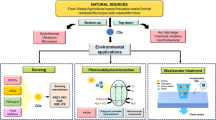
Abstract
Carbon dots (CDs) have emerged out as a potential material amongst the carbon family for a wide range of applications including chemical/biological sensing, photocatalysis, bioimaging, etc. The green synthesis of these CDs from natural sources is gaining the significant interest of peer community for their wide utility. Herein, we present a facile one-step pyrolysis method for CDs synthesis from Aloe-Vera extract, which show bright blue luminescence under UV light with a quantum yield of 12.3%. Further, ex-situ morphological, structural and optical characterizations reveal their high quality and excitation independent emission behavior with the presence of carboxyl, hydroxyl functional groups. Furthermore, these CDs were studied for Fe(III) sensing in water without any surface modifications and assessed for their light activated antibacterial activity against E.Coli and Staphylococcus aureus.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
T.N. Hoheisel, S. Schrettl, R. Szilluweit, H. Frauenrath, Nanostructured carbonaceous materials from molecular precursors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 6496–6515 (2010)
Y. Wang, A. Hu, Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 6921–6939 (2014)
Y.-P. Sun, B. Zhou, Y. Lin, W. Wang, K.S. Fernando, P. Pathak, M.J. Meziani, B.A. Harruff, X. Wang, H. Wang, Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 7756–7757 (2006)
V. Sharma, P. Tiwari, S.M. Mobin, Sustainable carbon-dots: recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 5, 8904–8924 (2017)
F. Yan, Y. Zou, M. Wang, X. Mu, N. Yang, L. Chen, Highly photoluminescent carbon dots-based fluorescent chemosensors for sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions and application of imaging in living cells. Sens. Actuators B 192, 488–495 (2014)
Y. Ma, Y. Chen, J. Liu, Y. Han, S. Ma, X. Chen, Ratiometric fluorescent detection of chromium (VI) in real samples based on dual emissive carbon dots. Talanta 185, 249–257 (2018)
A. Kumar, A.R. Chowdhury, D. Laha, T.K. Mahto, P. Karmakar, S.K. Sahu, Green synthesis of carbon dots from Ocimum sanctum for effective fluorescent sensing of Pb2+ ions and live cell imaging. Sens. Actuators B 242, 679–686 (2017)
P. Das, S. Ganguly, M. Bose, S. Mondal, A.K. Das, S. Banerjee, N.C. Das, A simplistic approach to green future with eco-friendly luminescent carbon dots and their application to fluorescent nano-sensor ‘turn-off probe for selective sensing of copper ions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 75, 1456–1464 (2017)
R. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Sun, One-step synthesis of self-doped carbon dots with highly photoluminescence as multifunctional biosensors for detection of iron ions and pH. Sens. Actuators B 241, 73–79 (2017)
X. Cui, Y. Wang, J. Liu, Q. Yang, B. Zhang, Y. Gao, Y. Wang, G. Lu, Dual functional N-and S-co-doped carbon dots as the sensor for temperature and Fe3+ ions. Sens. Actuators B 242, 1272–1280 (2017)
S. Chandra, A.R. Chowdhury, D. Laha, S.K. Sahu, Fabrication of nitrogen-and phosphorous-doped carbon dots by the pyrolysis method for iodide and iron (III) sensing. Luminescence 33, 336–344 (2018)
Q. Dou, X. Fang, S. Jiang, P.L. Chee, T.-C. Lee, X.J. Loh, Multi-functional fluorescent carbon dots with antibacterial and gene delivery properties. RSC Adv. 5, 46817–46822 (2015)
P. Karfa, E. Roy, S. Patra, S. Kumar, A. Tarafdar, R. Madhuri, P.K. Sharma, Amino acid derived highly luminescent, heteroatom-doped carbon dots for label-free detection of Cd2+/Fe3+, cell imaging and enhanced antibacterial activity. RSC Adv. 5, 58141–58153 (2015)
N.A. Travlou, D.A. Ginnakoudakis, M. Algarra, A.M. Labella, E. Rodríguez-Castellón, T.J. Bandosz, S-and N-doped carbon quantum dots: Surface chemistry dependent antibacterial activity, Carbon, 135, 104–111 (2018)
R. Beaulac, L. Schneider, P.I. Archer, G. Bacher, D.R. Gamelin, Light-induced spontaneous magnetization in doped colloidal quantum dots. Science 325, 973–976 (2009)
M. Thakur, S. Pandey, A. Mewada, V. Patil, M. Khade, E. Goshi, M. Sharon, Antibiotic conjugated fluorescent carbon dots as a theranostic agent for controlled drug release, bioimaging, and enhanced antimicrobial activity. J. Drug Deliv. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/282193
B.Z. Ristic, M.M. Milenkovic, I.R. Dakic, B.M. Todorovic-Markovic, M.S. Milosavljevic, M.D. Budimir, V.G. Paunovic, M.D. Dramicanin, Z.M. Markovic, V.S. Trajkovic, Photodynamic antibacterial effect of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 35, 4428–4435 (2014)
M.J. Meziani, X. Dong, L. Zhu, L.P. Jones, G.E. LeCroy, F. Yang, S. Wang, P. Wang, Y. Zhao, L. Yang, Visible-light-activated bactericidal functions of carbon “Quantum” dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 10761–10766 (2016)
K. Habiba, D.P. Bracho-Rincon, J.A. Gonzalez-Feliciano, J.C. Villalobos-Santos, V.I. Makarov, D. Ortiz, J.A. Avalos, C.I. Gonzalez, B.R. Weiner, G. Morell, Synergistic antibacterial activity of PEGylated silver–graphene quantum dots nanocomposites. Appl Mater. Today 1, 80–87 (2015)
S. Han, H. Zhang, Y. Xie, L. Liu, C. Shan, X. Li, W. Liu, Y. Tang, Application of cow milk-derived carbon dots/Ag NPs composite as the antibacterial agent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 328, 368–373 (2015)
