Abstract
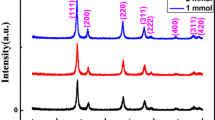
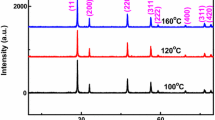
In the work, we explored an efficient synthetic platform to purposefully fabricate CeO2 nanostructures with different morphologies of by controlling the different solution conditions. All the obtained samples were characterized by means of XRD, SEM, TEM, XPS, Raman scattering, UV–Vis, Photoluminescence (PL) spectra and M–H curves. The results show that all the samples have a cubic fluorite structure and the samples synthesized in alkaline, acidic and neutral aqueous solution display nanorod/nanotube, nano-plate and nano-octahedron structure, respectively. It was also found that there is a red-shifting in the band gap of the obtained material compared to bulk one, which is mainly attributed to the influences of Ce3+ ions, oxygen vacancies and the change of sample morphology. The existence and increase of Ce3+ ions and oxygen defects in the CeO2 samples can lead to a smaller band gap, stronger PL diffraction and elevated ferromagnetism.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Gong, F.M. Meng, X. Yang, Z.H. Fan, H.J. Li, Controlled hydrothermal synthesis of triangular CeO2 nanosheets and their formation mechanism and optical properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 689, 606–616 (2016)
B. Xu, Q.T. Zhang, S.S. Yuan, M. Zhang, T. Ohno, Morphology control and characterization of broom-like porous CeO2. Chem. Eng. J. 260, 126–132 (2015)
R. Rao, M. Yang, C. Li, H. Dong, S. Fang, A. Zhang, A facile synthesis for hierarchical porous CeO2 nanobundles and their superior catalytic performance for CO oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 782–788 (2015)
F.M. Meng, L.N. Wang, J.B. Cui, Controllable synthesis and optical properties of nano-CeO2 via a facile hydrothermal route. J. Alloy. Compd. 556, 102–108 (2013)
S. Letichevsky, C.A. Tellez, R.R.D. Avillez, M.I.P.D. Silva, M.A. Fraga, L.G. Appel, Obtaining CeO2-ZrO2 mixed oxides by coprecipitation: role of preparation conditions. Appl. Catal. B 58, 203–210 (2005)
J.Y. Bai, Z.D. Xu, Y.F. Zheng, H.Y. Yin, Shape control of CeO2 nanostructure materials in microemulsion systems. Mater. Lett. 60, 1287–1290 (2006)
H.Y. Xiao, Z.H. Ai, L.Z. Zhang, Nonaqueous sol-gel synthesized hierarchical CeO2 nanocrystal microspheres as novel adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 16625–16630 (2009)
C. Paun, O.V. Safonova, J. Szlachetko, P.M. Abdala, M. Nachtegaal, J. Sa, E. Kleymenov, A. Cervellino, F. Krumeich, J.A.V. Bokhoven, Polyhedral CeO2 nanoparticles: size-dependent geometrical and electronic structure. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 7312–7317 (2012)
Y.Y. Zhang, J.P. Hu, B.A. Bernevig, X.R. Wang, X.C. Xie, W.M. Liu, Localization and the Kosterlitz-Thouless transition in disordered grapheme. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 106401 (2009)
A.C. Ji, W.M. Liu, J.L. Song, F. Zhou, Dynamical creation of fractionalized vortices and vortex lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 010402 (2008)
Y.H. Chen, H.S. Tao, D.X. Yao, W.M. Liu, Kondo metal and ferrimagnetic insulator on the triangular kagome lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 246402 (2012)
A.C. Ji, X.C. Xie, W.M. Liu, Quantum magnetic dynamics of polarized light in arrays of microcavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 183602 (2007)
D.S. Zhang, X.J. Du, L.Y. Shi, R.H. Gao, Shape-controlled synthesis and catalytic application of ceria nanomaterials. Dalton Trans. 41, 14455–14475 (2012)
K. J.Qi, G.D. Zhao, Y. Li, H.J. Gao, R.B. Zhao, Z.Y. Yu, Tang, Multi-shelled CeO2 hollow microspheres as superior photocatalysts for water oxidation. Nanoscale 6, 4072–4077 (2014)
Z.L. Zhan, S.A. Bamett, An octane-fueled solid oxide fuel cell. Science 308, 844–847 (2005)
Y. Chen, T.M. Liu, C.L. Chen, W.W. Guo, R. Sun, S.H. Lv, M. Saito, S. Tsukimoto, Z.C. Wang, Synthesis and characterization of CeO2 nano-rods. Ceram. Int. 39, 6607–6610 (2013)
