al., Surface defect elimination in microgrooving of electroless nickel phosphide plating layer by brittleness enhancement. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 94(1–4), 1327–1333 (2018)
J.W. Yoon, J.H. Bang, C.W. Lee et al., Interfacial reaction and intermetallic compound formation of Sn–1Ag/ENIG and Sn–1Ag/ENEPIG solder joints. J. Alloys Compds. 627, 276–280 (2015)
Y.S. Wu, P.T. Lee, Y.H. Huang et al., Interfacial microstructure and mechanical reliability of the Sn-Ag-Cu/Au/Pd (xP)/Ni (P) reactive system: P content effects. Surf. Coat. Technol. 350, 874–879 (2018)
K. Chu, Y. Sohn, C. Moon, A comparative study of Cn/Sn/Cu and Ni/Sn/Ni solder joints for low temperature stable transient liquid phase bonding. Scripta Mater. 109, 113–117 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFE0201300), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51805115), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded Project (Grant No. 2019M651280), Henan Industry-University- Research Cooperation Project of China (Grant No. 152107000072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhu, B., Zhou, X. et al. Wettability and interfacial morphology of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder on electroless nickel plated ZnS transparent ceramic. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 17972–17985 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02151-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02151-w