B. De, K. Gupta, M. Mandal, N. Karak, Biocide immobilized OMMT-carbon dot reduced Cu2O nanohybrid/hyperbranched epoxy nanocomposites: mechanical, thermal, antimicrobial and optical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng.: C 56, 74–83 (2015)
Y.J. Li, S.G. Harroun, Y.C. Su, C.F. Huang, B. Unnikrishnan, H.J. Lin, C.H. Lin, C.C. Huang, Synthesis of self-assembled spermidine-carbon quantum dots effective against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 5, 2545–2554 (2016)
M. Ngu-Schwemlein, S.F. Chin, R. Hileman, C. Drozdowski, C. Upchurch, A. Hargrove, Carbon nanodots as molecular scaffolds for development of antimicrobial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 1745–1749 (2016)
S.P. Chandran, M. Chaudhary, R. Pasricha, A. Ahmad, M. Sastry, Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloe vera plant extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 22, 577–583 (2006)
A. Surjushe, R. Vasani, D. Saple, Aloe vera: a short review. Indian J. Dermatol. 53, 163 (2008)
A.-M. Alam, B.-Y. Park, Z.K. Ghouri, M. Park, H.-Y. Kim, Synthesis of carbon quantum dots from cabbage with down-and up-conversion photoluminescence properties: excellent imaging agent for biomedical applications. Green Chem. 17, 3791–3797 (2015)
Y. Dong, J. Shao, C. Chen, H. Li, R. Wang, Y. Chi, X. Lin, G. Chen, Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 50, 4738–4743 (2012)
S. Mondal, P. Purkayastha, α-cyclodextrin functionalized carbon dots: pronounced photoinduced electron transfer by aggregated nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 14365–14371 (2016)
L. Chunduri, A. Kurdekar, S. Patnaik, B.V. Dev, T.M. Rattan, V. Kamisetti, Carbon quantum dots from coconut husk: evaluation for antioxidant and cytotoxic activity. Mater. Focus 5, 55–61 (2016)
J. Schmitt, H.-C. Flemming, FTIR-spectroscopy in microbial and material analysis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 41, 1–11 (1998)
W. Liu, H. Diao, H. Chang, H. Wang, T. Li, W. Wei, Green synthesis of carbon dots from rose-heart radish and application for Fe3+ detection and cell imaging. Sens. Actuators B 241, 190–198 (2017)
K. Qu, J. Wang, J. Ren, X. Qu, Carbon dots prepared by hydrothermal treatment of dopamine as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for the label-free detection of iron (III) ions and dopamine. Chem.-A Eur. J. 19 (2013) 7243–7249
N. Wang, Y. Wang, T. Guo, T. Yang, M. Chen, J. Wang, Green preparation of carbon dots with papaya as carbon source for effective fluorescent sensing of Iron (III) and Escherichia coli. Biosens. Bioelectron. 85, 68–75 (2016)
T.N.J.I. Edison, R. Atchudan, J.-J. Shim, S. Kalimuthu, B.-C. Ahn, Y.R. Lee, Turn-off fluorescence sensor for the detection of ferric ion in water using green synthesized N-doped carbon dots and its bio-imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 158, 235–242 (2016)
X. Yang, Y. Zhuo, S. Zhu, Y. Luo, Y. Feng, Y. Dou, Novel and green synthesis of high-fluorescent carbon dots originated from honey for sensing and imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 60, 292–298 (2014)
Z. Zhang, W. Sun, P. Wu, Highly photoluminescent carbon dots derived from egg white: facile and green synthesis, photoluminescence properties, and multiple applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 3, 1412–1418 (2015)
R. Atchudan, T.N.J.I. Edison, D. Chakradhar, S. Perumal, J.-J. Shim, Y.R. Lee, Facile green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots using Chionanthus retusus fruit extract and investigation of their suitability for metal ion sensing and biological applications. Sens. Actuators B 246, 497–509 (2017)
X. Sun, J. He, S. Yang, M. Zheng, Y. Wang, S. Ma, H. Zheng, Green synthesis of carbon dots originated from Lycii Fructus for effective fluorescent sensing of ferric ion and multicolor cell imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 175, 219–225 (2017)
J. Shi, G. Ni, J. Tu, X. Jin, J. Peng, Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for sensitive detection of Fe2+ and hydrogen peroxide. J. Nanopart. Res. 19, 209 (2017)
P. Das, S. Ganguly, P.P. Maity, M. Bose, S. Mondal, S. Dhara, A.K. Das, S. Banerjee, N.C. Das, Waste chimney oil to nano lights: a low cost chemosensor for tracer metal detection in practical field and its polymer composite for multidimensional activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 180, 56–67 (2018)
F. Edition, Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO Chron. 38, 104–108 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Prof. R. K. Sinha, Director CSIR-CSIO, Chandigarh for his constant support. PD acknowledges Department of Science and Technology New Delhi, India for the research project Grant (SYST, GAP 375). AT acknowledges DST INSPIRE fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, P., Thakur, A., Bhardwaj, S.K. et al. Metal ion sensing and light activated antimicrobial activity of aloe-vera derived carbon dots. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 17254–17261 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9819-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9819-0