A. Zarkov, A. Stanulis, T. Salkus, A. Kezionis, V. Jasulaitiene, R. Ramanauskas, S. Tautkus, A. Kareiva, Synthesis of nanocrystalline gadolinium doped ceria via sol-gel combustion and sol-gel synthesis routes. Ceram. Int. 42, 3972–3988 (2016)
Z.J. Li, X.Y. Niu, Z.J. Lin, N.N. Wang, H.H. Shen, W. Liu, K. Sun, Y.Q. Fu, Z.G. Wang, Hydrothermally synthesized CeO2 nanowires for H2S sensing at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 682, 647–653 (2016)
Y. Chen, C.J. Qiu, C.L. Chen, X.F. Fan, S.B. Xu, W.W. Guo, Z.C. Wang, Facile synthesis of ceria nanospheres by Ce(OH)CO3 precursors. Mater. Lett. 122, 90–93 (2014)
L.F. Wang, F.J. Liu, W.T. Yang, H.Y. Zhao, Y.Y. Zheng, X.B. Chen, W.J. Dong, Synthesis of multiple-shell porous CeO2 hollow spheres by a hydrogel template method. Mater. Lett. 107, 42–45 (2013)
F.M. Meng, J.F. Gong, Z.H. Fan, H.J. Li, J.T. Yuan, Hydrothermal synthesis and mechanism of triangular prism-like monocrystalline CeO2 nanotubes via a facile template-free hydrothermal route. Ceram. Int. 42, 4700–4708 (2016)
L.X. Pang, X.Y. Wang, X.D. Tang, Ceria nanotube formed by sacrificed precursors template through Oswald ripening, PLoS ONE 10, 0132536 (2015)
J.F. Gong, F.M. Meng, Z.H. Fan, H.J. Li, Controlled synthesis of CeO2 microstructures from 1D rod-like to 3D lotus-like and their morphology-dependent properties. Electron. Mater. Lett. 12, 846–855 (2016)
R.K. Singhal, P. Kumari, A. Samariya, S. Kumar, S.C. Sharma, Y.T. Xing, E.B. Saitovitch, Role of electronic structure and oxygen defects in driving ferromagnetism in nondoped bulk CeO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 172503–172506 (2010)
G.F. Wang, Q.Y. Mu, T. Chen, Y.D. Wang, Synthesis, characterization and photoluminescence of CeO2 nanoparticles by a facile method at room temperature. J. Alloy. Compd. 493, 202–207 (2010)
N.S. Ferreira, R.S. Angélica, V.B. Marques, C.C.O. de Lima, M.S. Silva, Cassava-starch-assisted sol-gel synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 165, 139–142 (2016)
D. Jampaiah, P. Venkataswamy, V.E. Coyle, B.M. Reddy, S.K. Bhargava, Low-temperature CO oxidation over manganese,cobalt, and nickel doped CeO2 nanorods. RSC Adv. 6, 80541–80548 (2016)
F.L. Liang, Y. Yu, W. Zhou, X.Y. Xu, Z.H. Zhu, Highly defective CeO2 as a promoter for efficient and stable water oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 634–640 (2015)
A. Younis, D. Chu, Y.V. Kaneti, S. Li, Tuning the surface oxygen concentration of {111} surrounded ceria nanocrystals for enhanced photocatalytic activities. Nanoscale 8, 378–387 (2016)
H. Li, A. Petz, H. Yan, J.C. Nie, S. Kunsagi-Mate, Morphology dependence of raman properties of carbon nanotube layers formed on nanostructured CeO2 films. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 1480–1483 (2011)
S. Colis, A. Bouaine, G. Schmerber, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, A. Dinia, S. Choua, P. Turek, High-temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped CeO2 synthesized by the coprecipitation technique. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 7256–7263 (2012)
A.C. Cabral, L.S. Cavalcante, R.C. Deus, E. Longo, A.Z. Simões, F. Moura, Photoluminescence properties of praseodymium doped cerium oxide nanocrystals. Ceram. Int. 40, 4445–4453 (2014)
H.R. Tan, J.P.Y. Tan, C. Boothroyd, T.W. Hansen, Y.L. Foo, M. Lin, Experimental evidence for self-assembly of CeO2 particles in solution: formation of single-crystalline porous CeO2 nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 242–247 (2012)
X.Y. Yang, X.J. Yu, G. Li, The effects of Nd doping on the morphology and optical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 9704–9709 (2016)
X.F. Niu, M. Li, B. Wu, H.Z. Li, Controlled synthesis and magnetic properties of thin CeO2. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 10198–10206 (2016)
J. Zdravković, B. Simović, A. Golubović, D. Poleti, I. Veljković, M. Šćepanović, G. Branković, Comparative study of CeO2 nanopowders obtained by the hydrothermal method from various precursors. Ceram. Int. 41, 1970–1979 (2015)
X.F. Niu, M. Li, B.M. Hao, H.Z. Li, Hydrothermal synthesis of 3D hierarchical porous CeO2 rugby-ball-like nanostructures with nanorods as building blocks. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 6845–6848 (2016)
H.L. Lin, C.Y. Wu, R.K. Chiang, Facile synthesis of CeO2 nanoplates and nanorods by [100] oriented growth. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 341, 12–17 (2010)
L. Qin, X.F. Niu, Controlled hydrothermal synthesis, excellent optical and magnetic properties of CeO2 nanocubes. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 12233–12239 (2016)
X.H. Liu, S.J. Chen, X.D. Wang, Synthesis and photoluminescence of CeO2:Eu3+ phosphor powders. J. Lumin. 127, 650–654 (2007)
B. Choudhury, A. Choudhury, Ce3+ and oxygen vacancy mediated tuning of structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 131, 666–671 (2012)
V. Ramasamy, G. Vijayalakshmi, Effect of Zn doping on structural, optical and thermal properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Superlatt. Microstruct. 85, 510–521 (2015)
J. Malleshappa, H. Nagabhushana, S.C. Sharma, Y.S. Vidya, K.S. Anantharaju, S.C. Prashantha, B.D. Prasad, H.R. Naika, K. Lingaraju, B.S. Surendra, Leucas aspera mediated multifunctional CeO2 nanoparticles: structural, photoluminescent, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Spectrochim. Acta A 149, 452–462 (2015)
C.R. Li, M.Y. Cui, Q.T. Sun, W.J. Dong, Y.Y. Zheng, K. Tsukamoto, B.Y. Chena, W.H. Tang, Nanostructures and optical properties of hydrothermal synthesized CeOHCO3 and calcined CeO2 with PVP assistance. J. Alloy. Compd. 504, 498–502 (2010)
F. Lu, F.M. Meng, L.N. Wang, Y. Sang, J.J. Luo, Controlled synthesis and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles by a N2H4·H2O-assisted hydrothermal method. Micro Nano Lett. 7, 624–627 (2012)
S.Y. Chen, Y.H. Lu, T.W. Huang, D.C. Yan, C.L. Dong, Oxygen vacancy dependent magnetism of CeO2 nanoparticles prepared by thermal decomposition method. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 19576–19581 (2010)
J.H. Chen, Y.J. Lin, H.C. Chang, Y.H. Chen, L. Horng, C.C. Chang, Effect of Co content on magnetic and optical properties of Zn1−xCoxOy nanorods. J. Alloy. Compd. 548, 235–238 (2013)
A. Thurber, K.M. Reddy, V. Shutthanandan, M.H. Engelhard, C. Wang, J. Hays, A. Punnoose, Ferromagnetism in chemically synthesized CeO2 nanoparticles by Ni doping. Phys. Rev. B 76, 165206 (2007)
A. Tiwari, V.M. Bhosle, S. Ramachandran, N. Sudhakar, J. Narayan, S. Budak, A. Gupta, Ferromagnetism in Co doped CeO2: observation of a giant magnetic moment with a high curie temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 142511 (2006)
P. Slusser, D. Kumar, A. Tiwari, Unexpected magnetic behavior of Cu-doped CeO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 142506 (2010)
M.Y. Ge, H. Wang, E.Z. Liu, J.F. Liu, J.Z. Jiang, Y.K. Li, Z.A. Xu, H.Y. Li, On the origin of ferromagnetism in CeO2 nanocubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 062505 (2008)
M.I.B. Bernardi, A. Mesquita, F. Beron, K.R. Pirota, A.O.D. Zevallos, A.C. Doriguetto, H.B.D. Carvalho, The role of oxygen vacancies and their location in the magnetic properties of Ce1−xCuxO2−δ nanorods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 3072–3080 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51072002, 51272003), Dr. Start-up capital of Suzhou University (2016jb10), the Natural Science Research Fund of Anhui Provincial Department of Education (KJ2016A775), and Academic Technical Leader of Suzhou University (2018xjxs01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Niu, X. Novel controlled hydrothermal synthesis of three different CeO2 nanostructures and their morphology-dependent optical and magnetic properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 17178–17186 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9809-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9809-2